Ejercicios: Cálculo de primitivas (2ºBach)
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 09:14 27 jun 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) |
||
| Línea 40: | Línea 40: | ||
| |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/006-ejercicio-11 | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/006-ejercicio-11 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'30" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{\sqrt{4-x^2}} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/007-ejercicio-10 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'04" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{x^2+3x+2}{(x-1)(x^2+2x+2)} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/008-ejercicio-10 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'44" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{cos^4 \, x} \cdot dx</math> mediante cambio de variable <math>tg \, x = z</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/009-ejercicio-9 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'41" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Hallar <math>f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}</math> tal que f(0)=0, f'(=)=5, f''(0)=1 y f'''(x)=x+1 | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/010-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 11 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'41" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{2x+5}{(x-1)(x+3)^2} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/011-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 12 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'03" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{1+e^x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/012-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 13 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'06" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{x}{x-\sqrt{x^2-1}} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/013-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 14 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'55" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{1+\sqrt{x+1}} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/014-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'04" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int (x^2 \cdot ln \, x -x \cdot ln \, x^2) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/015-ejercicio-7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 16 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'48" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Halla una primitiva de <math>f(x)=x \cdot (1-ln \, x)\;</math> que pase por el punto (1,1). | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/016-ejercicio-6 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 17 | ||
| + | |duracion=5'00" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Determina f(x) sabiendo que <math>f'(x)=e^{2x} \cdot sen \, x\;</math> y que <math>f(\cfrac{\pi}{2})=1</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/017-ejercicio-6 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 18 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'05" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Determina <math>f:(1, +\infty)\rightarrow \mathbb{R}</math> sabiendo que <math>f'(x)=\cfrac{x^4-x^3-x-1}{x^3-x^2}</math> y que <math>f(2)=ln \, 4</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/018-ejercicio-6 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 19 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'57" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{sen^3 \, x}{\sqrt{cos \, x} \cdot sen \, x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/019-ejercicio-5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 20 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'33" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int x^2 \cdot \sqrt{x+1} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/020-ejercicio-5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 21 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'33" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int (1+x^2) \cdot sen \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/021-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 22 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'15" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula una función que valga cero en el punto x=0 y cuya derivada sea f(x)=sen \, x \cdot cos \, x. | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/022-ejercicio-5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 23 | ||
| + | |duracion=4'36" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{x^4-1} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/023-ejercicio-5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 24 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'08" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{x^2+x-1} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/024-ejercicio-5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 25 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'56" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Determina las funciones cuya segunda derivada es f''(x)=x \cdot e^x, y obtener la que pasa por los puntos (0,2) y (2,0). | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/025-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 26 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'20" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Halla f(x) sabiendo que <math>f'(x)=\cfrac{2x}{x^2+x-2}</math> y que <math>f(2)=\cfrac{ln \, 4}{3}</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/026-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 27 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'10" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{\sqrt{5x^3}+\sqrt[3]{3x^2}}{\sqrt{2x}} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/027-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 28 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'12" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{x}{e^x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/028-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 29 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'06" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{1-e^x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/029-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 30 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'05" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int (x^2+x) \cdot e^{-2x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/030-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 31 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'24" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int \cfrac{1}{x^3+x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/031-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 32 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'22" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int x \cdot \sqrt{1-x^2} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/032-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 33 | ||
| + | |duracion=1'40" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=<math>\int x \cdot cos \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/prueba-de-acceso-a-la-universidad-problemas-de-examen/11-calculo-de-primitivas/033-ejercicio-4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{Web_enlace | ||
| + | |descripcion=Una completa colección de videos sobre integrales trigonométricas. | ||
| + | |enlace=[https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLPrT9FThiZ6RjYGlHynHw7f-BISprfoTG Integrales trigonométricas] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
Revisión actual
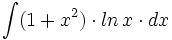
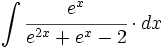
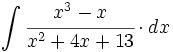
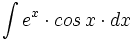
![\int \cfrac{1}{\sqrt[3]{x^2} \cdot (\sqrt[3]{x^2}+\sqrt[3]{x}+1)} \cdot dx](/wikipedia/images/math/b/a/5/ba5f7a6904dd982111c210de34296c2e.png)
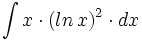
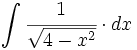

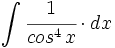 mediante cambio de variable
mediante cambio de variable 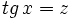 .
.
Hallar 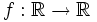 tal que f(0)=0, f'(=)=5, f(0)=1 y f'(x)=x+1
tal que f(0)=0, f'(=)=5, f(0)=1 y f'(x)=x+1
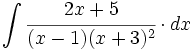
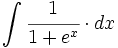
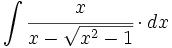
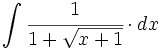
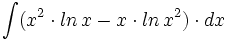
Halla una primitiva de 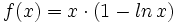 que pase por el punto (1,1).
que pase por el punto (1,1).
Determina f(x) sabiendo que 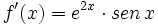 y que
y que 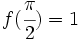 .
.
Determina 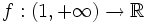 sabiendo que
sabiendo que 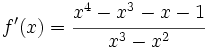 y que
y que 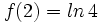 .
.
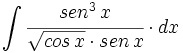
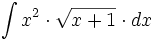
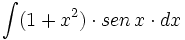
Calcula una función que valga cero en el punto x=0 y cuya derivada sea f(x)=sen \, x \cdot cos \, x.
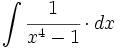
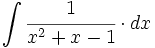
Determina las funciones cuya segunda derivada es f(x)=x \cdot e^x, y obtener la que pasa por los puntos (0,2) y (2,0).
Halla f(x) sabiendo que 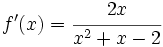 y que
y que 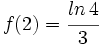 .
.
![\int \cfrac{\sqrt{5x^3}+\sqrt[3]{3x^2}}{\sqrt{2x}} \cdot dx](/wikipedia/images/math/4/9/8/4987e9a1ea90859a1d064232f35bfae1.png)
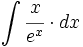
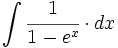
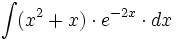
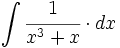
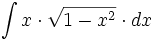
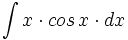
Una completa colección de videos sobre integrales trigonométricas.

