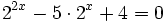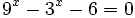Plantilla:Ecuaciones exponenciales
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 08:47 30 ago 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 09:08 30 ago 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 49: | Línea 49: | ||
| - | '''''Soluciones:''''' <math>x_1=2 , \ x_2=3;</math> | + | :'''''Soluciones:''''' <math>x_1=2 , \ x_2=3;</math> |
| ---- | ---- | ||
| '''c)''' | '''c)''' | ||
| Línea 60: | Línea 60: | ||
| :Aplicando la propiedad del logaritmo de una potencia: | :Aplicando la propiedad del logaritmo de una potencia: | ||
| - | <center><math>(1-x^2) log \ 3= log \ 2 \rightarrow 1-x^2= \cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3}</math></center> | + | <center><math>(1-x^2) \ log \ 3= log \ 2 </math></center> |
| :Y resolvemos la ecuación de segundo grado incompleta: | :Y resolvemos la ecuación de segundo grado incompleta: | ||
| - | <center><math>x^2=1-\cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3} \rightarrow \ x=\pm \sqrt{1-\cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3}} \approx \pm 0.6075 </math></center> | + | <center><math>1-x^2= \cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3} \rightarrow x^2=1-\cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3} \rightarrow \ x=\pm \sqrt{1-\cfrac{log \ 2}{log \ 3}} \approx \pm 0.6075 </math></center> |
| {{b}} | {{b}} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 70: | Línea 70: | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| + | '''d)''' | ||
| + | <center><math>2^x+2^{x+1}=12\;</math></center> | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
| + | :Haciendo el cambio de variable: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>2^x=y \;</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :tenemos que: | ||
| + | <center><math>2^{x+1}=2^x \cdot 2^1 = 2y \;</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Y la ecuación de partida queda: | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
| + | <center><math>y+2y=12\;</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Resolvemos la ecuación de primer grado: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>3y=12 \rightarrow y = 4 \;</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Y deshacemos el cambio de variable: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>y=4 \rightarrow 2^x=4 \rightarrow x = 2 \;</math></center> | ||
| + | {{b}} | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
| + | :'''''Solución:''''' <math>x=2 \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 78: | Línea 103: | ||
| |enunciado= | |enunciado= | ||
| - | Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciones: | + | :Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciones: |
| + | |||
| + | ::a) <math>3^x=\sqrt[3]{9} \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::b) <math>2^{2x}-5\cdot 2^x+4=0 \;</math> | ||
| - | :<math>a)\ 3^x=\sqrt[3]{9} \quad b)\ 2^{2x}-5\cdot 2^x+4=0 \quad c)\ 9^x-3^x-6=0 </math> | + | ::c) <math>9^x-3^x-6=0 \;</math> |
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| |sol= | |sol= | ||
| Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones: | Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones: | ||
| - | :a) {{consulta|texto=solve 3^x=3root (9) over the reals}} {{b4}} b) {{consulta|texto=solve 2^(2x)-5*2^x+4=0 over the reals}} {{b4}} c) {{consulta|texto=solve 9^x-3^x-6=0 over the reals}} | + | :a) {{consulta|texto=solve 3^x=3root (9) over the reals}} |
| + | :b) {{consulta|texto=solve 2^(2x)-5*2^x+4=0 over the reals}} | ||
| + | :c) {{consulta|texto=solve 9^x-3^x-6=0 over the reals}} | ||
| {{widget generico}} | {{widget generico}} | ||
Revisión de 09:08 30 ago 2016
Las ecuaciones exponenciales son aquellas en las que la incógnita aparece como exponente.
Ejercicios resueltos: Ecuación exponencial
Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciónes:
- a)
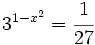
- a)
- b)
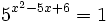
- b)
- c)
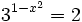
- c)
- d)
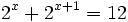
- d)
Solución:
a)
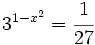
- Expresamos el segundo miembro como potencia de 2:
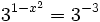
- Como
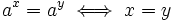 , los exponentes deben ser iguales:
, los exponentes deben ser iguales:
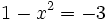
- Y resolvemos la ecuación de segundo grado incompleta:
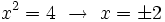
- Soluciones:
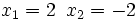
b)
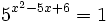
- Expresamos el segundo miembro como potencia de 5:
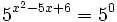
- Como
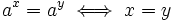 , los exponentes deben ser iguales:
, los exponentes deben ser iguales:
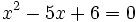
- Resolvemos la ecuación de segundo grado:
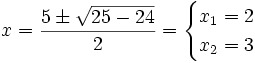
- Soluciones:
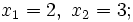
c)
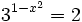
- Como el segundo miembro no podemos expresarlo como potencia de base 3, tomaremos logaritmos en ambos lados de la ecuación:
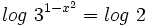
- Aplicando la propiedad del logaritmo de una potencia:
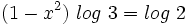
- Y resolvemos la ecuación de segundo grado incompleta:
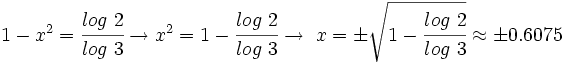
- Soluciones:
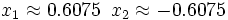
d)
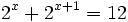
- Haciendo el cambio de variable:
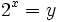
- tenemos que:
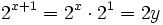
- Y la ecuación de partida queda:
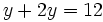
- Resolvemos la ecuación de primer grado:
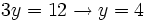
- Y deshacemos el cambio de variable:
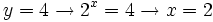
- Solución:
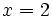
|
Actividad: Ecuaciones exponenciales
Solución: Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones:
|
![3^x=\sqrt[3]{9} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/d/b/0/db0233292d84043ca9d4101f6ac692a6.png)