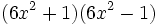Plantilla:Videos: identidades notables
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 15:10 7 sep 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) |
||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Identidades notables|enunciado= | + | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Productos notables|enunciado= |
| {{Video_enlace_tutomate | {{Video_enlace_tutomate | ||
| - | |titulo1=Identidades notables | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 1 |
| |duracion=9'38" | |duracion=9'38" | ||
| |sinopsis=Productos notables. Ejemplos. | |sinopsis=Productos notables. Ejemplos. | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dUgMB_NaLNg&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTcfeSnw_WhNua0bmjHpwort&index=5 | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dUgMB_NaLNg&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTcfeSnw_WhNua0bmjHpwort&index=5 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2a | ||
| + | |duracion=1'53" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Las tres identidades notables. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/4X-H2js9QYw?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2b | ||
| + | |duracion=5'43" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=La identidad notable cuadrado de una suma. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/vFLkDGOaxig?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2c | ||
| + | |duracion=4'29" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=La identidad notable cuadrado de una diferencia. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Xuyfj6rXj20?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 2d | ||
| + | |duracion=3'15" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=La identidad notable suma por diferencia. Ejemplos. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/UpOn7VfZWfs?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_paps | {{Video_enlace_paps | ||
| - | |titulo1=Cuadrado de un binomio | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 3a |
| |duracion=5'48" | |duracion=5'48" | ||
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| Línea 18: | Línea 42: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_paps | {{Video_enlace_paps | ||
| - | |titulo1=Suma por diferencia | + | |titulo1=Tutorial 3b |
| |duracion=6'08" | |duracion=6'08" | ||
| |sinopsis= | |sinopsis= | ||
| Línea 27: | Línea 51: | ||
| :c) <math>(x-a)(x+a)\;</math> | :c) <math>(x-a)(x+a)\;</math> | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_535040279&feature=iv&src_vid=pOeyG4ZQor4&v=DUm1tD_b-qA | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_535040279&feature=iv&src_vid=pOeyG4ZQor4&v=DUm1tD_b-qA | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 4 | ||
| + | |duracion=14'05" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Como se desarrollan un binomio al cuadrado y una suma por diferencia. | ||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mTkBiySoIzQ&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oxSaTeel6R_pQaMSalig8UR | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | ||
| + | |titulo1=Tutorial 5 | ||
| + | |duracion=25'26" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Explicación de las igualdades o identidades notables y ejemplos resueltos. | ||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/r15dHPFYNKo | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ---- | ---- | ||
| {{Video_enlace_abel | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1a |
| |duracion=8'39" | |duracion=8'39" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | ||
| Línea 41: | Línea 77: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_abel | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1b |
| |duracion=9'11" | |duracion=9'11" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | ||
| Línea 51: | Línea 87: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2a |
| |duracion=2'17" | |duracion=2'17" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(3x+5y)^2\,</math> | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(3x+5y)^2\,</math> | ||
| Línea 57: | Línea 93: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2b |
| |duracion=4'23" | |duracion=4'23" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(2x^3+9y^4)^2\,</math> | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(2x^3+9y^4)^2\,</math> | ||
| Línea 63: | Línea 99: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2c |
| |duracion=1'33" | |duracion=1'33" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(7m-3c)^2\,</math> | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(7m-3c)^2\,</math> | ||
| Línea 69: | Línea 105: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2d |
| |duracion=5'44" | |duracion=5'44" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(4K^2L-5K^6L^3)^2\,</math> | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(4K^2L-5K^6L^3)^2\,</math> | ||
| Línea 75: | Línea 111: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2e |
| |duracion=2'01" | |duracion=2'01" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(5m^3+3n^4)\cdot(5m^3-3n^4)\,</math> | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>(5m^3+3n^4)\cdot(5m^3-3n^4)\,</math> | ||
| |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nFWyn0j8Flw&index=23&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45}} | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nFWyn0j8Flw&index=23&list=PL9B9AC3136D2D4C45}} | ||
| {{Video_enlace_unicoos | {{Video_enlace_unicoos | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 8 | + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 |
| |duracion=5'54" | |duracion=5'54" | ||
| |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: | ||
| Línea 96: | Línea 132: | ||
| |url1=http://www.unicoos.com/video/matematicas/2-eso/expresiones-algebraicas/identidades-notables/identidades-notables-02 | |url1=http://www.unicoos.com/video/matematicas/2-eso/expresiones-algebraicas/identidades-notables/identidades-notables-02 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4a | ||
