Plantilla:Radicales (nivel básico)
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 17:02 7 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Operaciones con radicales) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales) |
||
| Línea 15: | Línea 15: | ||
| |duracion=3´14" | |duracion=3´14" | ||
| |sinopsis=Radicales: homogéneos y semejantes. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Radicales: homogéneos y semejantes. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=70igFycZ3-4 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=70igFycZ3-4 |
| }} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| ==Radicales equivalentes== | ==Radicales equivalentes== | ||
| - | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Dos o más radicales son '''equivalentes''' si los exponentes de las potencias asociadas son equivalentes.}} | + | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Dos o más radicales son '''equivalentes''' si se pueden poner como potencias de exponente fraccionario con la misma base y cuyos exponentes sean fracciones equivalentes.}} |
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{AI_descartes|titulo1=Radicales equivalentes. Amplificación y simplificación | + | {{Actividades|titulo=Radicales equivalentes|enunciado= |
| + | {{AI_descartes|titulo1=Actividad | ||
| |descripcion=Actividades en las que podrás aprender lo que son radicales equivalentes y cómo obtener radicales equivalentes con un índice superior (amplificación) o inferior (simplificación) | |descripcion=Actividades en las que podrás aprender lo que son radicales equivalentes y cómo obtener radicales equivalentes con un índice superior (amplificación) o inferior (simplificación) | ||
| Línea 26: | Línea 28: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{AI_vitutor | {{AI_vitutor | ||
| - | |titulo1=Autoevaluación: ''Radicales equivalentes'' | + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación |
| |descripcion=Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre radicales equivalentes. | |descripcion=Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre radicales equivalentes. | ||
| |url1=http://www.vitutor.com/di/re/r9e.html | |url1=http://www.vitutor.com/di/re/r9e.html | ||
| + | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 53: | Línea 56: | ||
| |duracion=4'53" | |duracion=4'53" | ||
| |sinopsis=Ordenación de radicales. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Ordenación de radicales. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RHlcHUCbCIE&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTf_vLErckNhkqH29aE696DA&index=9 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RHlcHUCbCIE&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTf_vLErckNhkqH29aE696DA&index=9 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| ==Operaciones con radicales== | ==Operaciones con radicales== | ||
| - | En los siguientes videotutoriales se presentan las operaciones más sencillas con radicales y puede servirte como punto de partida para abordar este apartado sobre operaciones con radicales. | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Operaciones básicas con radicales|enunciado= | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial | ||
| - | |duracion=17'15" | ||
| - | |sinopsis=*Definición de radical y de radicales semejantes. | ||
| - | *Suma de radicales semejantes. | ||
| - | *Radicales opuestos. | ||
| - | *Resta de radicales semejantes. | ||
| - | *Producto de radicales del mismo índice. | ||
| - | *División de radicales del mismo índice. | ||
| - | *Potencia de un radical. | ||
| - | *Raíz de un radical. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z9xLQJq4iaU&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=31'06" | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | 1) Radicales semejantes: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :1a) Escribe tres radicales semejantes y tres que no lo sean. | ||
| - | :1b) Escribe dos radicales semejantes opuestos. | ||
| - | |||
| - | 2) Calcula: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :2a) <math>30 \sqrt{10}+7 \sqrt{10}-3 \sqrt{10}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2b) <math>-2 \sqrt{5}-3 \sqrt{5}+ \sqrt{2}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2c) <math>\sqrt{20}+3 \sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2d) <math>-3 \sqrt[3]{11}+\sqrt[3]{11}-8 \sqrt[3]{11}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2e) <math>-8 \sqrt[3]{11}+4 \sqrt[3]{11}-2 \sqrt[3]{11}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2f) <math>\sqrt[3]{-5}-5 \sqrt[3]{-5}+2 \sqrt[3]{-5}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2g) <math>6 \sqrt[8]{3}+12 \sqrt[8]{3}-4 \sqrt[8]{3}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2h) <math>5 \sqrt[11{-8}+9 \sqrt[11{-8}- \sqrt[11{-8}\;</math> | ||
| - | :2i) <math>-\sqrt[5]{3}- \sqrt[5]{3}-4 \sqrt[5]{3}\;</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | 3) Halla el opuesto de los siguiente radicales y después suma cada radical con su opuesto: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :3a) <math>\sqrt{6}\;</math> | ||
| - | :3b) <math>7 \sqrt{4}\;</math> | ||
| - | :3c) <math>-5\sqrt[3]{2}\;</math> | ||
| - | :3d) <math>-8\sqrt[3]{-3}\;</math> | ||
