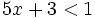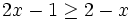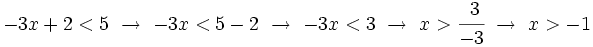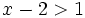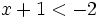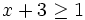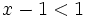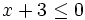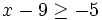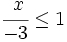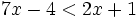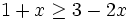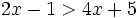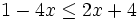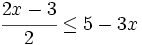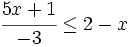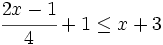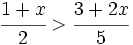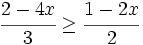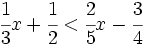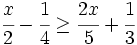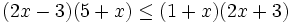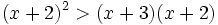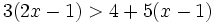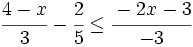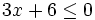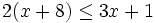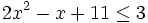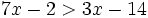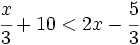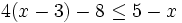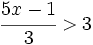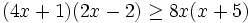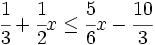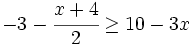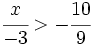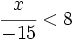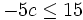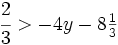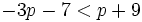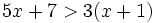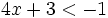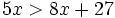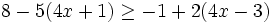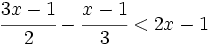Plantilla:Inecuaciones lineales con una incógnita
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 19:47 15 dic 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Método algebraico de resolución) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Método algebraico de resolución) |
||
| Línea 49: | Línea 49: | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o6cD4QCHVD0&list=PLZNmE9BEzVImx1PyuWcTPuA6KB6xxyLof&index=1 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o6cD4QCHVD0&list=PLZNmE9BEzVImx1PyuWcTPuA6KB6xxyLof&index=1 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matemovil | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| Línea 56: | Línea 56: | ||
| |sinopsis=Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aAsD-aPY-YM&index=79&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aAsD-aPY-YM&index=79&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 4a | ||
| + | |duracion=8'26" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/xHpZ-RHNboY?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBUhnGLJFSf8RU8VKAxVe_R | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 4b | ||
| + | |duracion=6'25" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Y4D1hs1o7Qw?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBUhnGLJFSf8RU8VKAxVe_R | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 4c | ||
| + | |duracion=8'38" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/izw5LDyCGow?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSBUhnGLJFSf8RU8VKAxVe_R | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| Línea 69: | Línea 90: | ||
| :c) <math>x+3 \ge 1\;</math> | :c) <math>x+3 \ge 1\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qBDCNL1opQ8&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=2 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qBDCNL1opQ8&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=2 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 80: | Línea 101: | ||
| :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=amQOmwK6kk4&index=3&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=amQOmwK6kk4&index=3&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 91: | Línea 112: | ||
| :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoRo2p-g6nA&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=5 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoRo2p-g6nA&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=5 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 102: | Línea 123: | ||
| :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | :c) <math>x-9 \ge -5\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OE8DqquznmE&index=6&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OE8DqquznmE&index=6&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 109: | Línea 130: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>7x-4<2x+1\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>7x-4<2x+1\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BCpUh1sSU2g&index=7&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BCpUh1sSU2g&index=7&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 116: | Línea 137: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>1+x \ge 3-2x\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>1+x \ge 3-2x\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cV5CW8jaIiI&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=8 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cV5CW8jaIiI&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=8 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 123: | Línea 144: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>2x-1 > 4x+5\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>2x-1 > 4x+5\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ibT1KyMXS38&index=9&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ibT1KyMXS38&index=9&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 130: | Línea 151: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>1-4x \le 2x+4\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>1-4x \le 2x+4\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UyL9yifNg_I&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=10 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UyL9yifNg_I&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=10 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 137: | Línea 158: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2x-3}{2} \le 5-3x\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2x-3}{2} \le 5-3x\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CmbNydtZ0J4&index=11&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CmbNydtZ0J4&index=11&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 144: | Línea 165: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{5x+1}{-3} \le 2-x\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{5x+1}{-3} \le 2-x\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oT1cJ63-Uj8&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=12 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oT1cJ63-Uj8&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=12 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 151: | Línea 172: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2x-1}{4} +1 \le