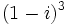Números complejos: Operaciones (1ºBach)
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 11:24 13 jun 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Ejercicios) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Operaciones con números complejos en forma binómica) |
||
| Línea 17: | Línea 17: | ||
| * '''División:''' <math>\,\frac{(a + bi)}{(c + di)} = \frac{(a + bi) (c - di)}{(c + di) (c - di)} = \left({ac + bd \over c^2 + d^2}\right) + \left( {bc - ad \over c^2 + d^2} \right)i\, </math>, siempre que <math>c+di\,</math> no sea nulo. | * '''División:''' <math>\,\frac{(a + bi)}{(c + di)} = \frac{(a + bi) (c - di)}{(c + di) (c - di)} = \left({ac + bd \over c^2 + d^2}\right) + \left( {bc - ad \over c^2 + d^2} \right)i\, </math>, siempre que <math>c+di\,</math> no sea nulo. | ||
| - | }}{{p}} | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales | ||
| - | |titulo=Operaciones con complejos en forma binómica | ||
| - | |enunciado= | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= Suma de números complejos | ||
| - | |duracion=8´53" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/04-suma-de-numeros-complejos#.VCrucRa7ZV8 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=*Definición de suma de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | *Representación gráfica. | ||
| - | *Ejemplos. | ||
| - | *Propiedades. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= Producto de números complejos | ||
| - | |duracion=11´26" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/05-producto-de-numeros-complejos#.VCrvwha7ZV8 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=*Definición de producto de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | *Ejemplos. | ||
| - | *Propiedades. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= Cociente de números complejos | ||
| - | |duracion=7´45" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/06-cociente-de-numeros-complejos#.VCrw-Ba7ZV8 | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | *Definición de cociente de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | *Ejemplos. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= Potenciación de números complejos expresados en forma binómica | ||
| - | |duracion=3´50" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/10-potenciacion-de-numeros-complejos-expresados-en-forma-binomica#.VCr30xa7ZV8 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Las potencias de números complejos hacen uso de la fórmula del binomio de Newton. No obstante, son mucho más fáciles si se realizan en [[Números complejos: Operaciones en forma polar (1ºBach)#Potencias de números complejos en forma polar|forma polar]] como se verá en otro apartado de este tema. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 81: | Línea 42: | ||
| {{ejercicio_cuerpo | {{ejercicio_cuerpo | ||
| |enunciado= | |enunciado= | ||
| - | 3. <math>\,(3 + 4i) (2 - 5i)</math> | + | 3. <math>\,(3 + 4i) \cdot (2 - 5i)</math> |
| |sol= | |sol= | ||
| '''Solución:''' | '''Solución:''' | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| - | <math>\,(3 + 4i) (2 - 5i)=6-15i+8i-20i^2=6-7i+20=26-7i</math> | + | <math>\,(3 + 4i) \cdot (2 - 5i)=6-15i+8i-20i^2=6-7i+20=26-7i</math> |
| {{b4}} | {{b4}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 101: | Línea 62: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales | + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Operaciones con complejos en forma binómica|enunciado= |
| - | |titulo=Ejercicios: ''Operaciones con complejos en forma binómica'' | + | |
| - | |enunciado= | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1a: ''Suma'' | ||
| + | |duracion=8´53" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lP7_h0XxEf8&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=6 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=*Definición de suma de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | *Representación gráfica. | ||
| + | *Ejemplos. | ||
| + | *Propiedades. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1b: ''Producto'' | ||
| + | |duracion=11´26" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hR6wP1Dfo9A&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=8 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=*Definición de producto de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | *Ejemplos. | ||
| + | *Propiedades. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1c: ''Cociente'' | ||
| + | |duracion=7´45" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lTyGy30GKhY&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=12 | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | *Definición de cociente de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | *Ejemplos. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1d: ''Potenciación'' | ||
