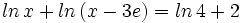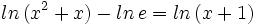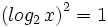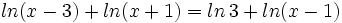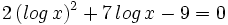Plantilla:Ecuaciones logaritmicas
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 09:31 30 ago 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) |
||
| Línea 8: | Línea 8: | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| {{Ejemplo|titulo=Ejemplos: ''Ecuaciones logarítmicas'' | {{Ejemplo|titulo=Ejemplos: ''Ecuaciones logarítmicas'' | ||
| - | |enunciado=:Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciónes: | + | |enunciado=Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciónes: |
| - | ::a) <math>log \ x + log \ 50 = 3</math> | + | :a) <math>log \ x + log \ 50 = 3</math> |
| - | ::b) <math>5\, log_2 \ (x+3)= log_2 \ 32</math> | + | :b) <math>5\, log_2 \ (x+3)= log_2 \ 32</math> |
| - | ::c) <math>2\, log \ x= log \ (10-3x)</math> | + | :c) <math>2\, log \ x= log \ (10-3x)</math> |
| |sol= | |sol= | ||
| '''a)''' | '''a)''' | ||
| <center><math>log \ x + log \ 50 = 3</math></center> | <center><math>log \ x + log \ 50 = 3</math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log \ A + log \ B = log \ (A \cdot B)</math> y que <math>3 = log \ 1000</math>, tenemos: | + | Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log \ A + log \ B = log \ (A \cdot B)</math> y que <math>3 = log \ 1000</math>, tenemos: |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| <center><math>log \ (50x) = log \ 1000</math></center> | <center><math>log \ (50x) = log \ 1000</math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Y teniendo en cuenta que <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: | + | Y teniendo en cuenta que <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: |
| <center><math>50x=1000 \ \rightarrow \ x=20</math></center> | <center><math>50x=1000 \ \rightarrow \ x=20</math></center> | ||
| - | :La solución se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida. | + | La solución se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida. |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :'''''Solución:''''' <math>x=20\;</math> | + | |
| + | '''''Solución:''''' <math>x=20\;</math> | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| '''b)''' | '''b)''' | ||
| <center><math>5\, log_2 \ (x+3)= log_2 \ 32</math></center> | <center><math>5\, log_2 \ (x+3)= log_2 \ 32</math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log_a \ B^n = n \ log_a \ B</math> y que <math>32=2^5\;</math>: | + | Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log_a \ B^n = n \ log_a \ B</math> y que <math>32=2^5\;</math>: |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| <center><math>log_2 \ (x+3)^5= log_2 \ 2^5</math></center> | <center><math>log_2 \ (x+3)^5= log_2 \ 2^5</math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Como <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: | + | Como <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: |
| <center><math>(x+3)^5= 2^5\;</math></center> | <center><math>(x+3)^5= 2^5\;</math></center> | ||
| - | :Y, como <math>a^x = b^x \iff a=b</math> | + | Y, como <math>a^x = b^x \iff a=b</math> |
| <center><math>x+3= 2 \ \rightarrow \ x=-1</math></center> | <center><math>x+3= 2 \ \rightarrow \ x=-1</math></center> | ||
| - | :Se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida. | + | Se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida. |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :'''''Solución:''''' <math>x=-1\;</math> | + | |
| + | '''''Solución:''''' <math>x=-1\;</math> | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| '''c)''' | '''c)''' | ||
| <center><math>2\, log \ x= log \ (10-3x)</math></center> | <center><math>2\, log \ x= log \ (10-3x)</math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log_a \ B^n = n \ log_a \ B</math>, tenemos: | + | Teniendo en cuenta que <math>log_a \ B^n = n \ log_a \ B</math>, tenemos: |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| <center><math>log \ x^2= log \ (10-3x) </math></center> | <center><math>log \ x^2= log \ (10-3x) </math></center> | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :Como <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: | + | Como <math>log \ A = log \ B \iff A=B</math>, se tiene: |
| <center><math>x^2= 10-3x \ \rightarrow \ x^2+3x-10=0 \ \rightarrow \ \begin{cases} x_1=2 \\ x_2=-5 \end{cases}</math></center> | <center><math>x^2= 10-3x \ \rightarrow \ x^2+3x-10=0 \ \rightarrow \ \begin{cases} x_1=2 \\ x_2=-5 \end{cases}</math></center> | ||
| - | :De las dos soluciones, <math>x_2=-5\;</math> no es válida, porque al comprobarla en la ecuación de partida, <math>log \ x\;</math> no se puede calcular para <math>x=-5\;</math> (El logaritmo de un número negativo no existe). | + | De las dos soluciones, <math>x_2=-5\;</math> no es válida, porque al comprobarla en la ecuación de partida, <math>log \ x\;</math> no se puede calcular para <math>x=-5\;</math> (El logaritmo de un número negativo no existe). |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | :'''''Solución:''''' <math>x=2\;</math> | + | |
| + | '''''Solución:''''' <math>x=2\;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | ===Videotutoriales sobre ecuaciones logarítmicas=== | + | {{p}} |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Ecuaciones logarítmicas |
| - | |titulo1=2 ejercicios | + | |enunciado= |
| + | {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1 | ||
| + | |duracion=21'07" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Tutorial que trabaja las ecuaciones logarítmicas, desde muy sencillas que se resuelven utilizando únicamente la definición, hasta otras más completas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *00:00 a 02:36: Repaso de las propiedades de los logaritmos. | ||
| + | *02:36 a 08:20: Ejercicios "base" para resolver ecuaciones. | ||
| + | *08:20 a 11:55: Ejercicios básicos de ecuaciones logarítmicas, usando la definición de logaritmo. | ||