| - | :3e) <math>14\sqrt[3]{5}\;</math> | ||
| - | :3f) <math>-5\sqrt[4]{7}\;</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | 4) Calcula: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :4a) <math>\sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{2} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4b) <math>\sqrt{3} \cdot \sqrt{3} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4c) <math>\sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4d) <math>\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4e) <math>\sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4f) <math>\sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4g) <math>\sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2}\;</math> | ||
| - | :4h) <math>\sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4i) <math>\sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \;</math> | ||
| - | :4j) <math>\sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2}\;</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m5gfQaggOug&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o&index=2 | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | ||
| - | |duracion=33'52" | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Operaciones con radicales. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x69WNJj8HWg&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o&index=3 | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| ===Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales=== | ===Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales=== | ||
| {{Teorema|titulo=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales|enunciado= | {{Teorema|titulo=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales|enunciado= | ||
| Línea 172: | Línea 102: | ||
| |duracion=23'07" | |duracion=23'07" | ||
| |sinopsis=Tutorial que explica las propiedades básicas de los radicales, con ejemplos resueltos. | |sinopsis=Tutorial que explica las propiedades básicas de los radicales, con ejemplos resueltos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_ehyRog7Fg&index=4&list=PLZNmE9BEzVImIKACrwlnJVOz_w7oxAoRy | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_ehyRog7Fg&index=4&list=PLZNmE9BEzVImIKACrwlnJVOz_w7oxAoRy |
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras |
| |titulo1=Tutorial 2 | |titulo1=Tutorial 2 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'46" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/gz2sN2QC4Dk?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSC9n7yjv8UoDKiokY6LF84S | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 3 | ||
| |duracion=10'19" | |duracion=10'19" | ||
| |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GgVW0-Yre9Q&index=1&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3PUSesWagsxJdOfANgK_LO | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GgVW0-Yre9Q&index=1&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3PUSesWagsxJdOfANgK_LO |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 184: | Línea 120: | ||
| |duracion=7'18" | |duracion=7'18" | ||
| |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptP3J7pXVX4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruMXl8lMqUrHqxIGFQvLw9aR&index=1 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ptP3J7pXVX4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruMXl8lMqUrHqxIGFQvLw9aR&index=1 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 190: | Línea 126: | ||
| |duracion=4'27" | |duracion=4'27" | ||
| |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ha5JcSlzs_Q&list=PLo7_lpX1yruMXl8lMqUrHqxIGFQvLw9aR&index=2 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ha5JcSlzs_Q&list=PLo7_lpX1yruMXl8lMqUrHqxIGFQvLw9aR&index=2 |
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejemplos | ||
| + | |duracion=6'28" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Ejemplos sencillos de aplicación de las propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/xHH4LECRQXM?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSC9n7yjv8UoDKiokY6LF84S | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| Línea 197: | Línea 140: | ||
| |duracion=3'07" | |duracion=3'07" | ||
| |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(3\sqrt {xy}) \cdot (-2\sqrt {x^2y}) \cdot (-3\sqrt {xy^4})</math> | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(3\sqrt {xy}) \cdot (-2\sqrt {x^2y}) \cdot (-3\sqrt {xy^4})</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Ri6V4wGWEE&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45&index=85 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Ri6V4wGWEE&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45&index=85 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| Línea 203: | Línea 146: | ||
| |duracion=2'43" | |duracion=2'43" | ||
| |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(-8\sqrt[3] {x^{10}y^2}) : (-4\sqrt[3] {xy^{11}})</math> | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(-8\sqrt[3] {x^{10}y^2}) : (-4\sqrt[3] {xy^{11}})</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uRQb6oLXyQo&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45&index=88 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uRQb6oLXyQo&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45&index=88 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| Línea 210: | Línea 153: | ||