| + | |duracion=3´50" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zo8y6EiPTVs&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=23 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Las potencias de números complejos hacen uso de la fórmula del binomio de Newton. No obstante, son mucho más fáciles si se realizan en [[Números complejos: Operaciones en forma polar (1ºBach)#Potencias de números complejos en forma polar|forma polar]] como se verá en otro apartado de este tema. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| |titulo1= Ejercicio 1 | |titulo1= Ejercicio 1 | ||
| |duracion=1´47" | |duracion=1´47" | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b0FFMwax2Oc | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b0FFMwax2Oc | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=5-3i\;</math> y <math>z_2=-4+2i\;</math>, halla <math>z_1+ z_2\;</math> y <math>z_1- z_2\;</math>. | + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=5-3i\;</math> y <math>z_2=-4+2i\;</math>, halla: |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | + | a) <math>z_1+ z_2\;</math> |
| - | |titulo1= Ejercicio 2 | + | |
| - | |duracion=4´15" | + | b) <math>z_1- z_2\;</math>. |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kteT6kMVFrM&index=47&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=3+2i\;</math> y <math>z_2=2-i\;</math>, halla <math>z_1+ z_2\;</math> y <math>z_1- z_2\;</math>. | + | |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1= Ejercicio 3 | + | |titulo1= Ejercicio 2 |
| |duracion=4´53" | |duracion=4´53" | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1LCiuis7rZE | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1LCiuis7rZE | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=7-i\;</math> y <math>z_2=3-5i\;</math>, halla <math>z_1 \cdot z_2\;</math> y <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. | + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=7-i\;</math> y <math>z_2=3-5i\;</math>, halla: |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | + | a) <math>z_1 \cdot z_2\;</math> |
| - | |titulo1= Ejercicio 4 | + | |
| - | |duracion=7´21" | + | b) <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q1p8uSBhpi4&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=48 | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=3+2i\;</math> y <math>z_2=2-i\;</math>, halla <math>z_1 \cdot z_2\;</math> y <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. | + | |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1= Ejercicio 5 | + | |titulo1= Ejercicio 3 |
| |duracion=16´47" | |duracion=16´47" | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ygJ6Tvda_Uc | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ygJ6Tvda_Uc | ||
| Línea 146: | Línea 134: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 |
| |duracion=9´48" | |duracion=9´48" | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ypGp3P68NxI | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ypGp3P68NxI | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=-3+4i\;</math> y <math>z_2=5-2i\;</math>, halla <math>(\overline{z_1})^2 - (z_2)^3\;</math> y <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. | + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=-3+4i\;</math> y <math>z_2=5-2i\;</math>, halla: |
| + | |||
| + | a) <math>(\overline{z_1})^2 - (z_2)^3\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | b) <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| + | |titulo1= Ejercicio 5 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´15" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kteT6kMVFrM&index=47&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=3+2i\;</math> y <math>z_2=2-i\;</math>, halla: | ||
| + | |||
| + | a) <math>z_1+ z_2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | b) <math>z_1- z_2\;</math>. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| + | |titulo1= Ejercicio 6 | ||
| + | |duracion=7´21" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q1p8uSBhpi4&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=48 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos <math>z_1=3+2i\;</math> y <math>z_2=2-i\;</math>, halla: | ||
| + | |||
| + | a) <math>z_1 \cdot z_2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | b) <math>z_1 : z_2\;</math>. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | ||
| + | |duracion=7´55" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eXDIkPZNXtk&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL&index=21 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los complejos: <math>z=5+7i\;</math> y <math>z'=-\sqrt{3}+2i\;</math>, calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>z+z'\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>z-z'\;</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>z \cdot z' \cdot z\;</math> | ||
