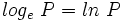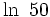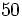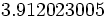Plantilla:Logaritmos (1ºBach)
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 16:29 26 sep 2018 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Logaritmos) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 16:30 26 sep 2018 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Propiedades de los logaritmos) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 5: | Línea 5: | ||
| ==Propiedades de los logaritmos== | ==Propiedades de los logaritmos== | ||
| + | {{Propiedades de los logaritmos}} | ||
| - | {{Teorema_sin_demo|titulo= | ||
| - | Propiedades de los logaritmos: | ||
| - | |enunciado= | ||
| - | '''1: Igualdad y orden:''' | ||
| - | :a) <math>P \ne Q \Rightarrow log_a \ P \ne log_a \ Q</math> o equivalentemente, | ||
| - | {{b4}}{{b4}}{{b}}{{b}}{{b}}<math> log_a \ P = log_a \ Q \Rightarrow P=Q</math> | ||
| - | :b) <math>P < Q \Rightarrow log_a \ P < log_a \ Q, \quad si~ a>1</math> | ||
| - | :c) <math>P < Q \Rightarrow log_a \ P > log_a \ Q, \quad si~ 0<a<1</math> | ||
| - | '''2: Logaritmo de la base:''' | ||
| - | :a) <math>log_a \ a=1</math> | ||
| - | :b) <math>log_a \ a^n=n</math> | ||
| - | :c) <math>log_a \ 1=0</math> | ||
| - | '''3: Logaritmo de números negativos o nulos:''' | ||
| - | : Si <math>P \le 0</math>, entonces <math>log_a \ P</math> no existe. | ||
| - | '''4: Logaritmo de un producto:''' | ||
| - | : <math>log_a \ (P \cdot Q)=log_a \ P + log_a \ Q</math> | ||
| - | '''5: Logaritmo de un cociente:''' | ||
| - | : <math>log_a \ \cfrac{P}{Q}=log_a \ P - log_a \ Q</math> | ||
| - | '''6: Logaritmo de una potencia:''' | ||
| - | : <math>log_a \ P^n=n \cdot log_a \ P</math> | ||
| - | '''7: Logaritmo de una raíz:''' | ||
| - | : <math>log_a \ \sqrt[n]{P}=\cfrac{1}{n} \cdot log_a \ P</math> | ||
| - | '''8: Cambio de base:''' | ||
| - | : <math>log_a \ P=\cfrac{log_b \ P}{log_b \ a}</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Ejemplo|titulo=Ejercicios resueltos: ''Propiedades de los logaritmos'' | ||
| - | |enunciado= | ||
| - | Sabiendo que <math>log_2 \ A=3.5 \ y \ log_2 \ B=-1.4</math>, calcula: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :a) <math>log_2 \ \cfrac{A \cdot B}{4}</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | :b) <math>log_2 \ \cfrac{2 \sqrt{A}} {B^3}</math> | ||
| - | |sol= | ||
| - | a) <math>log_2 \ \cfrac{A \cdot B}{4} | ||
| - | \begin{matrix}~_{[5]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} | ||
| - | log_2 \ (A \cdot B) - log_2 \ 4=</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | :<math>\begin{matrix}~_{[4]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} | ||
| - | log_2 \ A + log_2 \ B - log_2 \ 4=3.5-1.4-2=0.1</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{b4}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) <math>log_2 \ \cfrac{2 \sqrt{A}} {B^3} | ||
| - | \begin{matrix}~_{[5]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} | ||
| - | log_2 \ 2 \sqrt{A} - log_2 \ B^3 =</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | :<math>\begin{matrix}~_{[4]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} | ||
| - | log_2 \ 2+ log_2 \sqrt{A} - log_2 \ B^3=1+ log_2 \ A^{\frac{1}{2}} - log_2 B^3=</math> | ||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | :<math>\begin{matrix}~_{[6]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} | ||
| - | 1+ \cfrac{1}{2} ~log_2 \ A - 3 \, log_2 \ B=1+ \cfrac{1}{2} \cdot 3.5 - 3 \cdot (-1.4) = 6.95</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{p}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Propiedades de los logaritmos | ||
| - | |enunciado= | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=25'59" | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Tutorial que explica la definición de logaritmo y realiza el cálculo de algunos logaritmos exactos (resultado racional) para comprender el significado de esta operación matemática. | ||
| - | |||
| - | *00:00 a 03:10: Introducción a logaritmo. Ejercicios de repaso. | ||
| - | *03:10 a 06:25: Propiedades Básicas. | ||
| - | *06:25 a 08:30: Propiedad: Logaritmo de un Producto. Demostración. | ||
| - | *08:30 a 09:20: Propiedad: Logaritmo de una Potencia. Demostración. | ||
| - | *09:20 a 10:30: Propiedad: Logaritmo de un Cociente. Demostración. | ||
| - | *10:30 a 13:45: Propiedad: Cambio de Base. Demostración. | ||
| - | *13:45 a 25:59: Ejercicios de Logaritmos. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0r-1s2dTP-I&list=PLZNmE9BEzVIlcxDzg8OG4HYZGg0m7OHTh&index=2}} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 2 | ||
