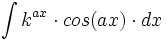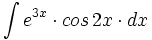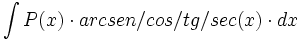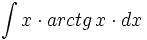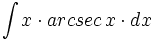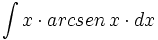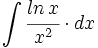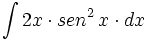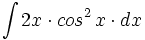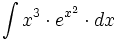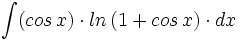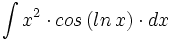Cálculo de primitivas por partes (2ºBach)
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 07:38 26 jun 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) |
||
| Línea 6: | Línea 6: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Cálculo de primitivas por partes|enunciado= | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1a | ||
| + | |duracion=8'36" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Fórmula de la integración por partes. Regla mnemotécnica. Ejemplo. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/o8tEQW9f250?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1b | ||
| + | |duracion=9'49" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Integración por partes. Regla mnemotécnica para la selección de las funciones. Ejemplo. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/r4QwORuC9jA?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Cálculo de primitivas por partes | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2 |
| |duracion=9'32" | |duracion=9'32" | ||
| |sinopsis=*Deducción de la fórmula de integración "por partes". | |sinopsis=*Deducción de la fórmula de integración "por partes". | ||
| *Casos típicos de aplicación. | *Casos típicos de aplicación. | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zh0bJoKucHQ&index=23&list=PLECA0C7A8B59E5534 | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zh0bJoKucHQ&index=23&list=PLECA0C7A8B59E5534 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejemplos 1 | ||
| + | |duracion=9'36" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot ln\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot e^{2x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/J9KNaPCWP6k?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejemplos 2 | ||
| + | |duracion=11'09" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | #<math>\int ln\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int arctg\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int arcsen\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/ndAhzOIFfKQ?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejemplos 3 | ||
| + | |duracion=9'22" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Integración por partes en varios pasos: | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot sen\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int e^x(x^2-3) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Ac3H12gln6c?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejemplos 4 | ||
| + | |duracion=10'21" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Integración por partes cíclica: | ||
| + | #<math>\int e^x \cdot sen\,x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int sen(ln\,x) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Q-Io234FjwM?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBA1KORgh0feSngW7ZUWF3b | ||
| + | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 24: | Línea 72: | ||
| #<math>\int x^2 \cdot e^x \cdot dx</math> | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot e^x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| #<math>\int x^3 \cdot e^x \cdot dx</math> | #<math>\int x^3 \cdot e^x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| - | #Determina las infinitas funciones cuya segunda derivada es <math>f''(x)=x \cdot e^x</math>, obteniendo la que pasa por el punto (0,2) y (2,0). | + | #Determina las infinitas funciones cuya segunda derivada es <math>f''(x)=x \cdot e^x</math>, obteniendo la que pasa por los puntos (0,2) y (2,0). |
| #<math>\int x^2 \cdot 3^x \cdot dx</math> | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot 3^x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| #<math>\int x^2 \cdot e^{3x} \cdot dx</math> | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot e^{3x} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| Línea 35: | Línea 83: | ||
| {{ejemplo2 | {{ejemplo2 | ||
| |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot sen(ax) \cdot dx</math>{{b4}}ó{{b4}}<math>\int (Polinomio) \cdot cos(ax) \cdot dx</math> donde <math>P(x)\;</math> es un polinomio. | + | |enunciado=Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot sen(ax) \cdot dx</math>{{b4}}ó{{b4}}<math>\int P(x) \cdot cos(ax) \cdot dx</math> donde <math>P(x)\;</math> es un polinomio. |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | |duracion=7'08" | + | |duracion=10'57" |
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cintegral/01/in01_06b_media/in01_06b.wmv | + | #<math>\int x \cdot sen \, x \cdot dx</math> |
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot cos \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot sen \, 4x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot cos \, 5x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot cos \, 3x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/introduccion-al-calculo-integral/01-calculo-de-primitivas-2/0602-cinco-ejercicios-del-caso-2 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 46: | Línea 99: | ||
| {{ejemplo2 | {{ejemplo2 | ||
| |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Primitivas del tipo <math>\int k^{ax} \cdot sen(ax) \cdot dx</math>{{b4}}ó{{b4}}<math>\int k^{ax} \cdot cos(ax) \cdot dx</math> | + | |enunciado=Primitivas del tipo <math>\int k^{ax} \cdot sen(ax) \cdot dx</math>{{b4}}ó{{b4}}<math>\int k^{ax} \cdot cos(ax) \cdot dx</math> |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | |duracion=8'59" | + | |duracion=10'26" |
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cintegral/01/in01_06c_media/in01_06c.wmv | + | #<math>\int e^x \cdot sen \, x \cdot dx</math> |