| + | :d) <math>(z')^{-1}\;</math> | ||
| + | :e) <math>2z-5\overline{z}\;</math> | ||
| + | :f) <math>z \cdot z'\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8 | ||
| + | |duracion=9´02" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hzCBQTfxecA&index=20&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(\cfrac{3}{2}+i)+(-2+\cfrac{1}{2}\,i)\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>(\sqrt{3}+2i)+(1-5i)\;</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>(-3-\cfrac{1}{2}\,i)-(\cfrac{1}{3}+\cfrac{1}{7}\,i)\;</math> | ||
| + | :d) <math>(6+4i)\cdot(-1-2i)\;</math> | ||
| + | :e) <math>-3i \cdot (2i+3)\;</math> | ||
| + | :f) <math>(\sqrt{3}+2i):(1-5i)\;</math> | ||
| + | :g) <math>-3i : (2i+3)\;</math> | ||
| + | :h) <math>\left( \cfrac{2i^5+3i^{17}}{1+i} \right)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| + | |duracion=13´39" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M6U7ArqqVPA&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlut1lGHmwYqQjl6-yDrsPf&index=5 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados <math>z=1-3i\;</math>, <math>w=-3+2i\;</math> y <math>t=-2i\;</math>, calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>z \cdot w \cdot t\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>z \cdot t -w \cdot (t+z)\;</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>\cfrac{w}{z}\cdot t\;</math> | ||
| + | :d) <math>\cfrac{2z-3t}{w}\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| + | |duracion=6´39" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cz6OVB695_o&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL&index=19 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula las potencias de exponente 2, 3 y 4 de los siguientes números complejos: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>2+3i\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>-2+i\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 11 | ||
| + | |duracion=1´12" | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/FQPN__V04DU | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Suma: <math>(5 + 2i) +(3 - 7i)\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 12 | ||
| + | |duracion=1´48" | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/txIeI1NUtJM | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resta: <math>(2 - 3i)-(6 - 18i)\;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 13 | ||
| + | |duracion=5´27" | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Hu0zAucbcl8 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Multiplica: <math>(1 - 3i) \cdot (2 + 5i)\;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 2 ejercicios (Suma) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 14 |
| |duracion=5´55" | |duracion=5´55" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0401-dos-ejercicios-5-2#.VCrvVha7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jPOoEjN3zwI&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=7 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis= |
| + | #Determina <math>m\;</math> y <math>n\;</math> de manera que los complejos <math>z_1=m+2i\;</math> y <math>z_2=2n-mi\;</math> sean tales que <math>z_1+z_2=1+3n+4i\;</math>. | ||
| + | #Determina <math>m\;</math> y <math>n\;</math> de manera que los complejos <math>z_1=m+ni\;</math> y <math>z_2=n+mi\;</math> sean tales que <math>z_1-z_2=3+4i\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 3 ejercicios (Ecuaciones con soluciones complejas) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 |
| - | |duracion=9´24" | + | |
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0501-tres-ejercicios-ecuaciones-con-soluciones-complejas#.VCrwORa7ZV8 | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | + | |
| - | |titulo1= 3 ejercicios (Producto) | + | |
| |duracion=9´19" | |duracion=9´19" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0502-tres-ejercicios#.VCrwdha7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Nqa_X-c62s&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=10 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Calcula <math>k\;</math> en los siguientes casos: |
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(2+3i) \cdot (4+ki)=5+14i</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>(3-2i) \cdot (k+5i)=k-7i</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>(2+ki) \cdot (k+3i)=-15+3i</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 3 ejercicios (Producto) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 16 |
| |duracion=7´05" | |duracion=7´05" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0503-tres-ejercicios#.VCrwxha7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X9No_AcbtI8&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=11 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Si <math>z_1=2+3i\;</math>, <math>z_2=5-4i\;</math> y <math>z_3=1+2i\;</math>, determina: |