| - | |duracion=13´22" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glD8VLbPqgQ&index=4&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de las propiedades de los logaritmos. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 3 | ||
| - | |duracion=12´43" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6XVI_xzLYw&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=62 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Definición del logaritmo de un número. Propiedades. Ejemplos | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Identidad fundamental del logaritmo | ||
| - | |duracion=7´58" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7tl-EhBIKXo | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Identidad fundamental del logaritmo. Ejemplos de aplicación. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Logaritmo de un producto | ||
| - | |duracion=15'28" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_Xb1hOmKUO4 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de un producto. Ejemplos de aplicación. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Logaritmo de un cociente | ||
| - | |duracion=12'34" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DZLqJGoY_10 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de un cociente. Ejemplos de aplicación. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Logaritmo de una potencia | ||
| - | |duracion=10'57" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oU3Fba5UUEc | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de una potencia. Ejemplos de aplicación. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Logaritmo de una raíz | ||
| - | |duracion=15'24" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=seWrZZaZHL0 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de una raíz. Ejemplos de aplicación. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | Desarrollo de logaritmos usando las propiedades: | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=2´34" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3zToR-gkGS0&index=1&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>log_4 \, 8^2 \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | ||
| - | |duracion=4´24" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u5dm5vQQe_Q&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo&index=2 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>ln \, 5x^3yz^4 \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 | ||
| - | |duracion=4´38" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2-At_0WIAj8&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo&index=3 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>ln \, \cfrac{xy^2}{e^3z^4} \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | ||
| - | |duracion=4´47" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=acI2PRISVNg&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo&index=4 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>log_e \, \sqrt[4]{e^3x^5} \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| - | |duracion=3´43" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mOROtNjT3DQ&index=5&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>log_3 \, \cfrac{\sqrt[5]{x}}{\sqrt[3]{y}} \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | ||
| - | |duracion=5´28" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vZfSh92I5F8&list=PLo7_lpX1yruPaD9IzJT-tjN_vFvI1YDjo&index=6 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla: <math>log_5 \, \cfrac{5^x(1-x)}{y^x(x-y^2)} \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | |||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | Expresar como un solo logaritmo: | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=2´07" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g68P8Lcssqg&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOQZzFEu7cxWeZffnOaDe4L&index=1 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Expresar como un solo logaritmo: <math>2 log \, x - 3 log \, y</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | ||
| - | |duracion=2´15" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=90VgizUzIhI&index=2&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOQZzFEu7cxWeZffnOaDe4L | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Expresar como un solo logaritmo: <math>2 ln \, 3 + y ln \, x</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 | ||
| - | |duracion=2´54" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RPRUgbs_K14&index=3&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOQZzFEu7cxWeZffnOaDe4L | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Expresar como un solo logaritmo: <math>ln \, 4 + 2x</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | ||
