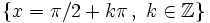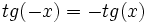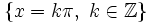Funciones trigonométricas o circulares (1ºBach)
De Wikipedia
(Diferencia entre revisiones)
| Revisión de 09:50 1 oct 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Función tangente) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 09:51 1 oct 2016 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 13: | Línea 13: | ||
| {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Se define la función '''seno''' como | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Se define la función '''seno''' como | ||
| - | <center><math>f(x)=sen(x) \, , \quad x \in \mathbb{R}</math></center> | + | <center><math>f(x)=sen(x) \, , \ x \in \mathbb{R}</math></center> |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 22: | Línea 22: | ||
| *'''Continuidad:''' Es continua en su dominio, <math>\mathbb{R}</math>. | *'''Continuidad:''' Es continua en su dominio, <math>\mathbb{R}</math>. | ||
| *'''Simetrías:''' Es impar, pués <math>sen(-x)=-sen(x)\,</math> | *'''Simetrías:''' Es impar, pués <math>sen(-x)=-sen(x)\,</math> | ||
| - | *'''Cortes con eje X:''' <math>\left \{ x=0+ \pi k \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Cortes con eje X:''' <math>\left \{ x=0+ \pi k \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| - | *'''Máximos:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi / 2+2 \pi k \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Máximos:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi / 2+2 \pi k \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| - | *'''Mínimos:''' <math>\left \{ x=3 \pi /2 +2 \pi k \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Mínimos:''' <math>\left \{ x=3 \pi /2 +2 \pi k \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| *'''Crecimiento:''' | *'''Crecimiento:''' | ||
| - | **Crece en <math>\big( 3 \pi / 2+2 \pi (k-1) , \, \pi /2 +2 \pi k \big), \quad k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. | + | **Crece en <math>\big( 3 \pi / 2+2 \pi (k-1) , \, \pi /2 +2 \pi k \big), \ k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. |
| - | **Decrece en <math>\big( \pi / 2+2 \pi k , \, 3 \pi /2 +2 \pi k \big), \quad k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. | + | **Decrece en <math>\big( \pi / 2+2 \pi k , \, 3 \pi /2 +2 \pi k \big), \ k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. |
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Línea 36: | Línea 36: | ||
| {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Se define la función '''coseno''' como | {{Caja_Amarilla|texto=Se define la función '''coseno''' como | ||
| - | <center><math>f(x)=cos(x) \, , \quad x \in \mathbb{R}</math></center> | + | <center><math>f(x)=cos(x) \, , \ x \in \mathbb{R}</math></center> |
| }} | }} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| Línea 45: | Línea 45: | ||
| *'''Continuidad:''' Es continua en su dominio, <math>\mathbb{R}</math>. | *'''Continuidad:''' Es continua en su dominio, <math>\mathbb{R}</math>. | ||
| *'''Simetrías:''' Es par, pués <math>cos(-x)=cos(x)\,</math> | *'''Simetrías:''' Es par, pués <math>cos(-x)=cos(x)\,</math> | ||
| - | *'''Cortes con eje X:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi /2 + \pi k \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Cortes con eje X:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi /2 + \pi k \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| - | *'''Máximos:''' <math>\left \{ x=2 \pi k \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Máximos:''' <math>\left \{ x=2 \pi k \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| - | *'''Mínimos:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi (2k+1) \, , \quad k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> | + | *'''Mínimos:''' <math>\left \{ x=\pi (2k+1) \, , \ k \in \mathbb{Z} \right \}</math> |
| *'''Crecimiento:''' | *'''Crecimiento:''' | ||
| - | **Crece en <math>\big( \pi (2k-1) , \, 2 \pi k \big), \quad k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. | + | **Crece en <math>\big( \pi (2k-1) , \, 2 \pi k \big), \ k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. |
| - | **Decrece en <math>\big( 2 \pi k , \, \pi (2k+1) \big), \quad k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. | + | **Decrece en <math>\big( 2 \pi k , \, \pi (2k+1) \big), \ k \in \mathbb{Z}</math>. |
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
Revisión de 09:51 1 oct 2016
Menú:
| Enlaces internos | Para repasar o ampliar | Enlaces externos |
| Indice Descartes Manual Casio | WIRIS Geogebra Calculadoras |
Vamos a estudiar las funciones que se obtienen a partir de las razones trigonométricas de un ángulo x al hacer variar éste. Dicho ángulo se suele expresar en radianes.
Función seno
Se define la función seno como 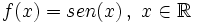 |
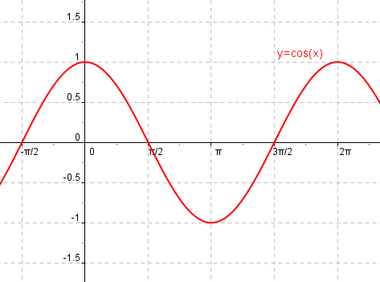
Función coseno
Se define la función coseno como 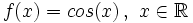 |
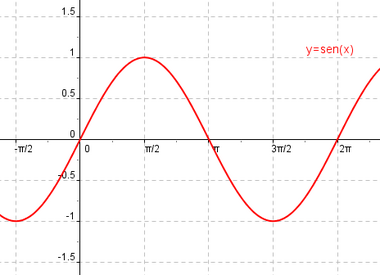
Estudio gráfico de las funciones seno y coseno.
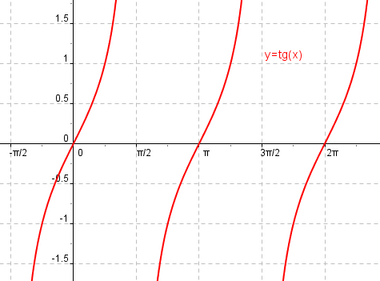
Función tangente
Se define la función coseno como 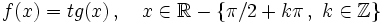 Propiedades de la función tangente
|
|
Actividad: Funciones trigonométricas
Solución: Para averiguar las soluciones debes escribir donde pone "Escribe tu consulta" las siguientes expresiones:
|
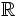
![[-1, 1]\,](/wikipedia/images/math/5/8/1/581a26dec23e9f937a02a278e20fc9c3.png)
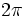 .
.
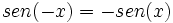
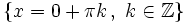
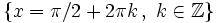

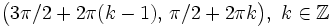 .
.
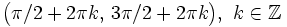 .
.
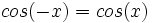
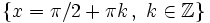
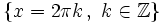
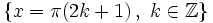
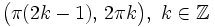 .
.
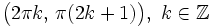 .
.
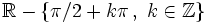
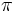 .
.