| + | :a) <math>z_1 \cdot \overline{z_2}</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>z_2 \cdot z_3^{-1}</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>z_3 \cdot (13z_1^{-1}+41z_2^{-1})</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 2 ejercicios (Cociente) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 17 |
| |duracion=6´46" | |duracion=6´46" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0601-dos-ejercicios-6#.VCrxMBa7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cwGyXm5n0AQ&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=13 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Si <math>z_1=2+3i\;</math>, <math>z_2=5-4i\;</math> y <math>z_3=1+2i\;</math>, determina: |
| + | :a) <math>\cfrac{z_1 + \overline{z_2}}{z_3}</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>\cfrac{z_2 + 2z_3}{z_1^{-1}}</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 3 ejercicios (Cociente) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 18 |
| |duracion=8´11" | |duracion=8´11" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0602-tres-ejercicios-3#.VCrxbBa7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FPS9_WouC_I&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=14 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Halla <math>z\;</math>: |
| - | }} | + | |
| + | :a) <math>1+4i=\cfrac{5+2i}{z}</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>1+4i=\cfrac{5}{5+zi}</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>(2-i) \cdot z + 4 =7-5i</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 3 ejercicios (Cociente) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 19 |
| |duracion=7´19" | |duracion=7´19" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/0603-tres-ejercicios-3#.VCrxixa7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4-CfluEYzzI&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=15 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Halla <math>z\;</math>: |
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>4+z-2i=z \cdot i-3</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>\cfrac{2+z \cdot i}{z}=3+4i</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>\cfrac{z}{1+z \cdot i}=3+i</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1= 2 ejercicios (Potencia) | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 20 |
| |duracion=6´49" | |duracion=6´49" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/12-numeros-complejos/1001-dos-ejercicios-9#.VCr5_ha7ZV8 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R5UcB9oP3ZY&list=PLB2E59B57C33C7B8D&index=24 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial. | + | |sinopsis=Calcula usando el [[Fórmula del binomio de Newton (1ºBach)| binomio de Newton]]: |
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(2+3i)^4\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>(2-3i)^5\;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Actividades|titulo=Operaciones con complejos en forma binómica|enunciado= | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Actividad | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma, resta y producto de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/multiplying-complex-numbers-algebra-2/a/complex-number-operations-review | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | '''Suma y resta:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/adding-and-subtracting-complex-numbers-algebra-2/e/adding_and_subtracting_complex_numbers | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | '''Multiplicación:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Actividad | ||
| + | |descripcion=Producto números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/multiplying-complex-numbers-algebra-2/a/multiplying-complex-numbers | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1a | ||
| + | |descripcion=Producto de un número real o un imaginario puro por un número complejo en forma binómica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/multiplying-complex-numbers-algebra-2/e/multiply-complex-numbers-by-real-or-imaginary-numbers | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1b | ||
| + | |descripcion=Producto de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/multiplying-complex-numbers-algebra-2/e/multiplying_complex_numbers | ||
| + | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| ==Representación gráfica de las operaciones con complejos en forma binómica== | ==Representación gráfica de las operaciones con complejos en forma binómica== | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Representación gráfica de las operaciones con complejos en forma binómica | ||
