Plantilla:Valor absoluto de una función (1ºBach)
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 20:02 11 dic 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Valor absoluto de una función) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Representación gráfica del valor absoluto de una función) |
||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| ==Función valor absoluto== | ==Función valor absoluto== | ||
| {{Tabla50|celda1= | {{Tabla50|celda1= | ||
| - | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=La función '''valor absoluto''' es aquella que a cada número <math>x\;</math> le asigna su [[Valor absoluto (1ºBach)|valor absoluto]]. Es decir: | + | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=La función '''valor absoluto''' es aquella que a cada número <math>x\;</math> le asigna su [[Números reales (1ºBach)#Valor absoluto de un número real|valor absoluto]]. Es decir: |
| {{b}} | {{b}} | ||
| <center><math>|x|=\begin{cases} \ \ \, x & si \ \ x \ge 0 | <center><math>|x|=\begin{cases} \ \ \, x & si \ \ x \ge 0 | ||
| Línea 8: | Línea 8: | ||
| \end{cases} | \end{cases} | ||
| </math></center> | </math></center> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| + | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| + | |descripcion=Representación de la función valor absoluto. | ||
| + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/Jssrej9J Función valor absoluto] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |celda2= | |celda2= | ||
| Línea 23: | Línea 27: | ||
| </math></center> | </math></center> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}}{{p}} | + | {{p}} |
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Valor absoluto de una función | ||
| + | |duracion=7'35" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | Siendo "f" y "u" funciones reales de variable real, escribimos <math>f = |u|</math> si <math>f(x) = |u(x)|</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *La gráfica de "f" coincide con la de "u" en los puntos en que ésta toma valores no negativos. | ||
| + | *En los puntos en que "u" toma valores negativos, la gráfica de "f" es simétrica de la de "u" respecto al eje de abcisas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/15-funciones-reales-de-variable-real/30-la-funcion-valor-absoluto-3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
| |descripcion=Representación conjunta de una función cualquiera y su valor absoluto. | |descripcion=Representación conjunta de una función cualquiera y su valor absoluto. | ||
| - | |enlace=[https://ggbm.at/b6uqNbJp Valor absoluto de una función] | + | |enlace=[http://ggbm.at/b6uqNbJp Valor absoluto de una función] |
| }} | }} | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
| + | ===Representación gráfica del valor absoluto de una función=== | ||
| + | {{Teorema_sin_demo|titulo=Procedimiento|enunciado= | ||
| + | Para representar gráficamente el valor absoluto de una función f: | ||
| - | ==Videos sobre el valor absoluto de una función== | + | #Representamos la función f. |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | #Hacemos una simetría respecto del eje X de la parte de la gráfica de f que está por debajo de dicho eje. |
| - | |titulo1=Valor absoluto de una función | + | #Borramos esa parte de f que está por debajo del eje X. |
| - | |duracion=7'35" | + | #La parte de la gráfica de f que está por encima del eje X la dejamos tal cual. |
| - | |sinopsis=Video tutorial de matematicasbachiller.com | + | #La gráfica resultante es la gráfica del valor absoluto de f. |
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cdiferencial/df_t_01/vdf0130.htm | + | |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{ejemplo2 | + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Representación gráfica del valor absoluto de una función|enunciado= |
| - | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Valor absoluto de una función'' | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |enunciado= | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | |duracion=10'04" |
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |sinopsis=Representa gráficamente: |
| - | |duracion='" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Video tutorial de matematicasbachiller.com | + | :a) <math>y=\left| x-2 \right|</math> |
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cdiferencial/df_t_01/vdf0130_01.htm | + | :b) <math>y=\left| 9-3x \right|</math> |
| + | :c) <math>y=\left| x^2-6x+5 \right|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/15-funciones-reales-de-variable-real/3001-tres-ejercicios-3 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=2. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 |
| - | |duracion='" | + | |duracion=8'36" |
| - | |sinopsis=Video tutorial de matematicasbachiller.com | + | |sinopsis=Representa gráficamente: |
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cdiferencial/df_t_01/vdf0130_02.htm | + | |
| + | :a) <math>y=x+ \left| x-2 \right|</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>y=x^2 - \left| x^2-4 \right|</math> | ||
| + | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/15-funciones-reales-de-variable-real/3002-dos-ejercicios-3 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=3. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 |
| - | |duracion='" | + | |duracion=4'27" |
| - | |sinopsis=Video tutorial de matematicasbachiller.com | + | |sinopsis=Representa gráficamente: <math>y=x^2 - \left| 4-x^2 \right|</math> |
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cdiferencial/df_t_01/vdf0130_03.htm | + | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/15-funciones-reales-de-variable-real/3003-ejercicio-6 |
| }} | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_unicoos | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | ||
| + | |duracion=30'33" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Representa gráficamente: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>f(x)=x+ | x-2 |</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>g(x)=\left| x^2-4 \right|</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>h(x)=| x | - x</math> | ||
| + | :d) <math>i(x)=\cfrac{x^2+1}{|x|}</math> | ||
| + | :e) <math>j(x)=\left| 2-\sqrt{1-x} \right|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.unicoos.com/video/matematicas/4-eso/funciones-elementales/funciones-a-trozos/funcion-a-trozos-valor-absoluto | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Representación gráfica del valor absoluto de una función | ||
| + | |descripcion=Autoevaluación. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/absolute-value-equations-functions/graphs-of-absolute-value-functions/e/graphs-of-absolute-value-functions | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
Revisión actual
[editar]
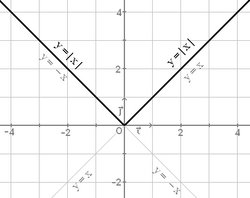
Función valor absoluto
La función valor absoluto es aquella que a cada número 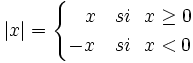 Representación de la función valor absoluto. |
[editar]
Valor absoluto de una función
El valor absoluto de una función se define como:
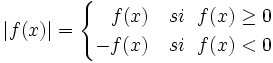
Siendo "f" y "u" funciones reales de variable real, escribimos f = | u | si f(x) = | u(x) | .
- La gráfica de "f" coincide con la de "u" en los puntos en que ésta toma valores no negativos.
- En los puntos en que "u" toma valores negativos, la gráfica de "f" es simétrica de la de "u" respecto al eje de abcisas.
Representación conjunta de una función cualquiera y su valor absoluto.
[editar]
Representación gráfica del valor absoluto de una función
Procedimiento
Para representar gráficamente el valor absoluto de una función f:
- Representamos la función f.
- Hacemos una simetría respecto del eje X de la parte de la gráfica de f que está por debajo de dicho eje.
- Borramos esa parte de f que está por debajo del eje X.
- La parte de la gráfica de f que está por encima del eje X la dejamos tal cual.
- La gráfica resultante es la gráfica del valor absoluto de f.
Representa gráficamente:
- a)
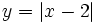
- b)
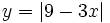
- c)
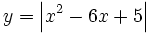
Representa gráficamente:
- a)
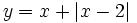
- b)
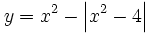
Representa gráficamente: 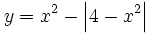
Representa gráficamente:
- a) f(x) = x + | x − 2 |
- b)
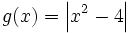
- c) h(x) = | x | − x
- d)
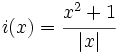
- e)
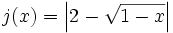
Autoevaluación.
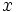 le asigna su
le asigna su