| |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>\sqrt[4]{\cfrac{81}{16}}</math> | |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>\sqrt[4]{\cfrac{81}{16}}</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PaT2DdRhkMo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PaT2DdRhkMo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_abel | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| Línea 220: | Línea 163: | ||
| - | |url1=https://youtu.be/ZZmTpbqg1mY?t=6m12s | + | |url1=http://youtu.be/ZZmTpbqg1mY?t=6m12s |
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 247: | Línea 190: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| + | ===Actividades=== | ||
| + | En los siguientes videotutoriales vamos a repasar las operaciones con radicales vistas hasta ahora, antes de pasar a ver otros casos de mayor dificultad. | ||
| + | {{p}} | ||
| + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Operaciones básicas con radicales|enunciado= | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial | ||
| + | |duracion=17'15" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=*Definición de radical y de radicales semejantes. | ||
| + | *Suma de radicales semejantes. | ||
| + | *Radicales opuestos. | ||
| + | *Resta de radicales semejantes. | ||
| + | *Producto de radicales del mismo índice. | ||
| + | *División de radicales del mismo índice. | ||
| + | *Potencia de un radical. | ||
| + | *Raíz de un radical. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z9xLQJq4iaU&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1a | ||
| + | |duracion=31'06" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | 1) Radicales semejantes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :1a) Escribe tres radicales semejantes y tres que no lo sean. | ||
| + | :1b) Escribe dos radicales semejantes opuestos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :2a) <math>30 \sqrt{10}+7 \sqrt{10}-3 \sqrt{10}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2b) <math>-2 \sqrt{5}-3 \sqrt{5}+ \sqrt{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2c) <math>\sqrt{20}+3 \sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2d) <math>-3 \sqrt[3]{11}+\sqrt[3]{11}-8 \sqrt[3]{11}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2e) <math>-8 \sqrt[3]{11}+4 \sqrt[3]{11}-2 \sqrt[3]{11}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2f) <math>\sqrt[3]{-5}-5 \sqrt[3]{-5}+2 \sqrt[3]{-5}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2g) <math>6 \sqrt[8]{3}+12 \sqrt[8]{3}-4 \sqrt[8]{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2h) <math>5 \sqrt[11]{-8}+9 \sqrt[11]{-8}- \sqrt[11]{-8}\;</math> | ||
| + | :2i) <math>-\sqrt[5]{3}- \sqrt[5]{3}-4 \sqrt[5]{3}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3) Halla el opuesto de los siguiente radicales y después suma cada radical con su opuesto: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :3a) <math>\sqrt{6}\;</math> | ||
| + | :3b) <math>7 \sqrt{4}\;</math> | ||
| + | :3c) <math>-5\sqrt[3]{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | :3d) <math>-8\sqrt[3]{-3}\;</math> | ||
| + | :3e) <math>14\sqrt[3]{5}\;</math> | ||
| + | :3f) <math>-5\sqrt[4]{7}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :4a) <math>\sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{2} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4b) <math>\sqrt{3} \cdot \sqrt{3} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4c) <math>\sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4d) <math>\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4e) <math>\sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4f) <math>\sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4g) <math>\sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2}\;</math> | ||
| + | :4h) <math>\sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4i) <math>\sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \;</math> | ||
| + | :4j) <math>\sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :5a) <math>2\sqrt{3} \cdot 3\sqrt{5} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5b) <math>3\sqrt{5} \cdot 2\sqrt{6} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5c) <math>3\sqrt{6} \cdot 5\sqrt{2} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5d) <math>-2\sqrt{3} \cdot 5\sqrt{3} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5e) <math>8\sqrt{7} \cdot (-2)\sqrt{7} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5f) <math>3\sqrt{3} \cdot (-7\sqrt{6}) \cdot 4\sqrt{6} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5g) <math>-5\sqrt{12} \cdot (-\sqrt{12}) \cdot 4\sqrt{12} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5h) <math>3\sqrt{3} \cdot (-3\sqrt{3}) \cdot (-4)\sqrt{3} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5h) <math>-3\sqrt{5} \cdot (-7\sqrt{5}) \cdot \sqrt{5} \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m5gfQaggOug&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o&index=2 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1b | ||