| + | |duracion=14´54" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XxV8SYFES-c&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlut1lGHmwYqQjl6-yDrsPf&index=4 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Ejemplos de suma, resta, multiplicación y división de números complejos en forma binómica. Interpretación gráfica. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Actividades|titulo=Representación gráfica de las operaciones con complejos en forma binómica|enunciado= | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la suma de números complejos en forma binómica. | |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la suma de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | |enlace=[https://ggbm.at/Zhm3k4Kk Suma de números complejos en forma binómica] | + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/Zhm3k4Kk Suma] |
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la resta de números complejos en forma binómica. | |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la resta de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | |enlace=[https://ggbm.at/GPYkzkJA Resta de números complejos en forma binómica] | + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/GPYkzkJA Resta] |
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la multiplicación de números complejos en forma binómica. | |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la multiplicación de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | |enlace=[https://ggbm.at/bm3Vb27Q Multiplicación de números complejos en forma binómica] | + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/bm3Vb27Q Multiplicación] |
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la división de números complejos en forma binómica. | |descripcion=En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la división de números complejos en forma binómica. | ||
| - | |enlace=[https://ggbm.at/knBnTDDU División de números complejos en forma binómica] | + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/knBnTDDU División] |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de números complejos de forma gráfica. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra2/introduction-to-complex-numbers-algebra-2/adding-and-subtracting-complex-numbers-algebra-2/e/complex_plane_operations | ||
| + | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| (Pág. 151) | (Pág. 151) | ||
| + | |||
| ==Propiedades de las operaciones con números complejos== | ==Propiedades de las operaciones con números complejos== | ||
| {{Teorema_sin_demo|titulo=Propiedades|enunciado= | {{Teorema_sin_demo|titulo=Propiedades|enunciado= | ||
| Línea 248: | Línea 387: | ||
| a) Obtener un polinomio de segundo grado cuyas raíces sean <math>5-2i\;</math> y <math>5+2i\;</math>. | a) Obtener un polinomio de segundo grado cuyas raíces sean <math>5-2i\;</math> y <math>5+2i\;</math>. | ||
| - | b) ¿Cuánto ha de valer x para que <math>(2x+i)^2\;</math> sea imaginario puro? | + | b) ¿Cuánto ha de valer <math>x\;</math> para que <math>(2x+i)^2\;</math> sea imaginario puro? |
| |sol= | |sol= | ||
| a) <math>P(x)= [x-(5-2i)][x-(5+2i)]= \cdots = x^2-10x+29\;</math> | a) <math>P(x)= [x-(5-2i)][x-(5+2i)]= \cdots = x^2-10x+29\;</math> | ||
| Línea 256: | Línea 395: | ||
| '''Solución:''' <math>x=\pm 2</math> | '''Solución:''' <math>x=\pm 2</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Operaciones con complejos|enunciado= | + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Ejercicios: ''Operaciones con complejos''|enunciado= |
| {{Video_enlace_matemovil | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| |titulo1= Ejercicio 1 | |titulo1= Ejercicio 1 | ||
| Línea 275: | Línea 414: | ||
| f) <math>|\overline{z_1}|\;</math> | f) <math>|\overline{z_1}|\;</math> | ||
| - | '''Nota:''' El módulo de un número complejo <math>z=a+bi\;</math> es igual a <math>|z|=\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\;</math>. Esto se verá más adelante. | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matemovil | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| Línea 296: | Línea 434: | ||
| a) Halla el valor de "x" sabiendo que <math>5+xi=6-3i\;</math>. | a) Halla el valor de "x" sabiendo que <math>5+xi=6-3i\;</math>. | ||
| - | b) Sea <math>M=(3+2xi)^2</math>.¿Qué valor debe tomar "x" para que M sea imaginario puro? ¿Y para que M sea un número real? | + | b) Sea <math>M=(3+2xi)^2\;</math>.¿Qué valor debe tomar "x" para que M sea imaginario puro? ¿Y para que M sea un número real? |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| + | |duracion=2´25" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xaUnHy6RxWs&index=15&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula "m" y "n" para que sea cierta la igualdad <math>(3m+2i)-(5-2ni)=2-6i\;</math>. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | ||
