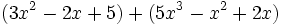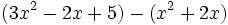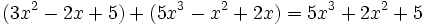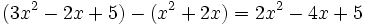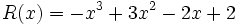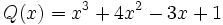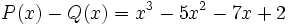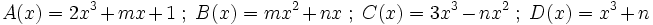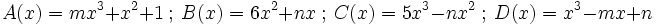Plantilla:Suma y resta de polinomios
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 11:18 28 jun 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) |
||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| - | Para sumar o restar polinomios, sumaremos o restaremos los monomios semejantes de ambos. | + | {{Teorema_sin_demo|titulo=Procedimiento|enunciado=Para sumar o restar polinomios, sumaremos o restaremos los monomios semejantes de ambos.}} |
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| {{Ejemplo | {{Ejemplo | ||
| Línea 16: | Línea 16: | ||
| {{Video_enlace_tutomate | {{Video_enlace_tutomate | ||
| |titulo1=Tutorial 1 | |titulo1=Tutorial 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=4'09" | + | |duracion=7'35" |
| |sinopsis=Aprende a sumar y restar polinomios | |sinopsis=Aprende a sumar y restar polinomios | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ueJtyB2Hg2I | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1L_zBNWEANk&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTcfeSnw_WhNua0bmjHpwort&index=1 |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | ||
| Línea 27: | Línea 27: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_paps | {{Video_enlace_paps | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 3 (Suma) | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 3a (Suma) |
| - | |duracion=7'35" | + | |duracion=4'09" |
| |sinopsis=Aprende a sumar polinomios | |sinopsis=Aprende a sumar polinomios | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1L_zBNWEANk&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTcfeSnw_WhNua0bmjHpwort&index=1 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ueJtyB2Hg2I |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_paps | {{Video_enlace_paps | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 4 (Resta) | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 3b (Resta) |
| |duracion=4'37" | |duracion=4'37" | ||
| |sinopsis=Aprende a restar polinomios | |sinopsis=Aprende a restar polinomios | ||
| Línea 39: | Línea 39: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 5 (Una variable) | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 4 |
| |duracion=6'57" | |duracion=6'57" | ||
| |sinopsis=Suma y resta de polinomios en una variable. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Suma y resta de polinomios en una variable. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KrAzy15tt3o&list=PL54E0E2B3C3F7EA2B&index=1 | + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4S87BeniINQ&index=2&list=PL54E0E2B3C3F7EA2B |
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 5a (Suma) | ||
| + | |duracion=12'33" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Suma de polinomios. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFBRc1qPvT4&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=1 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 5b (Propiedades de la suma I) | ||
| + | |duracion=14'39" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: conmutativa y asociativa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k4Q0CUqv8to&index=2&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 5c (Propiedades de la suma II) | ||
| + | |duracion=5'40" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: Elemento neutro y opuesto. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cQewbEXSqu8&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 5d (Resta) | ||
| + | |duracion=7'58" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resta de polinomios. Equivalencias fundamentales. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GAdjF2hF_vs&index=4&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 6 | ||
| + | |duracion=9'25" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Suma y resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/ROhYH07cdoA?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| Línea 77: | Línea 111: | ||
| b) <math>(x^2+x-3)+(2x^2-2x+1)-(3x^2-4x+5)\,</math> | b) <math>(x^2+x-3)+(2x^2-2x+1)-(3x^2-4x+5)\,</math> | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2KbR_siNsqc | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2KbR_siNsqc | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6a | ||
| + | |duracion=3'29" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(5x^2+8x-3)+(2x^2-7x+13x)\;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/BXngPyAAY9M | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6b | ||
| + | |duracion=2'17" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(16x+14)-(3x^2+x-9)\;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/hU5aasVpI8o | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6c | ||
| + | |duracion=7'38" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resta <math>-2x^2+4x-1\;</math> de <math>6x^2+3x-9\;</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/fcqZ-M60478 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6d | ||
| + | |duracion=3'57" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(x^3+3x-6)+(-2x^2+x-2)-(3x-4)\;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/ZMmqkr_WitA | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6e | ||
| + | |duracion=3'07" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(4x^2y-3x^2-2y)+(8xy-3x^2+2x^2y+4)\;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/y0Oy_3KEiiY | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6f | ||
| + | |duracion=2'47" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Simplifica: <math>(4x^2y-3xy+25)-(9y^2x+7xy-20)\;</math> | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/dU06gyo_0Dk | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6g | ||
| + | |duracion=4'14" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Resta <math>-6x^4-3x^2y^2+5y^4\;</math> de <math>2x^4-8x^2y^2-y^4\;</math>. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/eXFnHQ5Zm20 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6h | ||