| - | |duracion=3´59" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KFF_omy3iek&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOQZzFEu7cxWeZffnOaDe4L&index=4 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Expresar como un solo logaritmo: <math>2+log_6 \, x - log_6 \, z</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_virtual | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| - | |duracion=2´30" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6lMPBsrGqNs&list=PLo7_lpX1yruOQZzFEu7cxWeZffnOaDe4L&index=5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Expresar como un solo logaritmo: <math>log_7 \, x - log_7 \, y - log_7 \, z</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | Varios: | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=3´19" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GXtVPMmmEaE | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Si <math>a=ln \, 2</math> y <math>b=ln \, 3</math>, expresa <math>ln \, \cfrac{8}{9}</math> en términos de a y b. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 2 | ||
| - | |duracion=5´13" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gdcMNx1ptME | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Si <math>ln \, A=5</math>, <math>ln \, B=-2</math> y <math>ln \, C=-7</math>, encuentra el valor numérico de la expresión <math>ln \, \cfrac{A^3 B^4}{C^6}</math>. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_julioprofe | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 3 | ||
| - | |duracion=3´23" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IpQJT1SMx8U | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Escribe como un solo logaritmo: <math>\cfrac{1}{3}\,log\,A+\cfrac{1}{2}\,\left( log\,B - log\,C \right)</math>. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 4 | ||
| - | |duracion=10´38" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtQRsxiq2Yw&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=63 | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | a) Hallar "m" sabiendo que <math>log_m \, 5=2\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) Hallar "x" sabiendo que <math>log_{(x-1)} \, (x+5)=2\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) Sabiendo que <math>log \, 2=a\;</math> y que <math>log \, 2=b\;</math>, calcula <math>log \, 360\;</math>. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 5 | ||
| - | |duracion=15´11" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GI1BqXDr2gY&index=64&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | a) Hallar "x" sabiendo que <math>4^{log_x \, 6 \, \cdot \, log_6 \, y \, \cdot \, log_y \, x^4}=x^{log_x \, 4^x}\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) Sabiendo que <math>log \, ab^2=1\;</math> y que <math>log \, a^3b=1\;</math>, halla <math>a \cdot b\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 6 | ||
| - | |duracion=13´34" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OuT-XxlETMs&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=65 | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | a) Reduce: <math>P=\cfrac{1}{1+log_a \, bc}+ \cfrac{1}{1+log_b \, ac}+\cfrac{1}{1+log_c \, ab}</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) Hallar "x" si <math>1+2\,log \, x - log \, (x+2)=0\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 7 | ||
| - | |duracion=9´34" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p6inEJNKz6Y&index=5&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Desarrolla los siguientes logaritmos: | ||
| - | #<math>log \, \cfrac{5z^3u^2}{2x^7}</math> | ||
| - | #<math>log \, \cfrac{1}{2z^5 \sqrt{u}}</math> | ||
| - | #<math>log_6 \, \cfrac{2x+3z}{u^5}</math> | ||
| - | #<math>ln \, \sqrt[3]{\cfrac{x}{z^2u^7}}</math> | ||
| - | #<math>log_k \, \sqrt{ k \, \sqrt {k\, {\sqrt{k}}}}</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicios 8 | ||
| - | |duracion=8´45" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=td6Tqzafm_0&index=6&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Reduzca las siguientes expresiones a un solo logaritmo: | ||
| - | #<math>2 \, log \, x - 3 \, log \, z</math> | ||
| - | #<math>\cfrac{1}{3} \; log \, (x+z) - \cfrac{1}{2} \; log \, (x-z)</math> | ||
| - | #<math>2 - 3 \, log \, x + \cfrac{1}{5} \; log \, z</math> | ||
| - | #<math>3 - \cfrac{1}{2} \, log_2 \, (x-2z) - 6 \, log_2 \, x</math> | ||
| - | #<math>1 + 3 \, ln \ x^2 - \cfrac{2}{5} \; ln \, (1+x)</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 9 | ||
| - | |duracion=7´13" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ugfAdqs33A0&index=7&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Ejercicios: | ||
| - | #Expresa <math>log \, \cfrac{0.016^5 \cdot 20}{\sqrt{128}}</math> en función de log 2. | ||
| - | #Expresa <math>log \, \cfrac{12 \sqrt[3]{36}}{\sqrt{0.09^3 \cdot 160}}</math> en función de log 2 y log 3. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_fonemato | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 10 | ||
