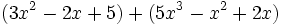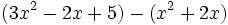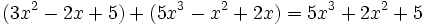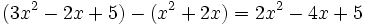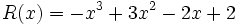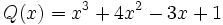Plantilla:Suma y resta de polinomios
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 08:58 5 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión de 09:01 5 nov 2017 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) Ir a siguiente diferencia → |
||
| Línea 118: | Línea 118: | ||
| 1) Ordena los polinomios y realiza las sumas que se indican: | 1) Ordena los polinomios y realiza las sumas que se indican: | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> | + | |
| 1a) P(x) + Q(x) | 1a) P(x) + Q(x) | ||
| Línea 139: | Línea 135: | ||
| |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios, realiza las sumas que se indican: | |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios, realiza las sumas que se indican: | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=5x^2-2x+6x^4\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>R(x)=2x^2-3x^3+2x^4+3x^5\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=-3x^2+4x^3-3x^4-2x^5\;</math> | + | |
| 1d) Q(x) + S(x) | 1d) Q(x) + S(x) | ||
| Línea 166: | Línea 158: | ||
| 3a) Escribe opuestos de los siguientes polinomios: | 3a) Escribe opuestos de los siguientes polinomios: | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> |
| - | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> | + | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | + | |
| 3b) Suma cada uno de los polinomios del apartado anterior con su opuesto. | 3b) Suma cada uno de los polinomios del apartado anterior con su opuesto. | ||
| Línea 189: | Línea 175: | ||
| |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios: | |sinopsis=Dados los siguientes polinomios: | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | + | |
| 3d) Calcula un polinomio B(x) tal que <math>Q(x)-B(x)=3x^3-x+2\;</math>. | 3d) Calcula un polinomio B(x) tal que <math>Q(x)-B(x)=3x^3-x+2\;</math>. | ||
| Línea 210: | Línea 192: | ||
| |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios: | |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios: | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=-2x^4-3x^2+2\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=x^3-4x+1\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> |
| - | :<math>R(x)=2x^4-3x^3-4x^2+3\;</math> | + | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=-x^3+5x+4\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>T(x)=x^2-x+1\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>M(x)=-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | + | |
| 4a) Calcula P(x) - Q(x). | 4a) Calcula P(x) - Q(x). | ||
| Línea 243: | Línea 219: | ||
| 6) Dados los polinomios | 6) Dados los polinomios | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=mx^3-5x+6\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=mx^3-5x+6\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=-4x^3-6x+7\;</math> |
| - | :<math>Q(x)=-4x^3-6x+7\;</math> | + | calcula el valor de <math>m\;</math> sabiendo que <math>P(x)+Q(x)=x^3-11x+13\;</math>. |
| - | + | ||
| - | calcula el valor de ''m'' sabiendo que <math>P(x)+Q(x)=x^3-11x+13\;</math>. | + | |
| 7) Escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de tal modo que su suma se el polinomio nulo. | 7) Escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de tal modo que su suma se el polinomio nulo. | ||
| Línea 271: | Línea 245: | ||
| |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios | |sinopsis=Dados los polinomios | ||
| - | :<math>P(x)=3x^2-1\;</math> | + | :<math>P(x)=3x^2-1\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>Q(x)=2x^3-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>Q(x)=2x^3-2x^2+4x-2\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>R(x)=3x^2+x+3\;</math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>S(x)=\cfrac{1}{2}x^2+2\;</math> | + | |
| - | :<math>T(x)=\cfrac{3}{2}x^2+3\;</math> | + | :<math>R(x)=3x^2+x+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>S(x)=\cfrac{1}{2}x^2+2\;</math> |
| - | :<math>V(x)=3x^2+1\;</math> | + | :<math>T(x)=\cfrac{3}{2}x^2+3\;</math> ; {{b4}} <math>V(x)=3x^2+1\;</math> |
| 12a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x). | 12a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x). | ||
Revisión de 09:01 5 nov 2017
Procedimiento
Para sumar o restar polinomios, sumaremos o restaremos los monomios semejantes de ambos.
Aprende a sumar y restar polinomios
En este tutorial se explica la suma y resta de polinomios comenzando con algunas definiciones básicas y terminando con ejemplos.
Aprende a sumar polinomios
Aprende a restar polinomios
Suma y resta de polinomios en una variable. Ejemplos.
Suma de polinomios. Ejemplos.
Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: conmutativa y asociativa.
Propiedades de la suma de polinomios: Elemento neutro y opuesto.
Resta de polinomios. Equivalencias fundamentales.