| + | |duracion=33'52" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | 5) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :5i) <math>2\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot 3\sqrt[3]{3} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5j) <math>3\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot 2\sqrt[3]{5} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5k) <math>3\sqrt[3]{6} \cdot 5\sqrt[3]{6} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5l) <math>-2\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot 5\sqrt[3]{3} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5m) <math>8\sqrt[3]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[3]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{-7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5n) <math>3\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot (-7\sqrt[3]{3}) \cdot 4\sqrt[3]{3} \;</math> | ||
| + | :5o) <math>-5\sqrt[3]{12} \cdot (-\sqrt[3]{12}) \cdot 4\sqrt[3]{12} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5p) <math>3\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot (-3\sqrt[3]{3}) \cdot (-4\sqrt[3]{3}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 5q) <math>-3\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot (-7\sqrt[3]{5}) \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6a) <math>\sqrt{14} : \sqrt{7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6b) <math>8\sqrt{30} : (-2\sqrt{3}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6c) <math>-10\sqrt{15} : 5\sqrt{5} \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6d) <math>6\sqrt{12} : (-\sqrt{2}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6e) <math>20\sqrt{7} : 10\sqrt{7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6f) <math>\sqrt[3]{14} : \sqrt[3]{7} \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6g) <math>9\sqrt[3]{14} : (-\sqrt[3]{-7}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6h) <math>-10\sqrt[3]{15} : 5\sqrt[3]{5} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6i) <math>12\sqrt[3]{18} : (-6\sqrt[3]{-9}) \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6j) <math>-30\sqrt[3]{14} : 6\sqrt[3]{7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6k) <math>\sqrt[4]{14} : \sqrt[4]{7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6l) <math>9\sqrt[4]{14} : (-\sqrt[4]{7}) \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6m) <math>-10\sqrt[4]{15} : 5\sqrt[4]{5} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6n) <math>12\sqrt[4]{18} : (-6\sqrt[4]{9}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6o) <math>-30\sqrt[4]{14} : 6\sqrt[4]{7}) \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :6p) <math>\sqrt[5]{14} : \sqrt[5]{7} \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6q) <math>9\sqrt[5]{14} : (-\sqrt[5]{7}) \;</math> ; {{b4}} 6r) <math>-10\sqrt[5]{15} : 5\sqrt[5]{5}) \;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(\sqrt{7})^2\;</math> ; {{b4}} b) <math>(\sqrt[3]{7})^3\;</math> ; {{b4}} c) <math>(\sqrt[4]{7})^4\;</math> ; {{b4}} d) <math>(\sqrt{5})^2\;</math> ; {{b4}} e) <math>(\sqrt[3]{5})^3\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :f) <math>(\sqrt[4]{21})^4\;</math> ; {{b4}} g) <math>(\sqrt{25})^2\;</math> ; {{b4}} h) <math>(\sqrt[3]{-25})^3\;</math> ; {{b4}} i) <math>(\sqrt[4]{100})^4\;</math> ; {{b4}} j) <math>(\sqrt{18})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :k) <math>(\sqrt[3]{-100})^3\;</math> ; {{b4}} l) <math>(\sqrt[5]{16})^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} m) <math>(\sqrt{100})^2\;</math> ; {{b4}} n) <math>(\sqrt[3]{18})^3\;</math> ; {{b4}} o) <math>(\sqrt[6]{12})^6\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8) Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>\sqrt{\sqrt{2}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} b) <math>\sqrt{\sqrt{3}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} c) <math>\sqrt{\sqrt{7}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} d) <math>\sqrt[3]{\sqrt{2}}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :e) <math>\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[3]{25}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} f) <math>\sqrt{\sqrt[3]{64}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} g) <math>\sqrt[4]{\sqrt[3]{2}}\;</math> ; {{b4}} h) <math>\sqrt[3]{\sqrt{128}}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x69WNJj8HWg&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3ozxW7jq_j3xSPsocWGGn25o&index=3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
Revisión actual
Tabla de contenidos |
Radical
- Un radical es cualquier expresión del tipo:
![k \cdot \sqrt[n]{a}~,~k \in \mathbb{R}](/wikipedia/images/math/c/2/6/c26445b313b501056047ed7787606a37.png)
- Si dos radicales tienen el mismo índice diremos que son homogéneos.
- Si dos radicales tienen el mismo índice y el mismo radicando diremos que son semejantes.
Radicales: homogéneos y semejantes. Ejemplos.
Radicales equivalentes
Dos o más radicales son equivalentes si se pueden poner como potencias de exponente fraccionario con la misma base y cuyos exponentes sean fracciones equivalentes.
Actividades en las que podrás aprender lo que son radicales equivalentes y cómo obtener radicales equivalentes con un índice superior (amplificación) o inferior (simplificación)
Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre radicales equivalentes.