| + | |duracion=2'52" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Encuentra el error cometido en la resta que se muestra en el video. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/GDQCuxhGaUU | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7a | ||
| + | |duracion=13'40" | ||
| + | |sinopsis= | ||
| + | 1) Ordena los polinomios y realiza las sumas que se indican: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1a) P(x) + Q(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1b) P(x) + R(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1c) P(x) + S(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7famqf0iloE&index=5&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7b | ||
| + | |duracion=10'49" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios, realiza las sumas que se indican: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1d) Q(x) + S(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1e) R(x) + S(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1f) Q(x) + R(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QA9QbWLP25I&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=6 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8a | ||
| + | |duracion=17'35" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=2) Sumas los siguientes polinomios y compara el grado del polinomio suma con el grado de los polinomios sumandos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=-x^3+3x^2-2x+2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>Q(x)=x^3+4x^2-3x+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3a) Escribe opuestos de los siguientes polinomios: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3b) Suma cada uno de los polinomios del apartado anterior con su opuesto. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3c) Calcula un polinomio A(x) tal que <math>P(x)+A(x)=x^2-1\;</math>, siendo <math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lu2s5qKQKAI&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=7 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8b | ||
| + | |duracion=16'45" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3d) Calcula un polinomio B(x) tal que <math>Q(x)-B(x)=3x^3-x+2\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3e) Calcula un polinomio C(x) tal que <math>P(x)+Q(x)-C(x)=R(x)\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3f) Calcula un polinomio D(x) tal que <math>R(x)+S(x)-D(x)=0\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n56tBwVdbeg&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=8 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| + | |duracion=12'30" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4a) Calcula P(x) - Q(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4b) Calcula P(x) - R(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4c) Calcula [P(x) + Q(x)]-[R(x) + S(x)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4d) Calcula [P(x) + S(x)]-[Q(x) + R(x)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4e) Calcula T(x) + M(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4f) Calcula T(x) - M(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mrckQrOh_Zw&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=9 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| + | |duracion=16'53" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=5) ¿Qué polinomio se ha de restar al polinomio <math>P(x)=2x^2-4x+2\;</math> para obtener el polinomio <math>x^3-3x+1\;</math>? | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6) Dados los polinomios | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=mx^3-5x+6\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=-4x^3-6x+7\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | calcula el valor de <math>m\;</math> sabiendo que <math>P(x)+Q(x)=x^3-11x+13\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7) Escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de tal modo que su suma se el polinomio nulo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8) Escribe dos polinomios reducidos de segundo grado y comprueba con ellos la conmutatividad de la suma. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IOXPUUt2dSs&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=10 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 11 | ||
| + | |duracion=14'20" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=9) Dado el polinomio <math>P(x)=2x^2-3x+2\;</math>, escribe su opuesto, -P(x). Calcula los valores numéricos de P(x) y -P(x) para x = 0, x = 1 y x = 2, y comprueba comprueba que son números opuestos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 10) ¿Qué polinomio tienes que sumar con <math>3x^2-2x-3\;</math> para que la suma sea 5x^3-6x? | ||
| + | |||
| + | 11) Dado el polinomio <math>P(x)=\cfrac{5}{4}x^4-2x^3+6x-\cfrac{1}{5}\;</math>, halla otro polinomio Q(x) tal que <math>P(x)+Q(x)=3x^2+6x-1\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RI3p2CzkFTo&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=11 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 12 | ||
| + | |duracion=7'27" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=3x^2-1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=2x^3-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>R(x)=3x^2+x+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=\cfrac{1}{2}x^2+2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>T(x)=\cfrac{3}{2}x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>V(x)=3x^2+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12b) Calcula P(x) - V(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12c) Calcula P(x) + R(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12d) Calcula P(x) - R(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12e) Calcula S(x) + T(x) + V(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | 12f) Calcula S(x) - T(x) + V(x). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wduetGOYCl8&index=12&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 13 | ||