| - | |duracion=6´18" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NE8MA8mSQkU&index=8&list=PL2287F157D20941E5 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Resuelve: | ||
| - | #Si un número se multiplica por 49, su logaritmo (en base desconocida) aumenta en 2 unidades. Halla la base. | ||
| - | #Resuelve la ecuación <math>log_x \, 12 + log_x \, 3 = 2</math> | ||
| - | #Determina el menor entero que satisface la condición <math>2.43^x > 13 \;</math> | ||
| - | #Determina el mayor real que satisface la condición <math>2.51^x \le 7 \;</math> | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=El antilogaritmo | ||
| - | |duracion=9´31" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0UBdJ4MmrSc&t=170s | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Definición del antilogaritmo de un número. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Nota: El antilogaritmo es como la inversa del logaritmo, es decir, la exponencial. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=El cologaritmo | ||
| - | |duracion=10´50" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1INfXiu7tTU | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Definición de cologaritmo de un número. Ejemplos. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Nota: El cologaritmo es igual al opuesto del logaritmo. | ||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Regla de la cadena | ||
| - | |duracion=16´55" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=giwItSOXW6E | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la regla de la cadena, una generalización de la fórmula del cambio de base: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :<math>log_b \, a \cdot log_a \, c \cdot log_c \, d = log_b \, d</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_abel | ||
| - | |titulo1=Regla del intercambio | ||
| - | |duracion=11´25" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OHuFiaKNvo4 | ||
| - | |sinopsis=Demostración de la regla del intercambio: | ||
| - | |||
| - | :<math>a^{log_b \, c} = c^{log_b \, a}</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | ---- | ||
| - | {{Video_enlace_matemovil | ||
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1 | ||
| - | |duracion=15´24" | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xaXbIb_x_BM&list=PL3KGq8pH1bFRmhsCe2sPnUj199NNvQWQZ&index=66 | ||
| - | |sinopsis= | ||
| - | a) Calcula: <math>antilog_2 \, (log_2 \, 8)\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | b) Halla "x": <math>antilog_{x/2} \, 4=x\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | c) Halla "x": <math>colog_3 \, (antilog_3 \, (log_3 \, 9))\;</math>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
Revisión de 16:30 26 sep 2018
Tabla de contenidos |
Logaritmos
Sea 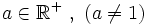 . Se define el logaritmo en base a de un número real
. Se define el logaritmo en base a de un número real 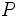 , y se designa por
, y se designa por 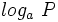 , al exponente
, al exponente 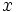 al que hay que elevar la base
al que hay que elevar la base 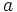 para obtener
para obtener 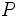 , es decir:
, es decir:
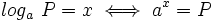
Por consiguiente, podemos ver al logaritmo como la operación inversa de la potenciación.
Logaritmos en su forma exponencial:
Expresa en su forma exponencial equivalente la siguiente expresión logarítmica: 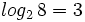
Expresa en su forma exponencial equivalente la siguiente expresión logarítmica: 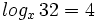
Expresa en su forma exponencial equivalente la siguiente expresión logarítmica: 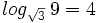
Expresa en su forma exponencial equivalente la siguiente expresión logarítmica: 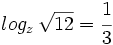
Exponenciales en forma logarítmica:
Expresa en su forma logarítmica equivalente la siguiente expresión exponencial: 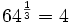
Expresa en su forma logarítmica equivalente la siguiente expresión exponencial: 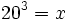
Expresa en su forma logarítmica equivalente la siguiente expresión exponencial: 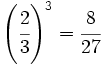
Expresa en su forma logarítmica equivalente la siguiente expresión exponencial: 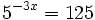
Expresa en su forma logarítmica equivalente la siguiente expresión exponencial: 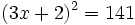
Ejercicios resueltos: Logaritmos
Hallar los siguientes logaritmos reconociendo la potencia correspondiente:
Tutorial que explica la definición de logaritmo y realiza el cálculo de algunos logaritmos exactos (resultado racional) para comprender el significado de esta operación matemática.