Reducción de radicales a índice común
La amplificación y simplificación de radicales nos va a permitir reducir radicales a índice común realizando el mínimo común múltiplo de los índice al igual que para reducir fracciones a común denominador se hacía el m.c.m. de los denominadores. No olvidemos que índice y denominador del exponente es lo mismo.
Reducción de radicales a índice común. Ejemplos.
Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre reducción de radicales a índice común.
Ordenación de radicales
La reducción de radicales a índice común nos va a permitir ordenar cómodamente varios radicales:
Ordenación de radicales. Ejemplos.
Operaciones con radicales
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales
1. ![\sqrt[np]{a^p}=\sqrt[n]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/1/9/0/19055926ec943d41884a4e4efb9e3958.png)
2. ![\left ( \sqrt[n]{a}\right )^p=\sqrt[n]{a^p}](/wikipedia/images/math/0/8/f/08f48fff6b28e5860652ad48624e9b54.png)
3. ![\sqrt[m]{\sqrt[n]{a}}=\sqrt[mn]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/8/8/2/882098878748f7e317a403bacf091e37.png)
4. ![\sqrt[n]{a} \cdot \sqrt[n]{b}=\sqrt[n]{a \cdot b}](/wikipedia/images/math/7/3/d/73d577cd0a118df1dda404e72e4a922d.png)
5. ![\cfrac{\sqrt[n]{a}}{\sqrt[n]{b}}=\sqrt[n]{\cfrac{a}{b}}](/wikipedia/images/math/4/8/d/48d4191b86a6079638a33f860884bd8e.png)
Para demostrar estas propiedades basta con expresar el radical como potencia de exponente fraccionario y aplicar sus propiedades.
Ejercicios resueltos: Radicales. Propiedades
Simplificar: a) ![\sqrt[12]{x^9}](/wikipedia/images/math/9/4/2/942b2336ccb4cf42b2cbd07ed9c75ede.png) , b)
, b) ![\left ( \sqrt[3]{a^2} \right )^6](/wikipedia/images/math/9/a/1/9a1db4aea08869857d67618e54707551.png) , c)
, c) ![\sqrt{\sqrt[3]{a}}](/wikipedia/images/math/4/7/3/473cf1ea29276b3cfe84680bf3548a10.png) , d)
, d) ![\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot \sqrt[3]{9}](/wikipedia/images/math/6/d/2/6d24beca08bdb942089cf6ad8b4c7d1c.png) , e)
, e) 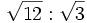
a) ![\sqrt[12]{x^9}=\sqrt[4 \cdot 3]{x^{3 \cdot 3}}=\sqrt[4]{x^{3}}](/wikipedia/images/math/d/1/9/d190b659acadff5f242846e5d6014e10.png) , usando la propiedad nº 1.
, usando la propiedad nº 1.
b) ![\left ( \sqrt[3]{a^2} \right )^6=\sqrt[3]{a^{12}}=a^{\frac{12}{3}}=a^4](/wikipedia/images/math/9/4/b/94b477fe13f98eac4d76261cf2c34d2c.png) , usando la propiedad nº 2 y transformando el radical en potencia de exponente fraccionario.
, usando la propiedad nº 2 y transformando el radical en potencia de exponente fraccionario.
c) ![\sqrt{\sqrt[3]{a}}=\sqrt[2 \cdot 3]{a}=\sqrt[6]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/9/4/a/94ad123ac81d4cf1d017be5a726de942.png) , usando la propiedad nº 3.
, usando la propiedad nº 3.
d) ![\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot \sqrt[3]{9}= \sqrt[3]{3 \cdot 9} =\sqrt[3]{27}=3](/wikipedia/images/math/b/7/b/b7b21e3525e1caa80c30fe91bbb85c77.png) , usando la propiedad nº 4.
, usando la propiedad nº 4.
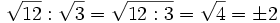 , usando la propiedad nº 5.
, usando la propiedad nº 5.Actividades en las que podrás aprender las propiedades de las operaciones con radicales del mismo índice.
Tutorial que explica las propiedades básicas de los radicales, con ejemplos resueltos.
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos.
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos.
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos.
Propiedades de las operaciones con radicales. Ejemplos.
Ejemplos sencillos de aplicación de las propiedades de las operaciones con radicales.