| + | |duracion=10´41" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xSYPDVvjy-4&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL&index=11 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Halla dos números complejos cuyo cociente sea imaginario puro, su suma sea 5 y el módulo del dividendo sea doble del módulo del divisor. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´01" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lrDzgloS3PM&index=9&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula el valor de "x" de manera que <math>\cfrac{x+i}{1-i}</math> sea: | ||
| + | |||
| + | a) Igual a 1+2i. | ||
| + | |||
| + | b) Un número real. | ||
| + | |||
| + | c)Un número imaginario puro. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´59" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bzHdxNiNKt4&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlrSJWmC0763mdectCCztgL&index=8 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los dos números complejos, 2-mi y 3-ni, halla los valores de "m" y "n" de manera que el producto de los complejos dados sea 8-4i. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| + | |duracion=14´49" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fvTN0G_BRXM&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlut1lGHmwYqQjl6-yDrsPf&index=11 | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | # Halla una ecuación de segundo grado que tengan como raíces a: <math>2+3i\;</math> y <math>2-3i\;</math>. | ||
| + | # Resuelve: <math>z^2+z+1=0\;</math> en el conjunto de los números complejos. | ||
| + | # Halla <math>b\;</math> para que el módulo de <math>\cfrac{b+4i}{1+i}</math> sea <math>\sqrt{26}\;</math>. | ||
| + | # La suma de un complejo y su conjugado es 24 y la suma de sus módulos es 26. Hállalo. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_8cifras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| + | |duracion=14´48" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BGKRzMRR_yQ&list=PLpbLLqs33gIlut1lGHmwYqQjl6-yDrsPf&index=6 | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | # Calcula: a) <math>i^{17}\;</math> ; b) <math>i^{210}\;</math> ; c) <math>i^{160}\;</math> | ||
| + | # Halla el valor de <math>k\;</math> para que \cfrac{2-ki}{k-i} sea: a) imaginario puro; b) real. | ||
| + | # Halla el valor de <math>m\;</math> y <math>n\;</math> para que <math>(2+mi)+(n+5i)=7-2i\;</math> | ||
| + | # Halla el valor de <math>a\;</math> y <math>b\;</math> para que <math>a-3i=\cfrac{2+bi}{5-3i}\;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
Revisión actual
| Enlaces internos | Para repasar o ampliar | Enlaces externos |
| Indice Descartes Manual Casio | WIRIS Geogebra Calculadoras |
Tabla de contenidos |
(Pág. 150)
Operaciones con números complejos en forma binómica
- Suma:
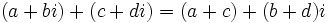
- Resta:
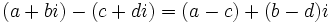
- Multiplicación:
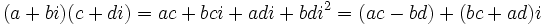
- División:
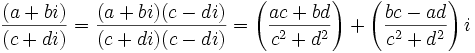 , siempre que
, siempre que 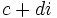 no sea nulo.
no sea nulo.
Ejemplos: Operaciones con complejos en forma binómica
Efectúa las siguientes operaciones:
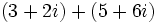
Solución:
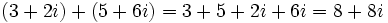
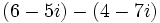
Solución:
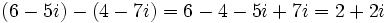
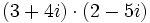
Solución:
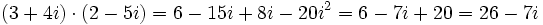
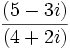
Solución:
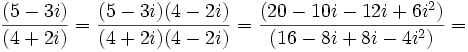
- Definición de suma de números complejos en forma binómica.
- Representación gráfica.
- Ejemplos.
- Propiedades.
- Definición de producto de números complejos en forma binómica.
- Ejemplos.
- Propiedades.
- Definición de cociente de números complejos en forma binómica.
- Ejemplos.
Las potencias de números complejos hacen uso de la fórmula del binomio de Newton. No obstante, son mucho más fáciles si se realizan en forma polar como se verá en otro apartado de este tema.
Dados los complejos 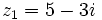 y
y 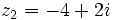 , halla:
, halla:
a) 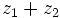
b) 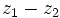 .
.
Dados los complejos 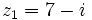 y
y 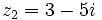 , halla:
, halla:
a) 
b)  .
.
Dados los complejos 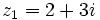 y
y 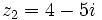 , halla:
, halla:
a) 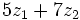
b) 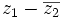
c) 
d) 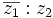
e) 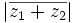
Dados los complejos 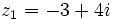 y
y 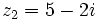 , halla:
, halla:
a) 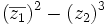
b)  .