| + | |duracion=11'55" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=13) Dados los polinomios | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=-x^3+2x^2+x\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=2x^3-3x+1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | calcula el polinomio M(x) tal que P(x) + M(x) = Q(x). | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 14 | ||
| + | |duracion=15'13" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=17) La diferencia de dos polinomios es: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)-Q(x)=x^3-5x^2-7x+2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Calcula <math>Q(x)\;</math> sabiendo que <math>P(x)=x^4+5x^3+2x-1\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 18) ¿Qué polinomio hay que sumar al polinomio <math>P(x)=x^2-6x+3\;</math> para obtener el polinomio opuesto de <math>Q(x)=-5x^3+2x^2-4x+1\;</math>? | ||
| + | |||
| + | 19) Dados los polinomios: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P(x)=x^4-3x^2+2x-3\;</math>; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=3x^3-4x^2+4\;</math>; {{b4}} <math>R(x)=2x^4-4x-1\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :19a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x) - R(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :19b) Calcula P(x) + R(x) - Q(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :19c) Calcula Q(x) + R(x) - P(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :19d) Calcula P(x) + Q(x) + R(x) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CWQypO7oKqo&index=14&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | 14) Escribe dos polinomios cualesquiera y súmalos. Contesta: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :14a) ¿Es mayor el grado de los sumandos o el de la suma? ¿Es igual? ¿Es menor? | ||
| + | |||
| + | :14b) ¿Puede en algún caso ser menor el grado de la suma que el de los sumandos? ¿Cuándo? Justifícalo con ejemplos. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 15) ¿Qué puedes decir del grado de la diferencia de dos polinomios? | ||
| + | |||
| + | 16) escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de modo que su suma se el polinomio <math>P(x)=3x^2-5x+3\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dU8lw09JouM&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oz2ZwbEq1hT9DGndGgcOi2z&index=13 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_fonemato | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 15 |
| |duracion=6'49" | |duracion=6'49" | ||
| - | |sinopsis=2 ejercicios. | + | |sinopsis=Determina el valor de "m" y "n" sabiendo que <math>A(x)+B(x) = C(x)-D(x)\;</math>, en los siguientes casos: |
| + | |||
| + | # <math>A(x)=2x^3+mx+1 \ ; \ B(x)=mx^2+nx \ ; \ C(x)=3x^3-nx^2 \ ; \ D(x)=x^3+n</math> | ||
| + | # <math>A(x)=mx^3+x^2+1 \ ; \ B(x)=6x^2+nx \ ; \ C(x)=5x^3-nx^2 \ ; \ D(x)=x^3-mx+n</math> | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=STagSTBlj28&list=PL54E0E2B3C3F7EA2B&index=3 | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=STagSTBlj28&list=PL54E0E2B3C3F7EA2B&index=3 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| + | {{Actividades|titulo=Suma y resta de polinomios|enunciado= | ||
| + | {{AI_cidead | ||
| + | |titulo1=Actividad 1 | ||
| + | |descripcion=Actividades para aprender y practicar la suma y resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://recursostic.educacion.es/secundaria/edad/3esomatematicas/3quincena2/3quincena2_contenidos_2a.htm | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_cidead | ||
| + | |titulo1=Actividad 2 | ||
| + | |descripcion=Ejercicios para practicar la suma y resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=http://recursostic.educacion.es/secundaria/edad/2esomatematicas/2quincena5/2quincena5_contenidos_3b.htm | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1a (suma) | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/adding-and-subtracting-polynomials/e/adding_and_subtracting_polynomials | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1b (resta) | ||
| + | |descripcion=Resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/adding-and-subtracting-polynomials/e/subtract-polynomials | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1c | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/adding-and-subtracting-polynomials/e/add---subtract-polynomials-challenge | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1d | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/add-subtract-poly-two-var/e/adding-and-subtracting-polynomials-2 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1e | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/add-subtract-poly-two-var/e/add---subtract-polynomials--two-variables-challenge | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_Khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 1f | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables: encuentra el error. | ||
| + | |url1=http://es.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/introduction-to-polynomial-expressions/add-subtract-poly-two-var/e/add---subtract-polynomials--find-the-error | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_upr | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 2a (suma) | ||
| + | |descripcion=Suma de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://quiz.uprm.edu/cgi-bin/Quiz/oneques.cgi?database=REVIEW/exp_alg_tut/exp_alg_tut3_sp.db&no_ques=3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_upr | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 2b (resta) | ||
| + | |descripcion=Resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://quiz.uprm.edu/cgi-bin/Quiz/oneques.cgi?database=REVIEW/exp_alg_tut/exp_alg_tut4_sp.db&no_ques=2 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{AI_vitutor | ||
| + | |descripcion=Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre suma y resta de polinomios. | ||
| + | |url1=http://www.vitutor.com/ab/p/poli_21_e.html | ||
| + | |titulo1=Autoevaluación 3 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
Revisión actual
Procedimiento
Para sumar o restar polinomios, sumaremos o restaremos los monomios semejantes de ambos.
Aprende a sumar y restar polinomios
En este tutorial se explica la suma y resta de polinomios comenzando con algunas definiciones básicas y terminando con ejemplos.
Aprende a sumar polinomios
Aprende a restar polinomios
Suma y resta de polinomios en una variable. Ejemplos.
Suma de polinomios. Ejemplos.
Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: conmutativa y asociativa.
Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: Elemento neutro y opuesto.
Resta de polinomios. Equivalencias fundamentales.
Suma y resta de polinomios.
Calcula la suma: 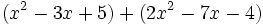
Calcula la suma: 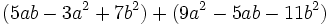
Calcula la resta: 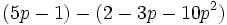
Calcula la resta: 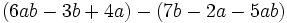
Calcula:
a) 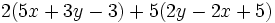 b)
b) 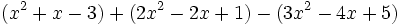
Simplifica: 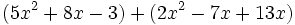
Simplifica: 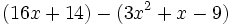
Resta 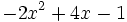 de
de 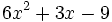 .
.
Simplifica: 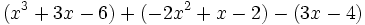
Simplifica: 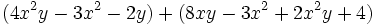
Simplifica: 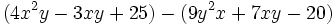
Resta 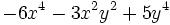 de
de 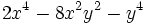 .
.
Encuentra el error cometido en la resta que se muestra en el video.
1) Ordena los polinomios y realiza las sumas que se indican:
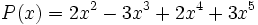 ;
; 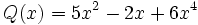
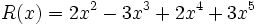 ;
; 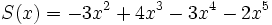
1a) P(x) + Q(x)
1b) P(x) + R(x)
1c) P(x) + S(x)
Dados los siguientes polinomios, realiza las sumas que se indican:
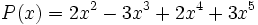 ;
; 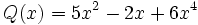
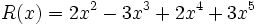 ;
; 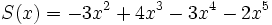
1d) Q(x) + S(x)
1e) R(x) + S(x)
1f) Q(x) + R(x)
2) Sumas los siguientes polinomios y compara el grado del polinomio suma con el grado de los polinomios sumandos.
3a) Escribe opuestos de los siguientes polinomios:
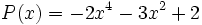 ;
; 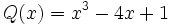
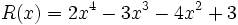 ;
; 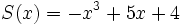
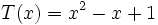 ;
; 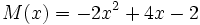
3b) Suma cada uno de los polinomios del apartado anterior con su opuesto.
3c) Calcula un polinomio A(x) tal que 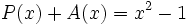 , siendo
, siendo 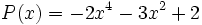 .
.
Dados los siguientes polinomios:
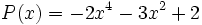 ;
; 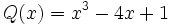
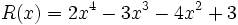 ;
; 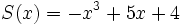
3d) Calcula un polinomio B(x) tal que 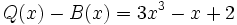 .
.
3e) Calcula un polinomio C(x) tal que 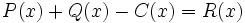 .
.
3f) Calcula un polinomio D(x) tal que 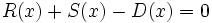 .
.
Dados los polinomios:
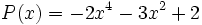 ;
; 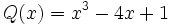
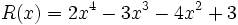 ;
; 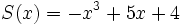
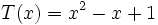 ;
; 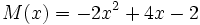
4a) Calcula P(x) - Q(x).
4b) Calcula P(x) - R(x).
4c) Calcula [P(x) + Q(x)]-[R(x) + S(x)]
4d) Calcula [P(x) + S(x)]-[Q(x) + R(x)]
4e) Calcula T(x) + M(x)
4f) Calcula T(x) - M(x)
5) ¿Qué polinomio se ha de restar al polinomio 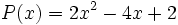 para obtener el polinomio
para obtener el polinomio 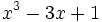 ?
?
6) Dados los polinomios
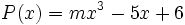 ;
; 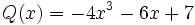
calcula el valor de 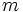 sabiendo que
sabiendo que 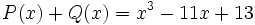 .
.
7) Escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de tal modo que su suma se el polinomio nulo.
8) Escribe dos polinomios reducidos de segundo grado y comprueba con ellos la conmutatividad de la suma.
9) Dado el polinomio 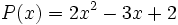 , escribe su opuesto, -P(x). Calcula los valores numéricos de P(x) y -P(x) para x = 0, x = 1 y x = 2, y comprueba comprueba que son números opuestos.
, escribe su opuesto, -P(x). Calcula los valores numéricos de P(x) y -P(x) para x = 0, x = 1 y x = 2, y comprueba comprueba que son números opuestos.
10) ¿Qué polinomio tienes que sumar con 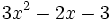 para que la suma sea 5x^3-6x?
para que la suma sea 5x^3-6x?
11) Dado el polinomio 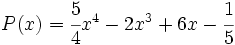 , halla otro polinomio Q(x) tal que
, halla otro polinomio Q(x) tal que 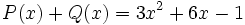 .
.
Dados los polinomios
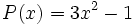 ;
; 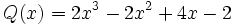
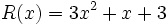 ;
; 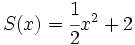
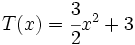 ;
; 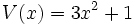
12a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x).
12b) Calcula P(x) - V(x).
12c) Calcula P(x) + R(x).
12d) Calcula P(x) - R(x).
12e) Calcula S(x) + T(x) + V(x).
12f) Calcula S(x) - T(x) + V(x).
13) Dados los polinomios
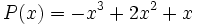 ;
; 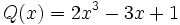
calcula el polinomio M(x) tal que P(x) + M(x) = Q(x).
17) La diferencia de dos polinomios es:
Calcula 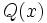 sabiendo que
sabiendo que 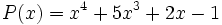 .
.
18) ¿Qué polinomio hay que sumar al polinomio 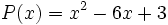 para obtener el polinomio opuesto de
para obtener el polinomio opuesto de 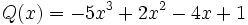 ?
?
19) Dados los polinomios:
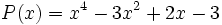 ;
; 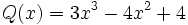 ;
; 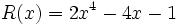
- 19a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x) - R(x)
- 19b) Calcula P(x) + R(x) - Q(x)
- 19c) Calcula Q(x) + R(x) - P(x)
- 19d) Calcula P(x) + Q(x) + R(x)
14) Escribe dos polinomios cualesquiera y súmalos. Contesta:
- 14a) ¿Es mayor el grado de los sumandos o el de la suma? ¿Es igual? ¿Es menor?
- 14b) ¿Puede en algún caso ser menor el grado de la suma que el de los sumandos? ¿Cuándo? Justifícalo con ejemplos.
15) ¿Qué puedes decir del grado de la diferencia de dos polinomios?
16) escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de modo que su suma se el polinomio 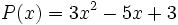 .
.
Determina el valor de "m" y "n" sabiendo que 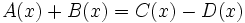 , en los siguientes casos:
, en los siguientes casos:
Actividades para aprender y practicar la suma y resta de polinomios.
Ejercicios para practicar la suma y resta de polinomios.
Suma de polinomios.
Resta de polinomios.
Suma y resta de polinomios.
Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables.
Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables.
Suma y resta de polinomios con dos variables: encuentra el error.
Suma de polinomios.
Resta de polinomios.
Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre suma y resta de polinomios.