| + | |duracion=8'05" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :2a) <math>(2a-b)(2a+b)\;</math> | ||
| + | :2b) <math>(\cfrac{2}{3}x-\cfrac{5}{6}y^2)(\cfrac{2}{3}x+\cfrac{5}{6}y^2)\;</math> | ||
| + | :2c) <math>(3x-2y)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :2d) <math>(3x+2y)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :2e) <math>(x^2+\cfrac{x}{3})(x^2-\cfrac{x}{3})\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_ulT2eX2VXQ&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oxSaTeel6R_pQaMSalig8UR&index=6 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4b | ||
| + | |duracion=4'33" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :4a) <math>(x-2a)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :4b) <math>(x+2a)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :4c) <math>(2x+1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :4d) <math>(2x-1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZyxhYXRHpWA&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oxSaTeel6R_pQaMSalig8UR&index=8 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_escuela | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4c | ||
| + | |duracion=10'51" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :5a) <math>(3x+1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5b) <math>(3x-1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5c) <math>(2x+3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5d) <math>(5x^2+3x)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5e) <math>(5x^2-3x)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5f) <math>(x+2)(x-2)\;</math> | ||
| + | :5g) <math>(3x^2+3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5h) <math>(x^2+6)(x^2-6)\;</math> | ||
| + | :5i) <math>(6x-3)(6x+3)\;</math> | ||
| + | :5j) <math>(2x-\cfrac{1}{2})(2x+\cfrac{1}{2})\;</math> | ||
| + | :5k) <math>(6x-3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | :5l) <math>(6x+3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cv3xDNwrh0I&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3oxSaTeel6R_pQaMSalig8UR&index=9 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5a | ||
| + | |duracion=5'56" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>(x+3)(x-3)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/Lb4v-gZ_KZ4 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5b | ||
| + | |duracion=7'19" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>(x+7)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/b0m1ZAuWX2M | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5c | ||
| + | |duracion=2'30" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>(2x+8)(2x-8)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/sBhNnSoP10w | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5d | ||
| + | |duracion=3'59" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: <math>(7x+10)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/4y4EzvTgSiY | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5e | ||
| + | |duracion=8'27" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Halla el área de un cuadrado cuyo lado mide <math>(6x-5y)\;</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/mXFr19ToYkQ | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_khan | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5f | ||
| + | |duracion=10'35" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(x+9)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :b) <math>(x+b)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :c) <math>(3x-7)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :d) <math>(4x^2+y^2)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :e) <math>(2x-1)(2x+1)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :f) <math>(5a-2b)(5a+2b)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/D6wANZkEEOI | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Video_enlace_pildoras | ||
| + | |titulo1=Ejercicios 6a | ||
| + | |duracion=7'50" | ||
| + | |sinopsis=Calcula: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :a) <math>(x+5)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :b) <math>(x-5)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :c) <math>(x+5)(x-5)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :d) <math>(x+\cfrac{1}{2})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :e) <math>(x-\cfrac{1}{2})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :f) <math>(x+\cfrac{1}{2})(x-\cfrac{1}{2})\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :g) <math>(x+\cfrac{3}{5})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :h) <math>(x-\cfrac{3}{5})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :i) <math>(x+\cfrac{3}{5})(x-\cfrac{3}{5})\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :j) <math>(4x+3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :k) <math>(4x-3)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :l) <math>(4x+3)(4x-3)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :m) <math>(2x+\cfrac{1}{3})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :n) <math>(2x-\cfrac{1}{3})^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :o) <math>(2x+\cfrac{1}{3})(2x-\cfrac{1}{3})\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :p) <math>(x^3+4)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :q) <math>(x^3-4)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :r) <math>(x^3+4)(x^3-4)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :s) <math>(6x^2+1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :t) <math>(6x^2-1)^2\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :u) <math>(6x^2+1)(6x^2-1)\;</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |url1=https://youtu.be/jrJ5eHbRpOI?list=PLwCiNw1sXMSDgbsuqToHr0F45-YoSUP7d | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| }} | }} | ||
Revisión actual
Productos notables. Ejemplos.