.
Dados los complejos 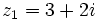 y
y 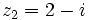 , halla:
, halla:
a) 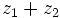
b) 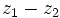 .
.
Dados los complejos 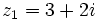 y
y 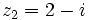 , halla:
, halla:
a) 
b)  .
.
Dados los complejos: 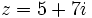 y
y 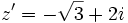 , calcula:
, calcula:
- a)
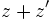
- b)
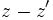
- c)
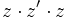
- d)
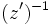
- e)
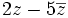
- f)
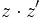
Calcula:
- a)
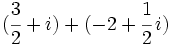
- b)
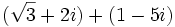
- c)
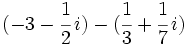
- d)
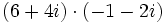
- e)
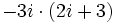
- f)
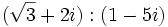
- g)
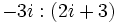
- h)
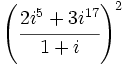
Dados 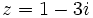 ,
, 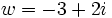 y
y 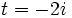 , calcula:
, calcula:
- a)
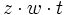
- b)
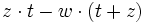
- c)
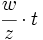
- d)
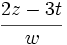
Calcula las potencias de exponente 2, 3 y 4 de los siguientes números complejos:
- a)
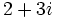
- b)
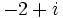
Suma: 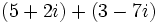
Resta: 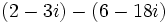
Multiplica: 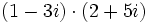
- Determina
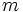 y
y 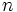 de manera que los complejos
de manera que los complejos 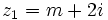 y
y 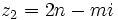 sean tales que
sean tales que 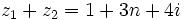 .
.
- Determina
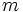 y
y 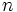 de manera que los complejos
de manera que los complejos 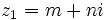 y
y 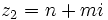 sean tales que
sean tales que 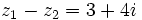 .
.
Calcula 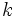 en los siguientes casos:
en los siguientes casos:
- a)
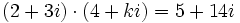
- b)
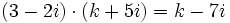
- c)
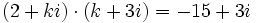
Si 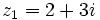 ,
, 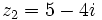 y
y 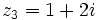 , determina:
, determina:
- a)
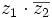
- b)
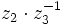
- c)
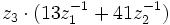
Si 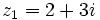 ,
, 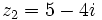 y
y 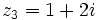 , determina:
, determina:
- a)
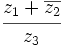
- b)
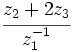
Halla 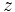 :
:
- a)
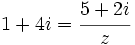
- b)
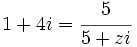
- c)
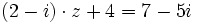
Halla 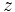 :
:
- a)
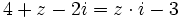
- b)
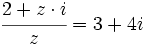
- c)
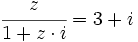
Suma, resta y producto de números complejos en forma binómica.
Suma y resta:
Suma y resta de números complejos en forma binómica.
Multiplicación:
Producto números complejos en forma binómica.
Producto de un número real o un imaginario puro por un número complejo en forma binómica.
Producto de números complejos en forma binómica.
Representación gráfica de las operaciones con complejos en forma binómica
Ejemplos de suma, resta, multiplicación y división de números complejos en forma binómica. Interpretación gráfica.
En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la suma de números complejos en forma binómica.
En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la resta de números complejos en forma binómica.
En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la multiplicación de números complejos en forma binómica.
En esta escena podrás ver como se representa la división de números complejos en forma binómica.
Suma y resta de números complejos de forma gráfica.
(Pág. 151)
Propiedades de las operaciones con números complejos
Propiedades
- Propiedades de la suma:
- Asociativa:
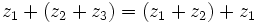
- Conmutativa:
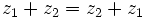
- Existencia de elemento neutro: El 0 es el elemento neutro de la suma.
- Existencia de opuesto: Todo número complejo,
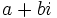 , tiene un opuesto,
, tiene un opuesto, 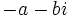
- Asociativa:
- Propiedades del producto:
- Asociativa:
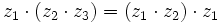
- Conmutativa:
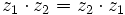
- Existencia de elemento neutro: El 1 es el elemento neutro del producto.