- 00:00 a 06:40: Introducción a logaritmo.
- 06:40 a 09:18: Definición de Logaritmo. Explicación.
- 09:18 a 15:52: Ejercicios con Logaritmos (I).
- 14:40 : Logaritmo no exacto.
- 15:52 a 21:03: Ejercicios de Logaritmos (II).
Concepto de logaritmo de un número.
Definición del logaritmo de un número. Ejemplos
Calcula: 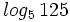
Calcula:
a) 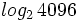 b)
b) 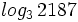 c)
c) 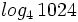 d)
d) 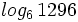
Calcula: 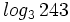
Calcula: 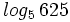
Calcula: 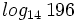
Calcula: 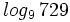
Calcula:
a) 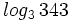 b)
b) ![log_9 \, \sqrt[3]{81}](/wikipedia/images/math/e/3/b/e3bf817a80c0d78b655afb1a5e6e46dd.png) c)
c) 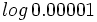 d)
d) 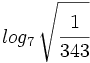 e)
e) 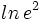
Calcula:
a) 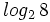 , b)
, b) 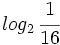 , c)
, c) 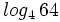 , d)
, d) 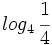
e) 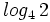 , f)
, f) 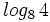 , g)
, g) 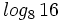 , h)
, h) 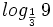
i) 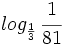 , j)
, j)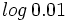 , k)
, k) 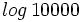 , l)
, l) 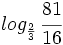
Resuelve:
Propiedades de los logaritmos
Propiedades de los logaritmos:
1: Igualdad y orden:
- a)
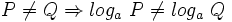 o equivalentemente,
o equivalentemente,
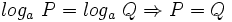
- b)
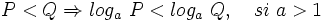
- c)
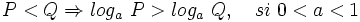
2: Logaritmo de la base:
- a)
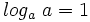
- b)
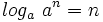
- c)
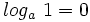
3: Logaritmo de números negativos o nulos:
- Si
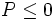 , entonces
, entonces 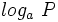 no existe.
no existe.
4: Logaritmo de un producto:
5: Logaritmo de un cociente:
6: Logaritmo de una potencia:
7: Logaritmo de una raíz:
8: Cambio de base:
Tutorial que explica la definición de logaritmo y realiza el cálculo de algunos logaritmos exactos (resultado racional) para comprender el significado de esta operación matemática.
- 00:00 a 03:10: Introducción a logaritmo. Ejercicios de repaso.
- 03:10 a 06:25: Propiedades Básicas.
- 06:25 a 08:30: Propiedad: Logaritmo de un Producto. Demostración.
- 08:30 a 09:20: Propiedad: Logaritmo de una Potencia. Demostración.
- 09:20 a 10:30: Propiedad: Logaritmo de un Cociente. Demostración.
- 10:30 a 13:45: Propiedad: Cambio de Base. Demostración.
- 13:45 a 25:59: Ejercicios de Logaritmos.
Demostración de las propiedades de los logaritmos.
Definición del logaritmo de un número. Propiedades. Ejemplos
Identidad fundamental del logaritmo. Ejemplos de aplicación.
Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de un producto. Ejemplos de aplicación.
Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de un cociente. Ejemplos de aplicación.
Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de una potencia. Ejemplos de aplicación.
Demostración de la propiedad del logaritmo de una raíz. Ejemplos de aplicación.
Desarrollo de logaritmos usando las propiedades:
Desarrolla: 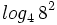
Desarrolla: 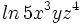
Desarrolla: 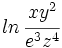
Desarrolla: ![log_e \, \sqrt[4]{e^3x^5} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/7/9/979eadabfb3b278c6e762d27ef7878e4.png)
Desarrolla: ![log_3 \, \cfrac{\sqrt[5]{x}}{\sqrt[3]{y}} \;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/6/1/16143fc979664aee83fe3ce7d48fd920.png)
Desarrolla: 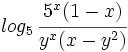
Expresar como un solo logaritmo:
Expresar como un solo logaritmo: 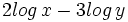
Expresar como un solo logaritmo: 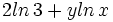
Expresar como un solo logaritmo: 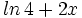
Expresar como un solo logaritmo: 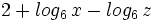
Expresar como un solo logaritmo: 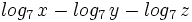
Varios:
Si 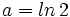 y
y 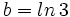 , expresa
, expresa 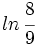 en términos de a y b.
en términos de a y b.