x+3\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2x-1}{4} +1 \le x+3\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2xQXrtYfaE&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=13 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2xQXrtYfaE&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=13 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 158: | Línea 179: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1+x}{2} > \cfrac{3+2x}{5}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1+x}{2} > \cfrac{3+2x}{5}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0e53WrWm-R4&index=14&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0e53WrWm-R4&index=14&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 165: | Línea 186: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2-4x}{3} \ge \cfrac{1-2x}{2}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{2-4x}{3} \ge \cfrac{1-2x}{2}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m7QfWpjB5tw&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=15 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m7QfWpjB5tw&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=15 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 172: | Línea 193: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1}{3}x+\cfrac{1}{2} < \cfrac{2}{5}x - \cfrac{3}{4}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1}{3}x+\cfrac{1}{2} < \cfrac{2}{5}x - \cfrac{3}{4}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DSBtRjjN2pM&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=16 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DSBtRjjN2pM&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=16 |
| }} | }} | ||
| - | |celda2= | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 | |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 | ||
| Línea 180: | Línea 200: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{x}{2}-\cfrac{1}{4} \ge \cfrac{2x}{5} + \cfrac{1}{3}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{x}{2}-\cfrac{1}{4} \ge \cfrac{2x}{5} + \cfrac{1}{3}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KdasymEoL6A&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=17 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KdasymEoL6A&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo&index=17 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| Línea 187: | Línea 207: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(2x-3)(5+x) \le (1+x)(2x+3)\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(2x-3)(5+x) \le (1+x)(2x+3)\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rZOjDFdrKgM&index=28&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rZOjDFdrKgM&index=28&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| {{Video_enlace_matefacil | {{Video_enlace_matefacil | ||
| |titulo1=Ejercicio 17 | |titulo1=Ejercicio 17 | ||
| Línea 194: | Línea 215: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(x+2)^2 > (x+3)(x+2)\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(x+2)^2 > (x+3)(x+2)\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qF267wzM97E&index=29&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qF267wzM97E&index=29&list=PL9SnRnlzoyX3WSvCry-ctW4l_yMH1Z9Xo |
| }} | }} | ||
| + | |celda2= | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| |titulo1=Ejercicio 18 | |titulo1=Ejercicio 18 | ||
| Línea 201: | Línea 223: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>3(2x-1) > 4+5(x-1)\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>3(2x-1) > 4+5(x-1)\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jSZWvCh2PqI | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jSZWvCh2PqI |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| Línea 208: | Línea 230: | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{4-x}{3}-\cfrac{2}{5} \le \cfrac{-2x-3}{-3}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{4-x}{3}-\cfrac{2}{5} \le \cfrac{-2x-3}{-3}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jSZWvCh2PqI | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jSZWvCh2PqI |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_unicoos | {{Video_enlace_unicoos | ||
| Línea 227: | Línea 249: | ||
| |duracion=3'57" | |duracion=3'57" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>7x-2 > 3x-14\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>7x-2 > 3x-14\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RqbH-Bwe_NY&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=1 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RqbH-Bwe_NY&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=1 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 233: | Línea 255: | ||
| |duracion=4'33" | |duracion=4'33" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{x}{3}+10 < 2x-\cfrac{5}{3}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{x}{3}+10 < 2x-\cfrac{5}{3}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ow8O24JNmrA&index=2&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ow8O24JNmrA&index=2&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 239: | Línea 261: | ||
| |duracion=3'54" | |duracion=3'54" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>4(x-3)-8 \le 5-x\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>4(x-3)-8 \le 5-x\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=etQLL6DKn5Y&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=3 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=etQLL6DKn5Y&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=3 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 245: | Línea 267: | ||
| |duracion=3'22" | |duracion=3'22" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{5x-1}{3} > 3\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{5x-1}{3} > 3\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YIKpW6v8lyM&index=4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YIKpW6v8lyM&index=4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 251: | Línea 273: | ||
| |duracion=5'51" | |duracion=5'51" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(4x+1)(2x-2) \ge 8x(x+5)\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>(4x+1)(2x-2) \ge 8x(x+5)\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RZ-1iShWhmg&index=5&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RZ-1iShWhmg&index=5&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 257: | Línea 279: | ||
| |duracion=6'39" | |duracion=6'39" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1}{3}+\cfrac{1}{2}x \le \cfrac{5}{6}x-\cfrac{10}{3}\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>\cfrac{1}{3}+\cfrac{1}{2}x \le \cfrac{5}{6}x-\cfrac{10}{3}\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sz1nI6X2mKA&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=6 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sz1nI6X2mKA&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=6 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_virtual | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| Línea 263: | Línea 285: | ||
| |duracion=5'37" | |duracion=5'37" | ||