Calcula la suma: 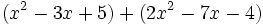
Calcula la suma: 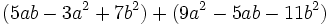
Calcula la resta: 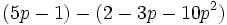
Calcula la resta: 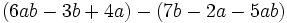
Calcula:
a) 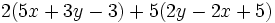 b)
b) 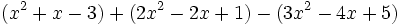
2 ejercicios.
1) Ordena los polinomios y realiza las sumas que se indican:
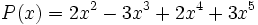 ;
; 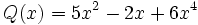
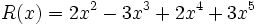 ;
; 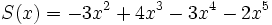
1a) P(x) + Q(x)
1b) P(x) + R(x)
1c) P(x) + S(x)
Dados los siguientes polinomios, realiza las sumas que se indican:
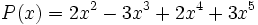 ;
; 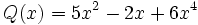
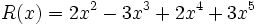 ;
; 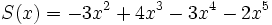
1d) Q(x) + S(x)
1e) R(x) + S(x)
1f) Q(x) + R(x)
2) Sumas los siguientes polinomios y compara el grado del polinomio suma con el grado de los polinomios sumandos.
3a) Escribe opuestos de los siguientes polinomios:
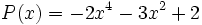 ;
; 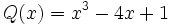
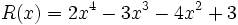 ;
; 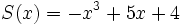
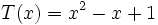 ;
; 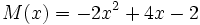
3b) Suma cada uno de los polinomios del apartado anterior con su opuesto.
3c) Calcula un polinomio A(x) tal que 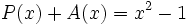 , siendo
, siendo 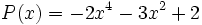 .
.
Dados los siguientes polinomios:
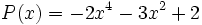 ;
; 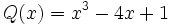
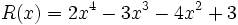 ;
; 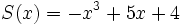
3d) Calcula un polinomio B(x) tal que 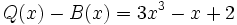 .
.
3e) Calcula un polinomio C(x) tal que 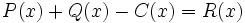 .
.
3f) Calcula un polinomio D(x) tal que 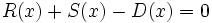 .
.
Dados los polinomios:
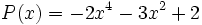 ;
; 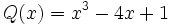
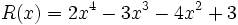 ;
; 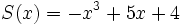
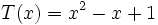 ;
; 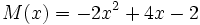
4a) Calcula P(x) - Q(x).
4b) Calcula P(x) - R(x).
4c) Calcula [P(x) + Q(x)]-[R(x) + S(x)]
4d) Calcula [P(x) + S(x)]-[Q(x) + R(x)]
4e) Calcula T(x) + M(x)
4f) Calcula T(x) - M(x)
5) ¿Qué polinomio se ha de restar al polinomio 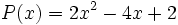 para obtener el polinomio
para obtener el polinomio 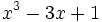 ?
?
6) Dados los polinomios
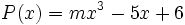 ;
; 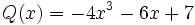
calcula el valor de 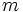 sabiendo que
sabiendo que 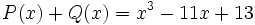 .
.
7) Escribe dos polinomios de tercer grado de tal modo que su suma se el polinomio nulo.
8) Escribe dos polinomios reducidos de segundo grado y comprueba con ellos la conmutatividad de la suma.
9) Dado el polinomio 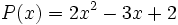 , escribe su opuesto, -P(x). Calcula los valores numéricos de P(x) y -P(x) para x = 0, x = 1 y x = 2, y comprueba comprueba que son números opuestos.
, escribe su opuesto, -P(x). Calcula los valores numéricos de P(x) y -P(x) para x = 0, x = 1 y x = 2, y comprueba comprueba que son números opuestos.
10) ¿Qué polinomio tienes que sumar con 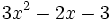 para que la suma sea 5x^3-6x?
para que la suma sea 5x^3-6x?
11) Dado el polinomio 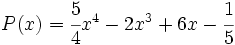 , halla otro polinomio Q(x) tal que
, halla otro polinomio Q(x) tal que 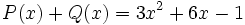 .
.
Dados los polinomios
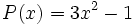 ;
; 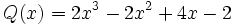
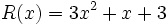 ;
; 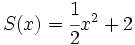
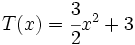 ;
; 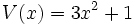
12a) Calcula P(x) + Q(x).
12b) Calcula P(x) - V(x).
12c) Calcula P(x) + R(x).
12d) Calcula P(x) - R(x).
12e) Calcula S(x) + T(x) + V(x).
12f) Calcula S(x) - T(x) + V(x).
Ejercicios 13-16: Contestar preguntas sobre polinomios.
Ejercicios 17-19: Sumar y restar polinomios. Aplicar equivalencias fundamentales.
Actividades para aprender y practicar la suma y resta de polinomios.
Ejercicios para practicar la suma y resta de polinomios.
Ejercicios de autoevaluación sobre suma y resta de polinomios.