Simplifica: 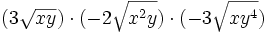
Simplifica: ![(-8\sqrt[3] {x^{10}y^2}) : (-4\sqrt[3] {xy^{11}})](/wikipedia/images/math/2/1/b/21b675f2e891ca1cd137acdf888cbcde.png)
Calcula: ![\sqrt[4]{\cfrac{81}{16}}](/wikipedia/images/math/9/e/d/9ed2bdc3b33dce510e788cce2d6938b7.png)
Calcula:
1) 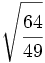 2)
2) ![\sqrt[4]{\cfrac{1}{81}}](/wikipedia/images/math/a/5/4/a54618bf9ee77a830fab9a825f43fad0.png) 3)
3) ![\sqrt[3]{\cfrac{-27~~}{125}}](/wikipedia/images/math/5/c/3/5c3b48c07709122b11aadf157c159924.png) 4)
4) ![\sqrt[5]{\cfrac{-32~~}{243}}](/wikipedia/images/math/7/5/8/758e101bb00fde536dd8dc589f2eab1d.png)
Suma y resta de radicales semejantes
Para sumar y restar radicales, éstos deben ser semejantes, es decir, tener el mismo radicando y el mismo índice. En tal caso el radical el radical resultante tiene como coeficiente la suma o resta de los coeficientes de cada uno de los radicales.
Ejemplo: Suma y resta de radicales semejantes
Efectúa las siguientes sumas y restas de radicales:
1. 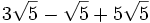
2. 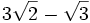
3. ![3\sqrt[3]{2}+\sqrt{2}](/wikipedia/images/math/f/5/5/f554a76b3698de9bd3d86d6600364c25.png)
1. 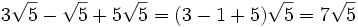
2. 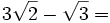 (No se puede simplificar)
(No se puede simplificar)
![3\sqrt[3]{2}+\sqrt{2}=](/wikipedia/images/math/a/6/e/a6edb4be927bfe44dff1ae00ac0eb772.png) (No se puede simplificar)
(No se puede simplificar)Actividades
En los siguientes videotutoriales vamos a repasar las operaciones con radicales vistas hasta ahora, antes de pasar a ver otros casos de mayor dificultad.
- Definición de radical y de radicales semejantes.
- Suma de radicales semejantes.
- Radicales opuestos.
- Resta de radicales semejantes.
- Producto de radicales del mismo índice.
- División de radicales del mismo índice.
- Potencia de un radical.
- Raíz de un radical.
1) Radicales semejantes:
- 1a) Escribe tres radicales semejantes y tres que no lo sean.
- 1b) Escribe dos radicales semejantes opuestos.
2) Calcula:
- 2a)
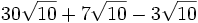
- 2b)
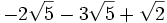
- 2c)
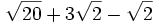
- 2d)
![-3 \sqrt[3]{11}+\sqrt[3]{11}-8 \sqrt[3]{11}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/3/8/6/386dda78a1c0a8e06a7d92ad446cca8a.png)
- 2e)
![-8 \sqrt[3]{11}+4 \sqrt[3]{11}-2 \sqrt[3]{11}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/b/c/9bc9cc4fe2abf85a102fd7edd8a91a3e.png)
- 2f)
![\sqrt[3]{-5}-5 \sqrt[3]{-5}+2 \sqrt[3]{-5}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/7/9/7/797db9d9f2a327215cf66dc0fd1a0989.png)
- 2g)
![6 \sqrt[8]{3}+12 \sqrt[8]{3}-4 \sqrt[8]{3}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/a/3/ea3c1128b9341e9ee92e9adf7dbf36e8.png)
- 2h)
![5 \sqrt[11]{-8}+9 \sqrt[11]{-8}- \sqrt[11]{-8}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/f/c/cfc360decb13c219ecfed5246e616bbc.png)
- 2i)
![-\sqrt[5]{3}- \sqrt[5]{3}-4 \sqrt[5]{3}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/d/0/cd013a1ff11c225a935a2891232efb7a.png)
3) Halla el opuesto de los siguiente radicales y después suma cada radical con su opuesto:
- 3a)
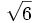
- 3b)

- 3c)
![-5\sqrt[3]{2}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/2/9/b/29ba151ca92717a7ec2fce60d9a43887.png)
- 3d)
![-8\sqrt[3]{-3}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/4/a/44af796a04099974506078fbdaa97c8e.png)
- 3e)
![14\sqrt[3]{5}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/a/8/b/a8b18bd1e94168e14bdfa178486c55de.png)
- 3f)
![-5\sqrt[4]{7}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/c/3/9c3b71fe66e4cd559e4c1c3e2d8f0d50.png)
4) Calcula:
- 4a)
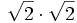
- 4b)
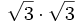
- 4c)
