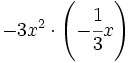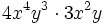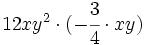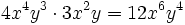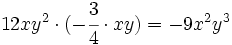Plantilla:Producto de monomios
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 16:27 4 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 16:34 4 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 69: | Línea 69: | ||
| |sinopsis=Multiplica los siguientes monomios: | |sinopsis=Multiplica los siguientes monomios: | ||
| - | :37) <math>5x \cdot (-2x^2) \cdot (-x)\;</math> | + | :37) <math>5x \cdot (-2x^2) \cdot (-x)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 38) <math>10x^3 \cdot 2x^2 \cdot (-4x)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 39) <math>5x \cdot (-4x) \cdot 2x\;</math> |
| - | :38) <math>10x^3 \cdot 2x^2 \cdot (-4x)\;</math> | + | :40) <math>3x^2 \cdot 6x \cdot (-x^2)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 41) <math>2x^2 \cdot 3x\;</math> ; {{b4}} 42) <math>5x \cdot (-3x)\;</math> |
| - | :39) <math>5x \cdot (-4x) \cdot 2x\;</math> | + | :43) <math>4x^2 \cdot (-2x) \cdot y\;</math> ; {{b4}} 44) <math>x^2 \cdot y \cdot (-3y)\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :40) <math>3x^2 \cdot 6x \cdot (-x^2)\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :41) <math>2x^2 \cdot 3x\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :42) <math>5x \cdot (-3x)\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :43) <math>4x^2 \cdot (-2x) \cdot y\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :44) <math>x^2 \cdot y \cdot (-3y)\;</math> | + | |
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsriEcQAGeU&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ow70kSFPZjp_toVtyxYkAaU&index=10 | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsriEcQAGeU&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ow70kSFPZjp_toVtyxYkAaU&index=10 | ||
| Línea 90: | Línea 80: | ||
| |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| |duracion=9'54" | |duracion=9'54" | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Ejercicios 45-53: Multiplicar monomios. | + | |sinopsis=Multiplica los siguientes monomios: |
| + | |||
| + | :45) <math>\cfrac{4}{3}x^2 \cdot (-2x)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 46) <math>\cfrac{4}{5}x^2 \cdot \cfrac{2}{3}x\;</math> ; {{b4}} 47) <math>\cfrac{4}{5}x^2 \cdot \cfrac{6}{5}x^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :48) <math>-5x^3 \cdot 2y^2\;</math> ; {{b4}} 49) <math>6x^2 \cdot (-7xy)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 50) <math>\cfrac{2}{3}x^2 \cdot \cfrac{2}{3}x\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :51) <math>\cfrac{4}{5}x^3 \cdot \left( -\cfrac{5}{4}x^4 \right)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 52) <math>2x^2 \cdot \left( -\cfrac{1}{2}x^3 \right)\;</math> ; {{b4}} 53) <math>-3x^2 \cdot \left( -\cfrac{1}{3}x \right)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qQ4X9Uh3zRk&index=11&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ow70kSFPZjp_toVtyxYkAaU | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qQ4X9Uh3zRk&index=11&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ow70kSFPZjp_toVtyxYkAaU | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
Revisión de 16:34 4 nov 2017
Procedimiento
Para multiplicar monomios, se multiplican los coeficientes de cada monomio y las potencias con la misma base se agrupan y se multiplican.
Recordemos que: para multiplicar potencias de la misma base se deja la misma base y se suman los exponentes.
Actividades en la que aprenderás y practicarás a multiplicar monomios.
Actividades para practicar la multiplicación de monomios.
Haz las siguientes multiplicaciones de monomios:
- a)
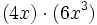
- b)
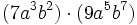
- c)
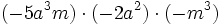
Haz las siguientes multiplicaciones de monomios:
- a)
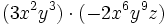
- b)
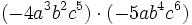
- c)
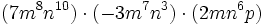
- d)
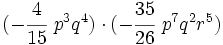
Haz las siguientes multiplicaciones de monomios:
- a)
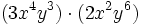
- b)
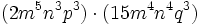
- c)
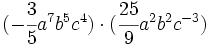
Multiplica los siguientes monomios:
- 37)
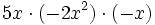 ; 38)
; 38) 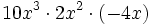 ; 39)
; 39) 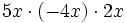
- 40)
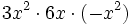 ; 41)
; 41) 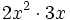 ; 42)
; 42) 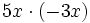
- 43)
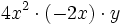 ; 44)
; 44) 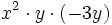
Multiplica los siguientes monomios:
- 45)
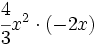 ; 46)
; 46) 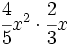 ; 47)
; 47) 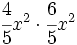
- 48)
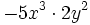 ; 49)
; 49) 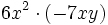 ; 50)
; 50) 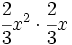
- 51)
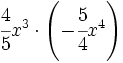 ; 52)
; 52) 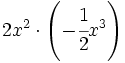 ; 53)
; 53)