| |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>-3-\cfrac{x+4}{2} \ge 10-3x\;</math> | |sinopsis=Resuelve: <math>-3-\cfrac{x+4}{2} \ge 10-3x\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f20Xl-zziU4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=7 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f20Xl-zziU4&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPw5I01U5DnBAn-vOkmBGvd&index=7 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_khan | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| Línea 274: | Línea 296: | ||
| :c) <math>\cfrac{x}{-3} > -\cfrac{10}{9}\;</math> | :c) <math>\cfrac{x}{-3} > -\cfrac{10}{9}\;</math> | ||
| :d) <math>\cfrac{x}{-15} < 8\;</math> | :d) <math>\cfrac{x}{-15} < 8\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D8dD9hI8yb4 | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D8dD9hI8yb4 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_khan | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| Línea 282: | Línea 304: | ||
| :<math>-5c \le 15\;</math> | :<math>-5c \le 15\;</math> | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?&v=DUETugOXhhw | + | |
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?&v=DUETugOXhhw | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 30 | ||
| + | |duracion=4'39" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\cfrac{2}{3}>-4y -8 \begin{matrix} \frac{1}{3} \end{matrix}\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?&v=DUETugOXhhw | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 31 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'28" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>-3p-7<p+9\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wq4YpVcb37s | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 32 | ||
| + | |duracion=4'25" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>5x+7>3(x+1)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NwAVsFtDO04 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 33 | ||
| + | |duracion=9'48" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>4x+3<-1\;</math> | ||
| + | :b) <math>5x>8x+27\;</math> | ||
| + | :c) <math>8-5(4x+1) \ge -1+2(4x-3)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ICS0W6ft7Mo | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_miguematicas | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 34 | ||
| + | |duracion=4'02" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: | ||
| + | |||
| + | : <math>\cfrac{3x-1}{2}-\cfrac{x-1}{3}<2x-1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/6V_42zOaOmI?list=PLLfTN7MHLxConbepI-_1OEy-pjAxI8IvH | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| {{Video_enlace_khan | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| - | |titulo1=Problema | + | |titulo1=Problema 1 |
| |duracion=2'11" | |duracion=2'11" | ||
| |sinopsis=Un contratista está comprando baldosas de piedra para un patio. Cada baldosa cuesta $3, y quiere gastar menos de $1000. El tamaño de cada baldosa es de 1 pie cuadrado. Escribe una desigualdad que represente el número de baldosas que puede comprar y averigua cómo de grande puede ser el patio. | |sinopsis=Un contratista está comprando baldosas de piedra para un patio. Cada baldosa cuesta $3, y quiere gastar menos de $1000. El tamaño de cada baldosa es de 1 pie cuadrado. Escribe una desigualdad que represente el número de baldosas que puede comprar y averigua cómo de grande puede ser el patio. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NyruwGxOqkE | + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NyruwGxOqkE |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Problema 2 | ||
| + | |duracion=2'42" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Una popular banda de blues regresó recientemente de una exitosa gira por tres ciudades donde tocaron para al menos 120 000 personas. Si tenían una audiencia de 45 000 en Ciudad de México y otras 33 000 en Guadalajara, ¿Qué puedes decir de las personas que asistieron en Acapulco? | ||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6gO27uNb5SI | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Problema 3 | ||
| + | |duracion=6'41" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=En los últimos años, Granja Arce ha cosechado alrededor de 1000 manzanas más que su principal rival de la región, Huerto Rio Grande. Debido al clima frio de este año, la cosecha bajó en un tercio. Sin embargo, ambas granjas compensaron parte de ese déficit mediante la compra de cantidades iguales de manzanas de las granjas de estados vecinos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) ¿Qué se puede decir del número de manzanas en cada granja? | ||
| + | :b) ¿Tiene una granja mayor cantidad de manzanas que la otra o tienen la misma cantidad? ¿Cómo lo sabes? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VOGpVI6S4_Y | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Actividades|titulo=Inecuaciones lineales|enunciado= | {{Actividades|titulo=Inecuaciones lineales|enunciado= | ||
| {{AI_Khan | {{AI_Khan | ||
| - | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1 | + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1a |
| - | |descripcion=Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales sencillas. | + | |descripcion=Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales de un paso. |
| - | |url1=https://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/one-variable-linear-inequalities/alg1-one-step-inequalities/e/one_step_inequalities | + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/one-variable-linear-inequalities/alg1-one-step-inequalities/e/one_step_inequalities |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1b | ||
| + | |descripcion=Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales de dos pasos. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/one-variable-linear-inequalities/alg1-two-step-inequalities/e/solving-2-step-inequalities | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1c | ||
| + | |descripcion=Autoevaluación sobre problemas de inecuaciones lineales de varios pasos. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/one-variable-linear-inequalities/multi-step-inequalities/e/linear_inequalities}} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1d | ||
| + | |descripcion=Autoevaluación sobre problemas de inecuaciones lineales. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/one-variable-linear-inequalities/alg1-two-step-inequalities/e/interpretting-solving-linear-inequalities | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Geogebra_enlace | {{Geogebra_enlace | ||
Revisión actual
Una inecuación lineal con una incógnita es una inecuación, en la que las expresiones matemáticas que intervienen en la desigualdad, son polinomios de primer grado en una sola variable. En consecuencia, puede ponerse, mediante transformaciones, de alguna de estas formas:
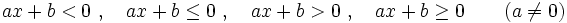
donde 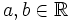 son los coeficientes y
son los coeficientes y 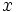 es la variable.
es la variable.