![\sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{2} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/b/7/8b72eb2e695638b1b598aa91906d2afd.png)
- 4d)
![\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/7/0/4706a180f7cecca86f552cb03bc61723.png)
- 4e)
![\sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \cdot \sqrt[4]{3} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/7/1/871aec8b9c551d588f6bb0f7652776b0.png)
- 4f)
![\sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \cdot \sqrt[6]{7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/6/1/c61ef44eacb7a1efa0af29b13e778c84.png)
- 4g)
![\sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[5]{-2}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/a/a/baaf1e13d7ae13183caee280ed997078.png)
- 4h)
![\sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[7]{-7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/3/0/4/3044aa9fbabf7c1d05d005d3d067c642.png)
- 4i)
![\sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \cdot \sqrt[8]{6} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/2/4/f24f9a63eafe40b3e6d366a5e52f6be1.png)
- 4j)
![\sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2} \cdot \sqrt[10]{2}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/5/6/9/5699ece51e33ce84d469d13405c1a662.png)
5) Calcula:
- 5a)
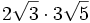
- 5b)
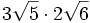
- 5c)
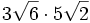
- 5d)
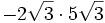
- 5e)
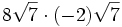
- 5f)
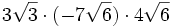
- 5g)
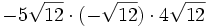
- 5h)
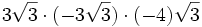
- 5h)
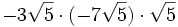
5) Calcula:
- 5i)
![2\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot 3\sqrt[3]{3} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/b/8/eb885ee9f22a7b60f1fba48b165a9bba.png) ; 5j)
; 5j) ![3\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot 2\sqrt[3]{5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/7/4/8/74817e09bd26600d541bc7f27acc2721.png) ; 5k)
; 5k) ![3\sqrt[3]{6} \cdot 5\sqrt[3]{6} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/d/7/4d731dfeb72737e5ea4b3fae68d986bc.png)
- 5l)
![-2\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot 5\sqrt[3]{3} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/d/0/bd0bdd2316e3647e561f42eea5e49432.png) ; 5m)
; 5m) ![8\sqrt[3]{-7} \cdot \sqrt[3]{-2} \cdot \sqrt[3]{-7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/d/e/6/de6d9da92635aa3ed672a1d37bbb9d1e.png) ; 5n)
; 5n) ![3\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot (-7\sqrt[3]{3}) \cdot 4\sqrt[3]{3} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/d/7/8d7ab02625222fb400fbef68aae4f1a9.png)
- 5o)
![-5\sqrt[3]{12} \cdot (-\sqrt[3]{12}) \cdot 4\sqrt[3]{12} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/2/4/d/24db05991b4866bee0cf063c06a2a5a4.png) ; 5p)
; 5p) ![3\sqrt[3]{3} \cdot (-3\sqrt[3]{3}) \cdot (-4\sqrt[3]{3}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/b/1/0b12fb80b6b5d9ab9cff8bdda29e3670.png) ; 5q)
; 5q) ![-3\sqrt[3]{5} \cdot (-7\sqrt[3]{5}) \cdot \sqrt[3]{5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/9/3/493e61292a0c10080a211793ad3d938a.png)
6) Calcula:
- 6a)
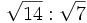 ; 6b)
; 6b) 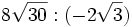 ; 6c)
; 6c) 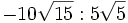
- 6d)
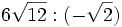 ; 6e)
; 6e) 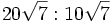 ; 6f)
; 6f) ![\sqrt[3]{14} : \sqrt[3]{7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/5/5/e55782cffbcf990bcc3401f1a26c47b6.png)
- 6g)
![9\sqrt[3]{14} : (-\sqrt[3]{-7}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/a/6/ea6ac7a2061e05e92f94b80d4af19663.png) ; 6h)
; 6h) ![-10\sqrt[3]{15} : 5\sqrt[3]{5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/3/0/c308580a14622890c46723f7fdf783fb.png) ; 6i)