| + | #<math>\int e^{3x} \cdot cos \, 2x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/introduccion-al-calculo-integral/01-calculo-de-primitivas-2/0603-dos-ejercicios-del-caso-2 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 57: | Línea 112: | ||
| {{ejemplo2 | {{ejemplo2 | ||
| |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot ln \, P(x) \cdot dx</math> | + | |enunciado=Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot ln \, P(x) \cdot dx</math> |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | |duracion=6'31" | + | |duracion=13'21" |
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cintegral/01/in01_06d_media/in01_06d.wmv | + | #<math>\int x \cdot ln \, x \cdot dx</math> |
| + | #<math>\int ln \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot ln \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^n \cdot ln \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int ln \, (1+x^2) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot ln \, (1+x^2) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #Determina la primitiva de <math>f(x)= x \cdot (1-ln \, x)</math> que pasa por el punto (1,1). | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/introduccion-al-calculo-integral/01-calculo-de-primitivas-2/0604-siete-ejercicios-del-caso-2 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 68: | Línea 130: | ||
| {{ejemplo2 | {{ejemplo2 | ||
| |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot arc sen(x) \cdot dx</math>{{b4}}ó{{b4}}<math>\int P(x) \cdot arc cos(x) \cdot dx</math> | + | |enunciado=Primitivas del tipo <math>\int P(x) \cdot arc sen/cos/tg/sec (x) \cdot dx</math> |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | |duracion=5'00" | + | |duracion=8'42" |
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cintegral/01/in01_06e_media/in01_06e.wmv | + | #<math>\int x \cdot arctg \, x \cdot dx</math> |
| + | #<math>\int arctg \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int arcsen \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot arcsec \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x \cdot arcsen \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/introduccion-al-calculo-integral/01-calculo-de-primitivas-2/0605-cinco-ejercicios-del-caso-2 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 79: | Línea 147: | ||
| {{ejemplo2 | {{ejemplo2 | ||
| |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | |titulo=Ejemplos: ''Cálculo de primitivas por partes'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Otros casos de primitivas | + | |enunciado=Otros casos de primitivas |
| {{Video_enlace2 | {{Video_enlace2 | ||
| - | |titulo1=1. Ejemplos | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 |
| - | |duracion=12'53" | + | |duracion=32'29" |
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | |url1=http://www.matematicasbachiller.com/videos/cintegral/01/in01_06f_media/in01_06f.wmv | + | #<math>\int \cfrac{ln \, x}{x^2} \cdot dx</math> |
| + | #<math>\int 2x \cdot sen^2 \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int 2x \cdot cos^2 \, x \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^3 \cdot e^{x^2} \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int (cos \, x) \cdot ln \, (1+ cos \, x) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\int x^2 \cdot cos \, (ln \, x) \cdot dx</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/2-bachillerato/introduccion-al-calculo-integral/01-calculo-de-primitivas-2/0606-ejemplos-de-otros-casos-2 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| [[Categoría: Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Funciones]] | [[Categoría: Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Funciones]] | ||
Revisión actual
Menú:
| Enlaces internos | Para repasar o ampliar | Enlaces externos |
| Indice Descartes Manual Casio | WIRIS Calculadora |
Fórmula de la integración por partes. Regla mnemotécnica. Ejemplo.
Integración por partes. Regla mnemotécnica para la selección de las funciones. Ejemplo.
- Deducción de la fórmula de integración "por partes".
- Casos típicos de aplicación.
Integración por partes en varios pasos:
Integración por partes cíclica:
Ejercicios resueltos: Cálculo de primitivas por partes
Primitivas del tipo 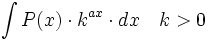 donde
donde 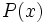 es un polinomio.
es un polinomio.
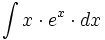
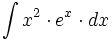
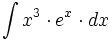
- Determina las infinitas funciones cuya segunda derivada es
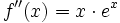 , obteniendo la que pasa por los puntos (0,2) y (2,0).
, obteniendo la que pasa por los puntos (0,2) y (2,0).
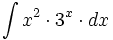
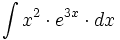
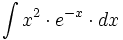
Ejemplos: Cálculo de primitivas por partes
Ejemplos: Cálculo de primitivas por partes
Primitivas del tipo 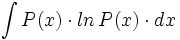
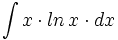
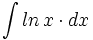
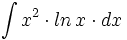
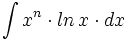
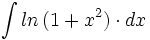
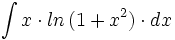
- Determina la primitiva de
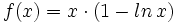 que pasa por el punto (1,1).
que pasa por el punto (1,1).
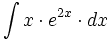
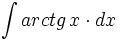
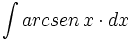
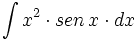
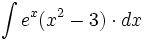
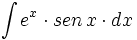
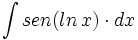
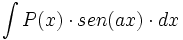 ó
ó 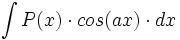 donde
donde 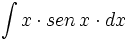
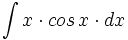
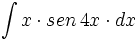
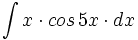
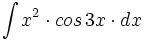
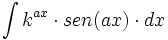 ó
ó