Resolución de una inecuación lineal con una incógnita
Método algebraico de resolución
El método algebraico aplica las anteriores transformaciones para conseguir dejar despejada la incógnita.
Ejemplo: Inecuaciones lineales con una incógnita (método algebraico)
Resuelve la siguiente inecuación:
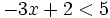
- Solución:
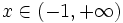
Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos.
Todo lo que necesitas saber para resolver inecuaciones de primer grado. Tutorial que explica de forma completa la resolución de inecuaciones de primer grado, empezando con algunos conceptos teóricos y resolviendo muchos ejericios desde muy sencillos, para entender mejor las propiedades de la regla de la suma y del producto.
- 00:00 a 09:00: Conceptos básicos. Definiciones. Desigualdades.
- 9:00 a 15:43: Reglas de la Suma y del Producto.
- 15:43 a 20:45: Ejemplos donde se aplica la regla del producto.
- 20:45 a 22:50: Algoritmo de resolución de inecuaciones de 1er grado.
- 22:50 a 32:41: Aplicación del algoritmo. Ejemplos resueltos.
Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos.
Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos.
Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos.
Inecuaciones de primer grado con una incógnita. Ejemplos.
Resuelve:
Resuelve:
Resuelve:
Resuelve:
Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: | Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: a) b) c) Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve: Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones:
Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones:
Resuelve y representa gráficamente las soluciones: |
Un contratista está comprando baldosas de piedra para un patio. Cada baldosa cuesta $3, y quiere gastar menos de $1000. El tamaño de cada baldosa es de 1 pie cuadrado. Escribe una desigualdad que represente el número de baldosas que puede comprar y averigua cómo de grande puede ser el patio.
Una popular banda de blues regresó recientemente de una exitosa gira por tres ciudades donde tocaron para al menos 120 000 personas. Si tenían una audiencia de 45 000 en Ciudad de México y otras 33 000 en Guadalajara, ¿Qué puedes decir de las personas que asistieron en Acapulco?
En los últimos años, Granja Arce ha cosechado alrededor de 1000 manzanas más que su principal rival de la región, Huerto Rio Grande. Debido al clima frio de este año, la cosecha bajó en un tercio. Sin embargo, ambas granjas compensaron parte de ese déficit mediante la compra de cantidades iguales de manzanas de las granjas de estados vecinos.
- a) ¿Qué se puede decir del número de manzanas en cada granja?
- b) ¿Tiene una granja mayor cantidad de manzanas que la otra o tienen la misma cantidad? ¿Cómo lo sabes?
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales de un paso.
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales de dos pasos.
Autoevaluación sobre problemas de inecuaciones lineales de varios pasos.
Autoevaluación sobre problemas de inecuaciones lineales.
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales.
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales.
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales sencillas.
Autoevaluación sobre inecuaciones lineales más complejas.
Método gráfico de resolución
Inecuaciones lineales con una incógnita (método gráfico)
Las soluciones de una inecuación lineal con una incógnita son los puntos de la semirrecta que se encuentra a uno de los dos lados del punto de corte de la recta 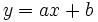 con el eje de abscisas, es decir del punto
con el eje de abscisas, es decir del punto 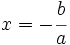 .
.
En una de las semirrectas con origen ese punto se cumple la condición 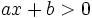 y en la otra, la condición
y en la otra, la condición 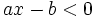 .
.
Así, para determinar la semirrecta solución, basta con fijarse en los valores de la variable x para los que la recta 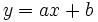 está por encima o por debajo del eje de abscisas.
está por encima o por debajo del eje de abscisas.
Si la inecuación no es estricta, el punto del extremo de la semirrecta, 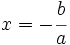 , es también solución, ya que para él se verifica la igualdad.
, es también solución, ya que para él se verifica la igualdad.
En la escena resolveremos la siguiente inecuación por el método gráfico:
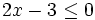
Para ello representamos la recta 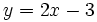 y nos fijamos para que valores de x, la gráfica está por debajo del eje X (es negativa) o vale cero.
y nos fijamos para que valores de x, la gráfica está por debajo del eje X (es negativa) o vale cero.