Razones trigonométricas de un ángulo agudo (1ºBach)
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 15:05 15 sep 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Funciones trigonométricas (recíprocas)) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 15:22 15 sep 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Razones trigonométricas de algunos ángulos importantes) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 157: | Línea 157: | ||
| ! cot | ! cot | ||
| |----- | |----- | ||
| - | | align="center" | <math> 0 \; </math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>0^o \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>0^o \,</math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>0 \;</math> | | align="center" | <math>0 \;</math> | ||
| Línea 166: | Línea 165: | ||
| | align="center" | <math>\not{\exists} \,\!</math> | | align="center" | <math>\not{\exists} \,\!</math> | ||
| |----- | |----- | ||
| - | | align="center" | <math> \frac{\pi}{6} </math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>30^o \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>30^o \,</math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>\frac{1}{2}</math> | | align="center" | <math>\frac{1}{2}</math> | ||
| Línea 175: | Línea 173: | ||
| | align="center" | <math>\sqrt{3}</math> | | align="center" | <math>\sqrt{3}</math> | ||
| |----- | |----- | ||
| - | | align="center" | <math> \frac{\pi}{4} </math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>45^o \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>45^o \,</math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math> | | align="center" | <math>\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math> | ||
| Línea 184: | Línea 181: | ||
| | align="center" | <math>1 \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>1 \,</math> | ||
| |----- | |----- | ||
| - | | align="center" | <math> \frac{\pi}{3} </math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>60^o \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>60^o \,</math> | ||
| | <math>\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}</math> | | <math>\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}</math> | ||
| Línea 193: | Línea 189: | ||
| | align="center" | <math>\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}</math> | | align="center" | <math>\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}</math> | ||
| |----- | |----- | ||
| - | | align="center" | <math> \frac{\pi}{2}</math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>90^o \,</math> | | align="center" | <math>90^o \,</math> | ||
| | align="center" | <math>1 \;</math> | | align="center" | <math>1 \;</math> | ||
Revisión de 15:22 15 sep 2016
| Enlaces internos | Para repasar o ampliar | Enlaces externos |
| Indice Descartes Manual Casio | WIRIS Geogebra Calculadoras |
Tabla de contenidos |
(Pág. 106)
Razones trigonométricas de un ángulo agudo
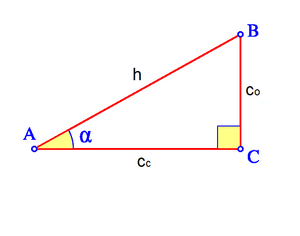
Dado un triángulo rectángulo ABC, se definen las razones trigonométricas del ángulo agudo 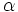 , de la siguiente manera:
, de la siguiente manera:
|
Razones trigonométricas inversas
Las razones trigonométricas inversas se definen de la siguiente manera:
- La cosecante (abreviado como csc o cosec), razón inversa del seno:
- La secante (abreviado como sec), razón inversa del coseno:
- La cotangente (abreviado como cot), razón inversa de la tangente:
- Razones trigonométricas de un ángulo agudo.
- Razones trigonométricas inversas.
- Ejemplos.
- Definición razonada de las razones trigonométricas de un ángulo agudo.
Videotutorial
Videotutorial
Videotutorial
- Si pulsas el botón "EJERCICIO" cambiarán los datos del triángulo.
- Si pulsas el botón "ángulo" cambiará el ángulo al que se le calculan las razones trigonométricas.
- Si pulsas el botón "OTRAS RAZONES" alternararás entre las razones trigonométricas y sus recíprocas.
- Si pulsas el botón "AUTOEVALUACIÓN" podrás realizar una tanda de ejercicios para comprobar lo que sabes.
Relaciones fundamentales de la trigonometría
Relaciones fundamentales de la trigonometría
1. 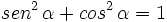
2. 
3. 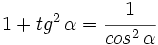
1. 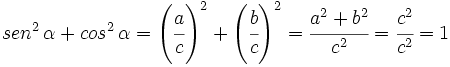
ya que, por el teorema de Pitágoras, 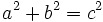 .
.
2. 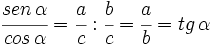
3. 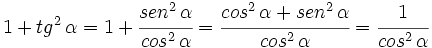
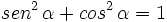
Videotutorial
Videotutorial
Razones trigonométricas de algunos ángulos importantes
A continuación las razones trigonométricas de algunos ángulos que es conveniente recordar:
| Radianes | Grados | sen | cos | tg | cosec | sec | cot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
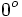
| 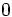
| 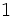
| 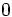
| 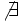
| 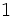
| 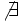
| |
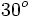
| 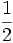
| 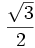
| 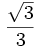
| 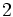
| 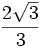
| 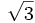
| |
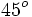
| 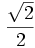
| 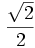
| 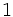
| 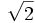
| 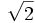
| 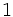
| |
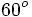
| 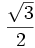
| 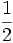
| 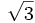
| 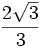
| 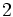
| 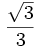
| |
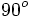
| 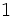
| 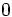
| 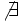
| 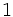
| 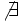
| 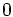
|
Videotutorial
Videotutorial
Calculadora
Funciones trigonométricas (directas)
Seno
|
Calculadora: Seno |
Coseno
|
Calculadora: Coseno |
Tangente
|
Calculadora: Tangente |
Funciones trigonométricas (recíprocas)
Aco seno
|
Calculadora: Arco seno Ejemplo:
Nota: La calculadora sólo da un valor del ángulo (el que se encuentra entre -90º y 90º). Hay otra solución en el segundo o tercer cuadrante que se obtiene restando a 180º la solución obtenida. En este ejemplo, la otra solución sería 180º-30º=150º. |
Arco coseno
|
Calculadora: Arco coseno Ejemplo:
Nota: La calculadora sólo da un valor del ángulo (el que se encuentra entre 0º y 180º). Hay otra solución en el tercer o cuarto cuadrante que se obtiene restando a 360º la solución obtenida. En este ejemplo, la otra solución sería 360º-60º=300º. |
Arco tangente
|
Calculadora: Arco tangente Ejemplo:
Nota: La calculadora sólo da un valor del ángulo (el que se encuentra entre -90º y 90º). Hay otra solución en el segundo o tercer cuadrante que se obtiene sumando 180º a la solución obtenida. En este ejemplo, la otra solución sería 180º+45º=225º. |
|
Actividad: Razones trigonométricas
Solución: Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones:
|
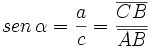
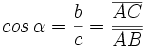
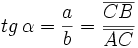
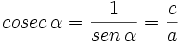
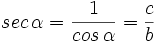
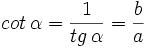
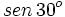
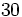
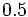
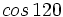
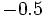
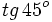
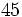
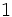
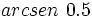
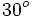 . Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).
. Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).
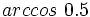
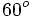 . Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).
. Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).
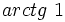
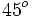 . Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).
. Si la calculadora está en modo DEG (grados sexagesimales).