Si 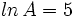 ,
, 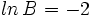 y
y 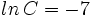 , encuentra el valor numérico de la expresión
, encuentra el valor numérico de la expresión 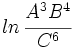 .
.
Escribe como un solo logaritmo: 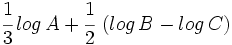 .
.
a) Hallar "m" sabiendo que 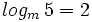 .
.
b) Hallar "x" sabiendo que 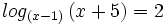 .
.
b) Sabiendo que 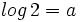 y que
y que 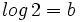 , calcula
, calcula 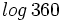 .
.
a) Hallar "x" sabiendo que 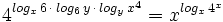 .
.
b) Sabiendo que 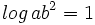 y que
y que 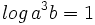 , halla
, halla 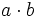 .
.
a) Reduce: 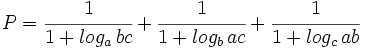 .
.
b) Hallar "x" si 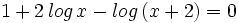 .
.
Desarrolla los siguientes logaritmos:
Reduzca las siguientes expresiones a un solo logaritmo:
Ejercicios:
- Expresa
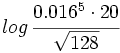 en función de log 2.
en función de log 2.
- Expresa
![log \, \cfrac{12 \sqrt[3]{36}}{\sqrt{0.09^3 \cdot 160}}](/wikipedia/images/math/a/0/3/a03392a26b8add15e65806e0e4e45f6c.png) en función de log 2 y log 3.
en función de log 2 y log 3.
Resuelve:
- Si un número se multiplica por 49, su logaritmo (en base desconocida) aumenta en 2 unidades. Halla la base.
- Resuelve la ecuación
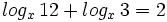
- Determina el menor entero que satisface la condición
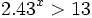
- Determina el mayor real que satisface la condición
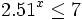
Definición del antilogaritmo de un número. Ejemplos.
Nota: El antilogaritmo es como la inversa del logaritmo, es decir, la exponencial.
Definición de cologaritmo de un número. Ejemplos.
Nota: El cologaritmo es igual al opuesto del logaritmo.
Demostración de la regla de la cadena, una generalización de la fórmula del cambio de base:
Demostración de la regla del intercambio:
a) Calcula: 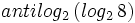 .
.
b) Halla "x": 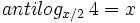 .
.
c) Halla "x": 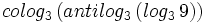 .
.
Logaritmos decimales
Los logaritmos decimales son aquellos de base 10. En vez de representarlos por 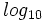 , los representaremos, simplemente, por
, los representaremos, simplemente, por 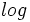 . Esto es:
. Esto es:
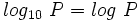
Calculadora
|
Calculadora: Logaritmo decimal |
Antes de la existencia de las calculadoras, los logaritmos decimales se obtenían a partir de las llamadas tablas logarítmicas.
Haciendo uso de la propiedad del cambio de base, vista en un apartado anterior, podemos calcular logaritmos en cualquier base utilizando logaritmos decimales. He aquí un ejemplo:
Ejemplo: Cambio de base
Usa la calculadora para hallar 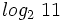 .
.
Como la calculadora científica no tiene logaritmos en base 2, mediante la fórmula del cambio de base haremos un cambio de base 2 a base 10:
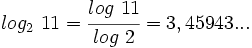
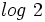 y
y 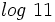 se pueden obtener directamente con la calculadora.
se pueden obtener directamente con la calculadora.Demostración de la fórmula del cambio de base y ejemplos usando la calculadora.