| + | *11:55 a 21:07: Ejercicios de ecuaciones logarítmicas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ybzYfvojnNE&index=10&list=PLZNmE9BEzVInJZxxpaxecd3SH4TK5eggR | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2 | ||
| + | |duracion=10'35" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Ecuaciones logarítmicas. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/n6Ua7uNDLw4?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBS-xkrGZm69M_Jc4bqmBKl | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{Tabla50|celda1= | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| + | |duracion=4'09" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_4 \, (x-3) = 1 - log_4 \, x\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=riqZcExsvcE | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'55" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_x \, (6-x) = 2 \, x\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1qVTH0Dr4C0 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 | ||
| + | |duracion=3'22" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_2 \, 3 + log_2 \, x = log_2 \, 5 + log_2 \, (x-2)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UcgsO70f5sU | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | ||
| + | |duracion=9'44" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log \, (4x+5) + log \, (x-1) = 2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LW_sP5jDBQA | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| + | |duracion=5'26" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_{x+2} \, 3\, + 4 = 6\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g3KhxSJVcSg | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | ||
| + | |duracion=7'05" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_3 \, x + log_9 \, x +log_27 \, x = \cfrac{55}{6}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EaxI046b7t8 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | ||
| + | |duracion=11'30" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>25^{log_5 \, (x-3)} - 3^{log_3 \, (5x)} + 10^{log \, 6} = 0\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZF47GJUB6iU | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8 | ||
| + | |duracion=10'41" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log \, (7x+1) = 2^log \, (x+3) -log \, 2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5KWcFn1jWDs | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| + | |duracion=15'53" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_3 \, (2x-1) - log_3 \, (5x+2) = log_3 \, (x-2)\, - 2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_dDp9BoFODI | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| + | |duracion=10'53" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_3 \, (x+1) - log_3 \, x = log_3 \, (x+9)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yLoA7aEGJz0 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 11 | ||
| + | |duracion=11'44" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_4 \, x + log_8 \, x = 1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dm8d4yUTqJ0 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 12 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'49" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>2ln \, x = ln \, (4x+6)- ln \, 2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZuYTDvLW4hw | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 13 | ||
| + | |duracion=14'17" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log_4 \, (2^x+48) = x-1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f1_ACPdtA-Q | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 14 | ||
| + | |duracion=7'51" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>(log_2)^2 \, x = log_2 \, x^2 \,+ 3\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dApslxUJMhU | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 | ||
| + | |duracion=8'44" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>log \, \sqrt[3]{x} = \sqrt{log \, x}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T1it4Pc0jlo | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_unicoos | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 16 | ||
| + | |duracion=10'26" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| + | :a) <math>log \, (22-x) = -1 + log \, x\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>3log \, x = 2log \, x + log \, 3 \;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=http://www.unicoos.com/video/matematicas/4-eso/ecuaciones-y-sistemas/ecuaciones-exponenciales-y-logaritmicas/ecuacion-logaritmica-01 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 17 | ||
| |duracion=6´39" | |duracion=6´39" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/14-logaritmos/0205-dos-ejercicios-ecuaciones-logaritmicas#.VCctKvl_u2E | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2xWsWOtUOjc&index=9&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial | + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: |
| + | #<math>log \, (x+1) - log \, x = 1 \;</math> | ||
| + | #<math>log \, (x-1) - log \, (x-9) = 3 \;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | + | |celda2= |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | |titulo1=2 ejercicios | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 18 |
| |duracion=8´55" | |duracion=8´55" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/14-logaritmos/0206-dos-ejercicios-ecuaciones-logaritmicas#.VCctnvl_u2E | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GbTtihJTxnA&index=10&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial | + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: |
| + | #<math>log \, (x-16) + log \, (x+5) = 2 \;</math> | ||
| + | #<math>2 \, log \, x = 1 + log \, (x-0.9) \;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 19 |
| - | |titulo1=2 ejercicios | + | |duracion=5´06" |
| - | |duracion=5´56" | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JYfNHvgavPA&index=11&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 |
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/14-logaritmos/0207-dos-ejercicios-ecuaciones-logaritmicas#.VCctyfl_u2E | + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial | + | #<math>3 \, log \, x - log \, (2x^2+x-2) = 0 \;</math> |
| + | #<math>log \, 2 + log \, (x-3) = log \, \sqrt{2x} \;</math> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | + | {{Video_enlace_fonemato |
| - | {{Video_enlace2 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 20 |
| - | |titulo1=3 ejercicios | + | |
| |duracion=7´29" | |duracion=7´29" | ||
| - | |url1=http://matematicasbachiller.com/videos/1-bachillerato/matematicas-de-primero-de-bachillerato/14-logaritmos/0208-tres-ejercicios-ecuaciones-logaritmicas#.VCct4fl_u2E | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oEdy4c0SUR8&index=12&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 |
| - | |sinopsis=Videotutorial | + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: |
| + | #<math>log \, (x-1) - log \, \sqrt{5+x} =log \, \sqrt{5-x} \;</math> | ||
| + | #<math>2 \, \left( log \, x \right)^2 - 3 \, log \, x \ + 1 = 0 \;</math> | ||
| + | #<math>\left( ln \, x \right)^3 - ln \, x = 0 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 21 | ||
| + | |duracion=5´06" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XXmXZK8fhGs&index=1&list=PLo7_lpX1yruM2gkXcbGVpW-Cqtp2oPZs7 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_5 \, x - log_25 \, x =1 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 22 | ||
| + | |duracion=9´33" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VC7LQz-0Ylc&list=PLo7_lpX1yruM2gkXcbGVpW-Cqtp2oPZs7&index=2 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_2 \, x + log_8 \, x - log_{32} \, x=\cfrac{34}{15} \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 23 | ||
| + | |duracion=9´09" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=19OiKjEdZ5Q&list=PLo7_lpX1yruM2gkXcbGVpW-Cqtp2oPZs7&index=3 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_3 \, 9x + log_{27} \, x=6 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 24 | ||
| + | |duracion=3´04" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL8UA2yNq78&index=1&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_3 \, (x+3)=2 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 25 | ||
| + | |duracion=5´17" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pPBJuT75Gk0&index=2&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_3 \, 36-log_3 \, (x-7)=2 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 26 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´53" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1s4epFHRZeI&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu&index=3 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_7 \, (x+9)+log_7 \, 49=3 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 27 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´02" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a8v_rI9IAXU&index=4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_2 \, \sqrt{3x+1}=2 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 28 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´08" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoQMGS_sXNo&index=5&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_6 \, (5x-9)^2=4 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 29 | ||
| + | |duracion=3´41" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kj0X2MI5314&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu&index=6 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve <math>log \, \sqrt{x^2+75}=1 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 30 | ||
| + | |duracion=5´56" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQk7xwqj-i0&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu&index=7 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log \, (x+3)^2=1+log \, (3x-11) \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 31 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´11" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YD_0_FUngEc&index=8&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{4x-1}=log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{9}+log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{x-4} \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 32 | ||
| + | |duracion=7´08" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MihEXM-QrIM&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu&index=9 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>ln \, x + ln \, (x-3e) = ln \, 4 + 2 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 33 | ||
| + | |duracion=4´46" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aCimqY1_SQE&index=10&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>ln \, (x^2+x) - ln \, e = ln \, (x+1) \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 34 | ||
| + | |duracion=5´07" | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7BgMPYqIVDw&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOdeP3Xnz5xYEjgB_u8fGgu&index=11 | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\left( log_2 \, x \right)^2 = 1 \;</math> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Ejercicios_vitutor | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicios: ''Ecuaciones logarítmicas'' | ||
| + | |descripcion=Ejercicios resueltos sobre ecuaciones logarítmicas''. | ||
| + | |url1=http://www.vitutor.com/al/log/l_e.html | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| + | {{wolfram desplegable|titulo=Ecuaciones logarítmicas|contenido= | ||
| {{wolfram | {{wolfram | ||
| |titulo=Actividad: ''Ecuaciones logarítmicas'' | |titulo=Actividad: ''Ecuaciones logarítmicas'' | ||
| Línea 104: | Línea 371: | ||
| :a) <math>ln(x-3)+ln(x+1)=ln\,3+ln(x-1) \;</math> | :a) <math>ln(x-3)+ln(x+1)=ln\,3+ln(x-1) \;</math> | ||
| - | :b) <math>2(log\,x)^2+7log\,x-9=0 \;</math> | + | :b) <math>2\,(log\,x)^2+7\,log\,x-9=0 \;</math> |
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| |sol= | |sol= | ||
| Línea 116: | Línea 383: | ||
| {{widget generico}} | {{widget generico}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | + | }} |
Revisión actual
Las ecuaciones logarítmicas son aquellas en las que la incógnita aparece como parte de un logaritmo.
Para su resolución hay que tener en cuenta las propiedades de los logaritmos.
Se deben comprobar siempre las soluciones en la ecuación de partida pues pueden obtenerse soluciones que no sean válidas, como puede verse en el ejemplo c) siguiente.
Ejemplos: Ecuaciones logarítmicas
Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciónes:
- a)
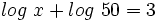
- b)
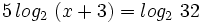
- c)
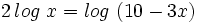
a)
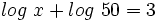
Teniendo en cuenta que 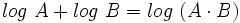 y que
y que 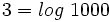 , tenemos:
, tenemos:
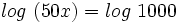
Y teniendo en cuenta que 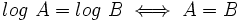 , se tiene:
, se tiene:
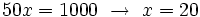
La solución se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida.
Solución: 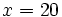
b)
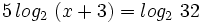
Teniendo en cuenta que 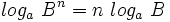 y que
y que 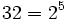 :
:
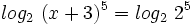
Como 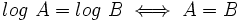 , se tiene:
, se tiene:
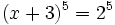
Y, como 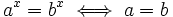
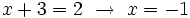
Se comprueba en la ecuación de partida y resulta ser válida.
Solución: 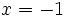
c)
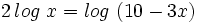
Teniendo en cuenta que 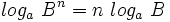 , tenemos:
, tenemos:
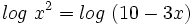
Como 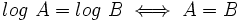 , se tiene:
, se tiene:
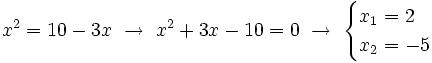
De las dos soluciones, 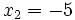 no es válida, porque al comprobarla en la ecuación de partida,
no es válida, porque al comprobarla en la ecuación de partida, 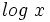 no se puede calcular para
no se puede calcular para 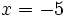 (El logaritmo de un número negativo no existe).
(El logaritmo de un número negativo no existe).
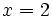
Tutorial que trabaja las ecuaciones logarítmicas, desde muy sencillas que se resuelven utilizando únicamente la definición, hasta otras más completas.
- 00:00 a 02:36: Repaso de las propiedades de los logaritmos.
- 02:36 a 08:20: Ejercicios "base" para resolver ecuaciones.
- 08:20 a 11:55: Ejercicios básicos de ecuaciones logarítmicas, usando la definición de logaritmo.
- 11:55 a 21:07: Ejercicios de ecuaciones logarítmicas.
Ecuaciones logarítmicas.
Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve:
Resuelve: | Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: |
Ejercicios resueltos sobre ecuaciones logarítmicas.
|
Actividad: Ecuaciones logarítmicas Resuelve las siguientes ecuaciones:
Solución: Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones:
Nota: En WolframAlpha log y loge simbolizan el logaritmo neperiano mientras que el logaritmo decimal es log10. |
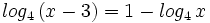
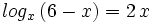
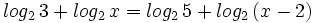
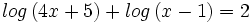
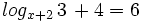
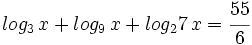
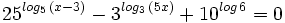
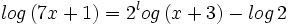
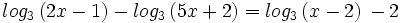
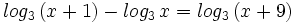
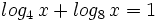
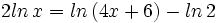
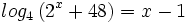
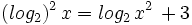
![log \, \sqrt[3]{x} = \sqrt{log \, x}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/6/c/c/6cc126bf04f02f1123358336f576a013.png)
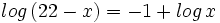
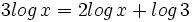
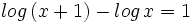
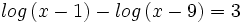
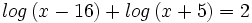
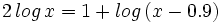
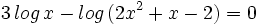
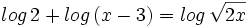
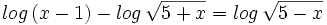
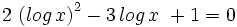
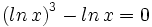
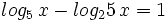
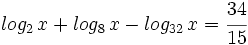
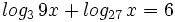
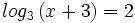
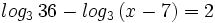
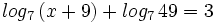
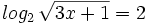
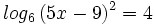
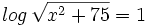
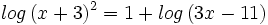
![log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{4x-1}=log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{9}+log_6 \, \sqrt[3]{x-4} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/6/9/3/693f53a3f8089ea15b162093daf2ef62.png)