- Existencia de inverso: Todo número complejo,
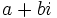 , distinto de 0, tiene inverso,
, distinto de 0, tiene inverso, 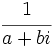 :
:
- Asociativa:
- Propiedad distributiva del producto respecto de la suma:
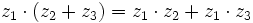
Ejercicios
Ejercicios resueltos
a) Obtener un polinomio de segundo grado cuyas raíces sean 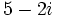 y
y 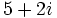 .
.
b) ¿Cuánto ha de valer 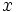 para que
para que 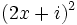 sea imaginario puro?
sea imaginario puro?
a) ![P(x)= [x-(5-2i)][x-(5+2i)]= \cdots = x^2-10x+29\;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/8/e/88e9c5ab01582d012973933375683cfa.png)
b) Hay que desarrollar el cuadrado e igualar la parte real a cero.
Solución: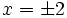
Dados los complejos 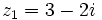 ,
, 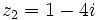 ,
, 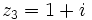 y
y 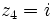 , calcula:
, calcula:
a) 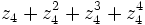 .
.
b) 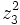
c) 
d) 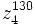
e) 
f) 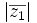
Dados los complejos 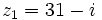 y
y 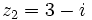 , halla el módulo de
, halla el módulo de 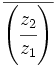 .
.
Calcula: 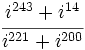 .
.
a) Halla el valor de "x" sabiendo que 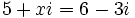 .
.
b) Sea 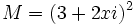 .¿Qué valor debe tomar "x" para que M sea imaginario puro? ¿Y para que M sea un número real?
.¿Qué valor debe tomar "x" para que M sea imaginario puro? ¿Y para que M sea un número real?
Calcula "m" y "n" para que sea cierta la igualdad 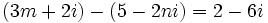 .
.
Halla dos números complejos cuyo cociente sea imaginario puro, su suma sea 5 y el módulo del dividendo sea doble del módulo del divisor.
Calcula el valor de "x" de manera que 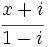 sea:
sea:
a) Igual a 1+2i.
b) Un número real.
c)Un número imaginario puro.
Dados los dos números complejos, 2-mi y 3-ni, halla los valores de "m" y "n" de manera que el producto de los complejos dados sea 8-4i.
- Halla una ecuación de segundo grado que tengan como raíces a:
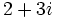 y
y 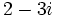 .
.
- Resuelve:
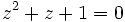 en el conjunto de los números complejos.
en el conjunto de los números complejos.
- Halla
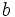 para que el módulo de
para que el módulo de 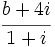 sea
sea 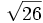 .
.
- La suma de un complejo y su conjugado es 24 y la suma de sus módulos es 26. Hállalo.
- Calcula: a)
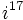 ; b)
; b) 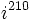 ; c)
; c) 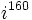
- Halla el valor de
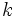 para que \cfrac{2-ki}{k-i} sea: a) imaginario puro; b) real.
para que \cfrac{2-ki}{k-i} sea: a) imaginario puro; b) real.
- Halla el valor de
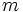 y
y 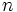 para que
para que 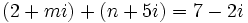
- Halla el valor de
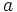 y
y 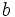 para que
para que 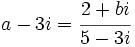
|
Actividad: Operaciones con complejos a) Halla un polinomio de segundo grado cuyas raíces sean b) Halla x para que c) Halla la parte imaginaria de Solución: Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones: a) expand [x-(2+i)][x-(2-i)] b) solve Re[(2+x*i)^2]=0 c) Im[(1-i)^3] |
Ejercicios propuestos
|
Ejercicios propuestos: Operaciones con números complejos |
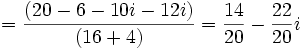
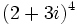
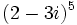
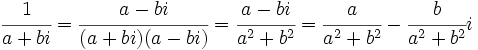
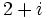 y
y 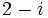 .
.
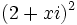 sea imaginario puro.
sea imaginario puro.