Sin usar la calculadora:
Sin usar la calculadora, calcula: 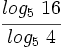
Sin usar la calculadora, calcula: 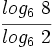
Sin usar la calculadora, calcula: 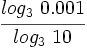
Sin usar la calculadora y teniendo en cuenta que 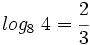 ,
,
calcula: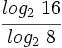
Usando la calculadora:
Calcula: 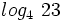
Calcula: 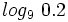
Calcula: 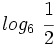
Calcula: 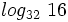
Logaritmos neperianos
Calculadora
|
Ejercicios resueltos: Propiedades de los logaritmos
Averiguar la relación que hay entre x e y, sabiendo que se verifica: 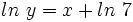
Partiendo de la relación dada:
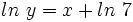
Como por la definición de logaritmo, 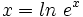 , entonces:
, entonces:
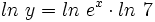
Por la propiedad 4 de los logaritmos:
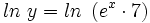
Por la propiedad 1a de los logaritmos:
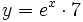
Por tanto, la relación pedida es:
|
|
Ejercicios
Ejercicios resueltos sobre logaritmos.
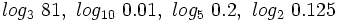
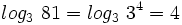
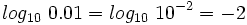
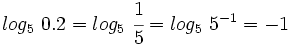
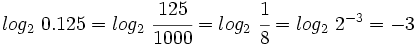
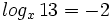
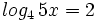
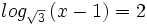
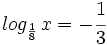
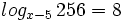
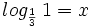
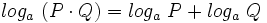
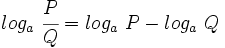
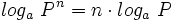
![log_a \ \sqrt[n]{P}=\cfrac{1}{n} \cdot log_a \ P](/wikipedia/images/math/6/c/9/6c919bb3863e8ae2142390b915b8c519.png)
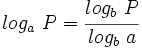
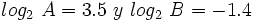 , calcula:
, calcula:
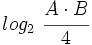
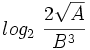
![log_2 \ \cfrac{A \cdot B}{4} \begin{matrix}~_{[5]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} log_2 \ (A \cdot B) - log_2 \ 4=](/wikipedia/images/math/2/6/d/26d0034bc52ab7b3a2b2d941c430aca1.png)
![\begin{matrix}~_{[4]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} log_2 \ A + log_2 \ B - log_2 \ 4=3.5-1.4-2=0.1](/wikipedia/images/math/9/7/0/970be2109f6e4e59d97c656098cb0849.png)
![log_2 \ \cfrac{2 \sqrt{A}} {B^3} \begin{matrix}~_{[5]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} log_2 \ 2 \sqrt{A} - log_2 \ B^3 =](/wikipedia/images/math/0/6/d/06da2c510b8a5216f092a5e9fc5c8b52.png)
![\begin{matrix}~_{[4]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} log_2 \ 2+ log_2 \sqrt{A} - log_2 \ B^3=1+ log_2 \ A^{\frac{1}{2}} - log_2 B^3=](/wikipedia/images/math/0/f/9/0f9259f963826fa4b14149c91a6d5f6b.png)
![\begin{matrix}~_{[6]}~ \\ ~=~ \\ ~ \end{matrix} 1+ \cfrac{1}{2} ~log_2 \ A - 3 \, log_2 \ B=1+ \cfrac{1}{2} \cdot 3.5 - 3 \cdot (-1.4) = 6.95](/wikipedia/images/math/a/8/4/a84d83f66b2b9058af143a2ae4231ef0.png)
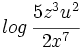
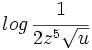
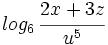
![ln \, \sqrt[3]{\cfrac{x}{z^2u^7}}](/wikipedia/images/math/c/8/5/c851424eddb3c75b5feb58d378224ae7.png)
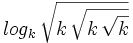
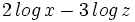
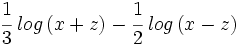
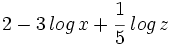
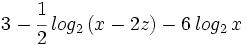
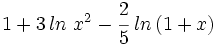
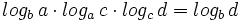
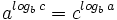
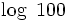
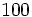
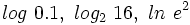 .
.
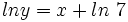 .
.
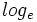 , los representaremos, simplemente, por
, los representaremos, simplemente, por 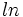 . Esto es:
. Esto es: