Plantilla:Raíces: definición y propiedades
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 17:26 16 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 17:28 16 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 5: | Línea 5: | ||
| {{Propiedades de las raíces n-esimas}} | {{Propiedades de las raíces n-esimas}} | ||
| {{p}} | {{p}} | ||
| - | {{Videotutoriales|titulo=Raíz n-ésmina de un número|enunciado= | + | {{Videos: raíz n-esima}} |
| - | {{Video_enlace_clasematicas | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 1 | + | |
| - | |duracion=9´53" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Tutorial que explica la definición de raíz (radical) realizando el cálculo de alguna raíces exactas de números racionales (enteros y decimales). | + | |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OGeUwOWowGQ&index=1&list=PLZNmE9BEzVImIKACrwlnJVOz_w7oxAoRy | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_tutomate | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 2a | + | |
| - | |duracion=6´38" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Raíz n-ésmina de un número. Ejemplos sencillos. | + | |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=01c_83EBAKc&index=5&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTf_vLErckNhkqH29aE696DA | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_tutomate | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 2b | + | |
| - | |duracion=6´38" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis=Raíz n-ésmina de un número. Ejemplos más complejos. | + | |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_b8Vha5epFU&index=6&list=PLWRbPOo5oaTf_vLErckNhkqH29aE696DA | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Tutorial 3 | + | |
| - | |duracion=32´48" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis= | + | |
| - | *Raíces de un número entero. | + | |
| - | *Raíces cuadradas y cúbicas. | + | |
| - | *Partes de una raíz. | + | |
| - | *Raíces de números positivo, negativos y del cero. | + | |
| - | *Raíz exacta y raíz entera. | + | |
| - | *Calculo manual de raíces cuadradas. | + | |
| - | *Los radicales. | + | |
| - | *Extracción de factores de un radical. | + | |
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nkEQ382ueoI&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3owuqG2cbSRKduUPNpu4q7i9&index=1 | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | ---- | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1a | + | |
| - | |duracion=30´30" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis= | + | |
| - | 1) Completa: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :1a) <math>Como \ \ 6^2=36 \ \ y \ \ (-6)^2 =36 \rightarrow \sqrt{36}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :1b) <math>Como \ \ 7^2=49 \ \ y \ \ (-7)^2 =49 \rightarrow \sqrt{49}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :1c) <math>Como \ \ 9^2=81 \ \ y \ \ (-9)^2 =81 \rightarrow \sqrt{81}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :1d) <math>Como \ \ 3^2=9 \ \ y \ \ (-3)^2 =9 \rightarrow \sqrt{9}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 2) Completa: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :2a) <math>Como \ \ 6^3=216 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{216}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :2b) <math>Como \ \ (-6)^3=-216 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-216}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :2c) <math>Como \ \ 5^3=125 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{125}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :2d) <math>Como \ \ (-5)^3=-125 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-125}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :2e) <math>Como \ \ 7^3=343 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{343}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :2f) <math>Como \ \ (-7)^3=-343 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-343}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 3) Completa: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :3a) <math>Como \ \ 6^4=216 \ \ y \ \ (-6)^4 =216 \rightarrow \sqrt[4]{216}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3b) <math>Como \ \ 2^5=32 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^5 =32 \rightarrow \sqrt[5]{32}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[5]{-32}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3c) <math>Como \ \ 3^6=729 \ \ y \ \ (-3)^6 =729 \rightarrow \sqrt[6]{729}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3d) <math>Como \ \ 2^7=128 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^7 =-128 \rightarrow \sqrt[7]{128}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[7]{-128}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3e) <math>Como \ \ 3^8=6561 \ \ y \ \ (-3)^8 =6561 \rightarrow \sqrt[8]{6561}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3f) <math>Como \ \ 2^9=512 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^9 =-512 \rightarrow \sqrt[9]{512}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[9]{-512}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | :3g) <math>Como \ \ 2^{10}=1024 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^{10} =1024 \rightarrow \sqrt[10]{1024}= ...</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 4) Contesta: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :4a) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé -25? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt{-25}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4b) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé -36? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt{-36}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4c) ¿hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé un número negativo? | + | |
| - | :4d) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé -27? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt[3]{-27}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4e) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé -64? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt[3]{-64}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4f) ¿hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé un número negativo? | + | |
| - | :4g) ¿Hay algún número que elevado a la cuarta dé -81? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt[4]{-81}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4h) ¿Hay algún número que elevado a la quinta dé -243? ¿Existe <math>\sqrt[5]{-243}\;</math>? | + | |
| - | :4i) ¿De qué depende que exista una raíz de radicando negativo? | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 5) Calcula: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :5a) <math>\sqrt{1}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-1}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5b) <math>\sqrt{4}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-4}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5c) <math>\sqrt{9}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-9}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5d) <math>\sqrt{16}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-16}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5e) <math>\sqrt{25}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-25}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5f) <math>\sqrt{36}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-36}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5g) <math>\sqrt{49}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-49}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5h) <math>\sqrt{64}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-64}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5i) <math>\sqrt{81}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-81}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :5j) <math>\sqrt{100}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt{-10}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 6) Calcula: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :6a) <math>\sqrt[3]{1}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[3]{-1}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :6b) <math>\sqrt[3]{8}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[3]{-8}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :6c) <math>\sqrt[3]{27}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[3]{-27}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :6d) <math>\sqrt[3]{64}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[3]{-64}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :6e) <math>\sqrt[3]{125}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[3]{-125}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 6) Calcula: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :7a) <math>\sqrt[4]{1}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[4]{-1}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :7b) <math>\sqrt[5]{32}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[5]{-32}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :7c) <math>\sqrt[6]{729}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[6]{-729}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :7d) <math>\sqrt[7]{128}\;</math> ; {{b4}}<math>\sqrt[7]{-128}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mi_mLFTP0Jo&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3owuqG2cbSRKduUPNpu4q7i9&index=2 | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1b | + | |
| - | |duracion=28´06" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis= | + | |
| - | 8) Indica, en cada caso, la raíz, el índice y el radicando: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :8a) <math>\sqrt{25}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :8b) <math>\sqrt[3]{-64}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :8c) <math>\sqrt[4]{81}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 9) Completa: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :9a) <math>\sqrt{4}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9b) <math>\sqrt{9}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9c) <math>\sqrt[3]{-8}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9d) <math>\sqrt[3]{8}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9e) <math>\sqrt[4]{16}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9f) <math>\sqrt[5]{32}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9g) <math>\sqrt[5]{-32}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | :9f) <math>\sqrt[6]{1}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 10) Calcula las raíces enteras por exceso y por defecto: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :10a) <math>\sqrt{14}\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>\sqrt[3]{14}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :10b) <math>\sqrt{20}\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>\sqrt[3]{20}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :10c) <math>\sqrt{39}\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>\sqrt[3]{39}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 11) Calcula a mano las siguientes raíces: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :11a) <math>\sqrt{4069}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :11b) <math>\sqrt{8315}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s2ClRckLlGc&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3owuqG2cbSRKduUPNpu4q7i9&index=3 | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | {{Video_enlace_escuela | + | |
| - | |titulo1=Ejercicio 1c | + | |
| - | |duracion=31´57" | + | |
| - | |sinopsis= | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | 11) Calcula a mano las siguientes raíces: | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :11c) <math>\sqrt{49625}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :11d) <math>\sqrt{987654}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :11e) <math>\sqrt{448056}\;</math> | + | |
| - | :11f) <math>\sqrt{865432}\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |url1=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6DjUvSGLVOs&index=4&list=PLw7Z_p6_h3owuqG2cbSRKduUPNpu4q7i9 | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
| - | }} | + | |
Revisión de 17:28 16 nov 2017
Raíz n-ésima de un número
La raíz n-ésima 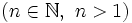 de un número
de un número 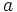 es otro número
es otro número 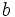 tal que
tal que 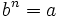 y que escribimos simbólicamente
y que escribimos simbólicamente ![b=\sqrt[n]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/c/e/0/ce05f9d287d25fe0a5fd8e680bd177f5.png) .
.
![\sqrt[n]{a}=b \iff b^n =a](/wikipedia/images/math/f/f/7/ff79017c635440f207b67b250c3660fb.png)
El número 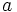 se llama radicando, el número
se llama radicando, el número 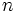 índice y
índice y 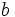 la raíz.
la raíz.
Si el índice es 2 las llamaremos raíces cuadradas; si el índice es 3, raíces cúbicas; si es 5, 6, ..., raíces cuartas, quintas, ....
Propiedades de las raíces
Propiedades
![\sqrt[n]{1}=1](/wikipedia/images/math/f/2/3/f2301fcbef74b110ad8d373f2b32a16b.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[n]{0}=0](/wikipedia/images/math/8/6/5/865db751c6cb2e12533fccdf8de1e1df.png) , para cualquier valor del índice
, para cualquier valor del índice 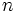 .
.
- Si
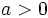 ,
, ![\sqrt[n]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/9/a/2/9a2b6d33f3d62a1e8bd99c76f3cb79f5.png) existe cualquiera que sea el índice
existe cualquiera que sea el índice 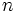 .
.
- Si
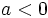 ,
, ![\sqrt[n]{a}](/wikipedia/images/math/9/a/2/9a2b6d33f3d62a1e8bd99c76f3cb79f5.png) sólo existe si el índice
sólo existe si el índice 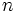 es impar.
es impar.
- Si el índice
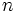 es par y el radicando
es par y el radicando 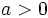 , la raíz tiene dos soluciones: una positiva y otra negativa, pero iguales en valor absoluto.
, la raíz tiene dos soluciones: una positiva y otra negativa, pero iguales en valor absoluto.
- Si el índice
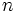 es impar, siempre tiene una única solución, que tiene el mismo signo que el radicando
es impar, siempre tiene una única solución, que tiene el mismo signo que el radicando 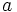 .
.
Tutorial que explica la definición de raíz (radical) realizando el cálculo de alguna raíces exactas de números racionales (enteros y decimales).
Raíz n-ésmina de un número. Ejemplos sencillos.
Raíz n-ésmina de un número. Ejemplos más complejos.
Raíz n-ésmina de un número. Ejemplos sencillos.
- Raíces de un número entero.
- Raíces cuadradas y cúbicas.
- Partes de una raíz.
- Raíces de números positivo, negativos y del cero.
- Raíz exacta y raíz entera.
- Calculo manual de raíces cuadradas.
- Los radicales.
- Extracción de factores de un radical.
1) Completa:
- 1a)
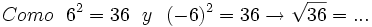
- 1b)
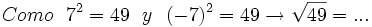
- 1c)
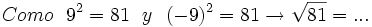
- 1d)
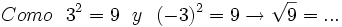
2) Completa:
- 2a)
![Como \ \ 6^3=216 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{216}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/3/c/3/3c378630d2615778e963ac624db86d87.png)
- 2b)
![Como \ \ (-6)^3=-216 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-216}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/6/5/8/6587736293705d54e8f32954028d084c.png)
- 2c)
![Como \ \ 5^3=125 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{125}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/b/d/b/bdb68c764c3249b6a9780aa720742319.png)
- 2d)
![Como \ \ (-5)^3=-125 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-125}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/e/7/0/e705216d0789f62aef7ec241081fabeb.png)
- 2e)
![Como \ \ 7^3=343 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{343}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/5/f/2/5f298eabe3ed377592f625e71f6488c0.png)
- 2f)
![Como \ \ (-7)^3=-343 \rightarrow \sqrt[3]{-343}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/c/e/5/ce577674faca3babb2d3dfaac0413e21.png)
3) Completa:
- 3a)
![Como \ \ 6^4=216 \ \ y \ \ (-6)^4 =216 \rightarrow \sqrt[4]{216}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/c/b/4/cb4b33e4c8e211ead755140a2c66bba9.png)
- 3b)
![Como \ \ 2^5=32 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^5 =32 \rightarrow \sqrt[5]{32}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[5]{-32}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/c/c/c/ccc2a79c409e95a6ea8eb4d3dd464bae.png)
- 3c)
![Como \ \ 3^6=729 \ \ y \ \ (-3)^6 =729 \rightarrow \sqrt[6]{729}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/b/5/5/b554d8cc9395627f020eb1f365124e4e.png)
- 3d)
![Como \ \ 2^7=128 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^7 =-128 \rightarrow \sqrt[7]{128}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[7]{-128}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/a/d/6/ad64ef0e208078f3159cae14f80cd300.png)
- 3e)
![Como \ \ 3^8=6561 \ \ y \ \ (-3)^8 =6561 \rightarrow \sqrt[8]{6561}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/7/b/a/7ba166f1a52a30e3ea2be20046fc6f29.png)
- 3f)
![Como \ \ 2^9=512 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^9 =-512 \rightarrow \sqrt[9]{512}= ... \ \ y \ \ \sqrt[9]{-512}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/3/a/9/3a962574019bdc46ed38d924b83f207c.png)
- 3g)
![Como \ \ 2^{10}=1024 \ \ y \ \ (-2)^{10} =1024 \rightarrow \sqrt[10]{1024}= ...](/wikipedia/images/math/7/e/d/7edae10fccfe7b465c672d8c9c045b91.png)
4) Contesta:
- 4a) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé -25? ¿Existe
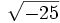 ?
?
- 4b) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé -36? ¿Existe
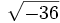 ?
?
- 4c) ¿hay algún número que elevado al cuadrado dé un número negativo?
- 4d) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé -27? ¿Existe
![\sqrt[3]{-27}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/7/f/9/7f964050f55904a351871c909842d531.png) ?
?
- 4e) ¿Hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé -64? ¿Existe
![\sqrt[3]{-64}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/a/c/1ac847b9288b852f7e2cd46adb661650.png) ?
?
- 4f) ¿hay algún número que elevado al cubo dé un número negativo?
- 4g) ¿Hay algún número que elevado a la cuarta dé -81? ¿Existe
![\sqrt[4]{-81}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/3/8/9380cfbe25a5f6b1f53b0e98557d5cb3.png) ?
?
- 4h) ¿Hay algún número que elevado a la quinta dé -243? ¿Existe
![\sqrt[5]{-243}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/0/d/00d129c231e444389e6e90b5a1a8e808.png) ?
?
- 4i) ¿De qué depende que exista una raíz de radicando negativo?
5) Calcula:
- 5a)
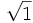 ;
; 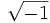
- 5b)
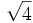 ;
; 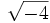
- 5c)
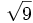 ;
; 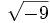
- 5d)
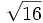 ;
; 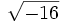
- 5e)
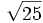 ;
; 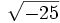
- 5f)
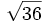 ;
; 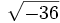
- 5g)
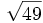 ;
; 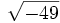
- 5h)
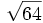 ;
; 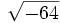
- 5i)
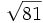 ;
; 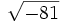
- 5j)
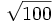 ;
; 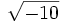
6) Calcula:
- 6a)
![\sqrt[3]{1}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/a/9/e/a9ed184fd0349444d061cc1d272e67c6.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{-1}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/1/7/917ae3af6a2d50278779cc91cbbdea73.png)
- 6b)
![\sqrt[3]{8}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/3/2/132c2f74c8498afa99586eeab29a92a8.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{-8}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/2/2/3/2232a48fe703bd572c3668d1f57c0066.png)
- 6c)
![\sqrt[3]{27}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/f/d/ffdb842d7cefcf30ac4e11b74ccdc8f3.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{-27}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/7/f/9/7f964050f55904a351871c909842d531.png)
- 6d)
![\sqrt[3]{64}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/b/d/4bd0c615f84c6543e9f004c6bcfce737.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{-64}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/a/c/1ac847b9288b852f7e2cd46adb661650.png)
- 6e)
![\sqrt[3]{125}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/9/b/0/9b0b656102d06b662a6c1cfa6f46ee4c.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{-125}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/d/6/bd68acb8f905cf5984575d47adbbe028.png)
6) Calcula:
- 7a)
![\sqrt[4]{1}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/2/3/42348ffb6e4d069c36b7529b4c3d61c7.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[4]{-1}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/3/0/4/3041c7b2e1985e0ce2b4e12419b1adfd.png)
- 7b)
![\sqrt[5]{32}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/5/a/4/5a4316aef4d84ea09023226c0b455ef1.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[5]{-32}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/4/b/e4b2e7ef8b833cd852ca9c1bedfade9b.png)
- 7c)
![\sqrt[6]{729}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/6/4/5/645cad2d63e42973a6e2a66d954d5272.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[6]{-729}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/8/9/c89f55205c50d79be31feca9e8e7fe21.png)
- 7d)
![\sqrt[7]{128}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/4/e/e4e24abf54c49df327ec72213ca1b2bd.png) ;
; ![\sqrt[7]{-128}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/5/7/f/57ff532d80dc61569bbab4448a648df4.png)
8) Indica, en cada caso, la raíz, el índice y el radicando:
- 8a)
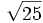
- 8b)
![\sqrt[3]{-64}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/1/a/c/1ac847b9288b852f7e2cd46adb661650.png)
- 8c)
![\sqrt[4]{81}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/0/4/d/04d103e445158aa43cb56526c68b98c2.png)
9) Completa:
- 9a)
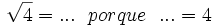
- 9b)
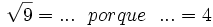
- 9c)
![\sqrt[3]{-8}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/b/b/c/bbc65bbad66511345d7cb3ac4f7a001c.png)
- 9d)
![\sqrt[3]{8}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/3/e/c/3ec4111d51daf4478bc80d3d1bd1ef0a.png)
- 9e)
![\sqrt[4]{16}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/2/0/8/208788fa3a4920a05007fa9edad8dbc6.png)
- 9f)
![\sqrt[5]{32}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/5/5/f552d101987249877deb51a2875a57db.png)
- 9g)
![\sqrt[5]{-32}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/a/b/9/ab988d19836d333dfc399b9f3fefee8c.png)
- 9f)
![\sqrt[6]{1}=... \ \ porque \ \ ... = 4\;](/wikipedia/images/math/7/0/6/70646a208681230895b71a7e18b7317b.png)
10) Calcula las raíces enteras por exceso y por defecto:
- 10a)
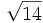 ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{14}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/4/d/9/4d90b08a8a7ba14e1c60f25be0fb24ef.png)
- 10b)
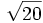 ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{20}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/f/a/a/faaf025a7b9f3b036eb836c60d8e4e34.png)
- 10c)
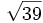 ;
; ![\sqrt[3]{39}\;](/wikipedia/images/math/c/9/f/c9f16a3fa799c3b21b4f313600db621c.png)
11) Calcula a mano las siguientes raíces:
- 11a)
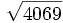
- 11b)

11) Calcula a mano las siguientes raíces:
- 11c)
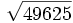
- 11d)
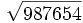
- 11e)
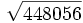
- 11f)
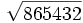
![\sqrt[5]{32}=2\;](/wikipedia/images/math/e/f/a/efae07f29bbbaaef03acb5b46afffb59.png) porque
porque 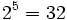 .
.
![\sqrt[3]{1}=1](/wikipedia/images/math/d/5/3/d53d30c7123945d21786c0fb38eeeb18.png) .
.
![\sqrt[5]{0}=0](/wikipedia/images/math/e/9/5/e95b8cee4e9e352608032036b0bd68d7.png) .
.
![\sqrt[4]{16}=\pm 2](/wikipedia/images/math/3/5/c/35cc75069a6350b569ad8c8f72bf6ae2.png) porque
porque 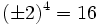 .
.
![\sqrt[3]{64}=4](/wikipedia/images/math/f/2/4/f2482a82a1ce97518a3bbef09d9575b5.png) porque
porque 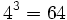 .
.
![\sqrt[3]{-8}=-2](/wikipedia/images/math/1/5/4/154ab22db729e6b6490caa36d8669830.png) porque
porque 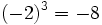 .
.
![\sqrt[4]{-8}= no \ existe](/wikipedia/images/math/a/2/1/a21d3d89fedd78f5c9a6378b3cf240f3.png) porque ningún número elevado a 4 puede dar negativo (-8).
porque ningún número elevado a 4 puede dar negativo (-8).