Las tres identidades notables.
La identidad notable cuadrado de una suma. Ejemplos.
La identidad notable cuadrado de una diferencia. Ejemplos.
La identidad notable suma por diferencia. Ejemplos.
- Fórmulas del cuadrado de una suma y de una diferencia.
- Ejemplos::
- a)

- b)
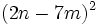
- Fórmula de la suma por diferencia.
- Ejemplos:
- a)
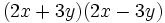
- b)
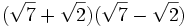
- c)
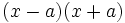
Como se desarrollan un binomio al cuadrado y una suma por diferencia.
Explicación de las igualdades o identidades notables y ejemplos resueltos.
Desarrolla:
- a)
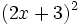
- b)
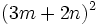
- c)
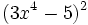
- d)
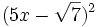
Desarrolla:
- a)
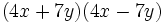
- b)
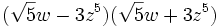
- c)

Desarrolla: 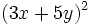
Desarrolla: 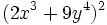
Desarrolla: 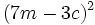
Desarrolla: 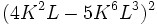
Desarrolla: 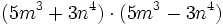
Desarrolla:
a) 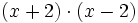
b) 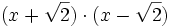
c) 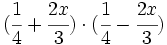
d) 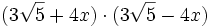
e) 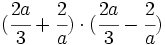
Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables:
- 2a)
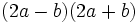
- 2b)
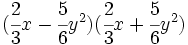
- 2c)
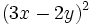
- 2d)
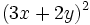
- 2e)
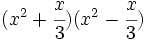
Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables:
- 4a)
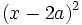
- 4b)
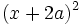
- 4c)
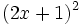
- 4d)
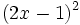
Desarrolla los siguientes productos notables:
- 5a)
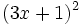
- 5b)
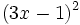
- 5c)
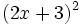
- 5d)
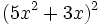
- 5e)
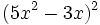
- 5f)
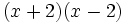
- 5g)
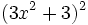
- 5h)
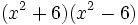
- 5i)
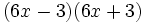
- 5j)
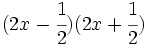
- 5k)
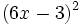
- 5l)
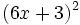
Calcula: 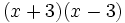
Calcula: 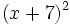
Calcula: 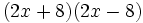
Calcula: 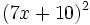
Halla el área de un cuadrado cuyo lado mide 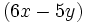 .
.
Calcula:
- a)
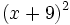
- b)
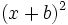
- c)
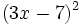
- d)
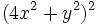
- e)
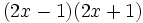
- f)
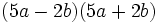
Calcula:
- a)
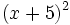
- b)
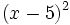
- c)
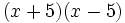
- d)
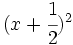
- e)
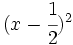
- f)
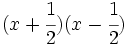
- g)
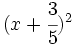
- h)
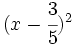
- i)
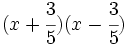
- j)
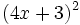
- k)
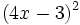
- l)
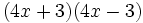
- m)
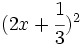
- n)
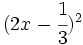
- o)
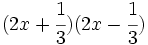
- p)
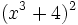
- q)
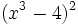
- r)
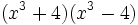
- s)
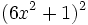
- t)
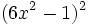
- u)