; 6i) ![12\sqrt[3]{18} : (-6\sqrt[3]{-9}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/5/9/05982cd16e41d3ae4cdc9d011905ad4b.png)
- 6j)
![-30\sqrt[3]{14} : 6\sqrt[3]{7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/0/9/00930632b62d29b0446beb2eb4585c39.png) ; 6k)
; 6k) ![\sqrt[4]{14} : \sqrt[4]{7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/3/7/d/37d6db29364ddf586bf938556c44bf69.png) ; 6l)
; 6l) ![9\sqrt[4]{14} : (-\sqrt[4]{7}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/1/2/c12d93323a255c0807c702a7d1c4fd3a.png)
- 6m)
![-10\sqrt[4]{15} : 5\sqrt[4]{5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/b/4/fb47b8279375acea84ad3b6776fe52d9.png) ; 6n)
; 6n) ![12\sqrt[4]{18} : (-6\sqrt[4]{9}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/e/e/0ee9a8d792aa42be622074880b8c1737.png) ; 6o)
; 6o) ![-30\sqrt[4]{14} : 6\sqrt[4]{7}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/8/6/f86747fe7edf79f2f565ae3b47c5f5cc.png)
- 6p)
![\sqrt[5]{14} : \sqrt[5]{7} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/e/d/cedeedebf22023c7095857fdb5f89cd9.png) ; 6q)
; 6q) ![9\sqrt[5]{14} : (-\sqrt[5]{7}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/a/0/8/a0809badb27cd335d6d595e07efabe29.png) ; 6r)
; 6r) ![-10\sqrt[5]{15} : 5\sqrt[5]{5}) \;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/9/9/b99dbf9eb1bd9e64b5651116476d3105.png)
7) Calcula:
- a)
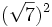 ; b)
; b) ![(\sqrt[3]{7})^3\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/3/6/e3645d99093cd9065fb2082d8c6c6c01.png) ; c)
; c) ![(\sqrt[4]{7})^4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/4/f/84f808c115fe3de548ae9bfe5824709f.png) ; d)
; d) 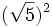 ; e)
; e) ![(\sqrt[3]{5})^3\;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/2/b/f2bf6748d06d16bcaae81f483dfd71c9.png)
- f)
![(\sqrt[4]{21})^4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/d/e/7/de71424f30904a433e21926aea5c19ea.png) ; g)
; g) 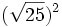 ; h)
; h) ![(\sqrt[3]{-25})^3\;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/7/8/478cc6706fac0d47cfc87e4c40c1a9fa.png) ; i)
; i) ![(\sqrt[4]{100})^4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/6/1/d/61d8bd6207295d4b3de801045656acdb.png) ; j)
; j) 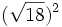
- k)
![(\sqrt[3]{-100})^3\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/1/6/e16420641a6f36c33546ff527203864c.png) ; l)
; l) ![(\sqrt[5]{16})^5\;](/wikipedia/images/math/8/0/2/802fdd52c9cc6b2275f4ecb0a8ca4ae1.png) ; m)
; m) 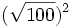 ; n)
; n) ![(\sqrt[3]{18})^3\;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/c/c/bcc549d18d80fd5c5888a59db21937bf.png) ; o)
; o) ![(\sqrt[6]{12})^6\;](/wikipedia/images/math/5/9/7/597c0afad70f17b1f3788787dfd0974a.png)
8) Calcula:
- a)
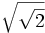 ; b)
; b) 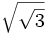 ; c)
; c) 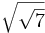 ; d)
; d) ![\sqrt[3]{\sqrt{2}}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/5/7/5/5750c75c078868e9954cfd490001321d.png)
- e)
![\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[3]{25}}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/a/6/1/a61140b4f250a3cb23f5d4156fc505bd.png) ; f)
; f) ![\sqrt{\sqrt[3]{64}}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/2/3/e23312ed4b7fe23d8f48d5afad9e73be.png) ; g)
; g) ![\sqrt[4]{\sqrt[3]{2}}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/7/7/17747fd8e1ef3646625fd5f03e380c01.png) ; h)
; h) ![\sqrt[3]{\sqrt{128}}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/7/e/17e0360d6aab8d041cd7f8c090dbc6c1.png)
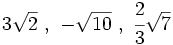
![3\sqrt[3]{2} \ , \ -\sqrt[3]{2} \ , \ \cfrac{2}{3}\sqrt[3]{2}](/wikipedia/images/math/1/1/c/11ca38664b260e771d7b6b60dd01d52b.png)

