Brahmagupta
De Wikipedia
| Revisión de 20:08 24 dic 2008 Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Algebra) ← Ir a diferencia anterior |
Revisión actual Coordinador (Discusión | contribuciones) (→Astronomía) |
||
| Línea 7: | Línea 7: | ||
| Aunque Brahmagupta estaba familiarizado con las obras de los astrónomos siguiendo la tradición de Aryabhatiya, no se sabe si está familiarizado con la labor de Bhaskara I, un contemporáneo. Brahmagupta tenía una cantidad de críticas dirigidas hacia la labor de los astrónomos rivales, y en su ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' se encuentra uno de los primeros cismas de fe entre matemáticos indios. La división fue principalmente sobre la aplicación de las matemáticas al mundo físico, más que sobre las matemáticas en si mismas. En el caso de Brahmagupta, los desacuerdos se debieron en gran parte de la elección de las teorías y parámetros astronómicos. A lo largo de los primeros diez capítulos astronómicos aparecen críticas a las teorías rivales, y el undécimo capítulo está completamente dedicado a la crítica de estas teorías, aunque las críticas no aparecen en el duodécimo y décimo octavo capítulos. | Aunque Brahmagupta estaba familiarizado con las obras de los astrónomos siguiendo la tradición de Aryabhatiya, no se sabe si está familiarizado con la labor de Bhaskara I, un contemporáneo. Brahmagupta tenía una cantidad de críticas dirigidas hacia la labor de los astrónomos rivales, y en su ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' se encuentra uno de los primeros cismas de fe entre matemáticos indios. La división fue principalmente sobre la aplicación de las matemáticas al mundo físico, más que sobre las matemáticas en si mismas. En el caso de Brahmagupta, los desacuerdos se debieron en gran parte de la elección de las teorías y parámetros astronómicos. A lo largo de los primeros diez capítulos astronómicos aparecen críticas a las teorías rivales, y el undécimo capítulo está completamente dedicado a la crítica de estas teorías, aunque las críticas no aparecen en el duodécimo y décimo octavo capítulos. | ||
| - | Lo que sigue está por traducir | + | == Matemáticas == |
| - | + | La obra más famosa de Brahmagupta es su ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta''. Compuesta en verso elíptico, practica común en las matemáticas indueshematics]], la obra tiene, en consecuencia, un cierto halo poético. Como en ella no se dan demostraciones, no se sabe como Brahmagupta obtenía los resultados matemáticos. | |
| - | == Mathematics == | + | |
| - | Brahmagupta's most famous work is his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta''. It is composed in elliptic verse, as was common practice in [[Indian mathematics]], and consequently has a poetic ring to it. As no proofs are given, it is not known how Brahmagupta's mathematics was derived.<ref>[http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/Biographies/Brahmagupta.html Brahmagupta biography<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> | + | |
| ===Algebra === | ===Algebra === | ||
| - | Brahmagupta gave the solution of the general [[linear equation]] in chapter eighteen of ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', | + | Brahmagupta da la solución de la '''ecuación lineal general''' en el capítulo dieciocho de ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', que aunque expresada en el libro en palabras, viene a ser equivalente a la siuiente expresión algebraica: |
| - | + | ||
| - | <blockquote>18.43 The difference between ''rupas'', when inverted and divided by the difference of the unknowns, is the unknown in the equation. The ''rupas'' are [subtracted on the side] below that from which the square and the unknown are to be subtracted.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Which is a solution equivalent to <math>x = \cfrac{e-c}{b-d}</math>, where ''rupas'' represents constants. He further gave two equivalent solutions to the general [[quadratic equation]], | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <blockquote>18.44. Diminish by the middle [number] the square-root of the ''rupas'' multiplied by four times the square and increased by the square of the middle [number]; divide the remainder by twice the square. [The result is] the middle [number].<BR> | + | |
| - | 18.45. Whatever is the square-root of the ''rupas'' multiplied by the square [and] increased by the square of half the unknown, diminish that by half the unknown [and] divide [the remainder] by its square. [The result is] the unknown.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Which are, respectively, solutions equivalent to, | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>x = \frac{\sqrt{4ac+b^2}-b}{2a} </math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | and | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | :<math>x = \frac{\sqrt{ac+\cfrac{b^2}{4}}-\cfrac{b}{2}}{a} </math> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | He went on to solve systems of simultaneous [[indeterminate equations]] stating that the desired variable must first be isolated, and then the equation must be divided by the desired variable's [[coefficient]]. In particular, he recommended using "the pulverizer" to solve equations with multiple unknowns. | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <blockquote>18.51. Subtract the colors different from the first color. [The remainder] divided by the first [color's coefficient] is the measure of the first. [Terms] two by two [are] considered [when reduced to] similar divisors, [and so on] repeatedly. If there are many [colors], the pulverizer [is to be used].<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Like the algebra of [[Diophantus]], the algebra of Brahmagupta was syncopated. Addition was indicated by placing the numbers side by side, subtraction by placing a dot over the subtrahend, and division by placing the divisor below the dividend, similar to our notation but without the bar. Multiplication, evolution, and unknown quantities were represented by abbreviations of appropriate terms.<ref name="Boyer Brahmagupta Indeterminate equations">{{Harv|Boyer|1991|loc="China and India" p. 221}} "he was the first one to give a ''general'' solution of the linear Diophantine equation ax + by = c, where a, b, and c are integers. [...] It is greatly to the credit of Brahmagupta that he gave ''all'' integral solutions of the linear Diophantine equation, whereas Diophantus himself had been satisfied to give one particular solution of an indeterminate equation. Inasmuch as Brahmagupta used some of the same examples as Diophantus, we see again the likelihood of Greek influence in India - or the possibility that they both made use of a common source, possibly from Babylonia. It is interesting to note also that the algebra of Brahmagupta, like that of Diophantus, was syncopated. Addition was indicated by juxtaposition, subtraction by placing a dot over the subtrahend, and division by placing the divisor below the dividend, as in our fractional notation but without the bar. The operations of multiplication and evolution (the taking of roots), as well as unknown quantities, were represented by abbreviations of appropriate words."</ref> The extent of Greek influence on this [[History of algebra|syncopation]], if any, is not known and it is possible that both Greek and Indian syncopation may be derived from a common Babylonian source.<ref name="Boyer Brahmagupta Indeterminate equations"/> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | === Arithmetic === | + | |
| - | In the beginning of chapter twelve of his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', entitled ''Calculation'', Brahmagupta details operations on fractions. The reader is expected to know the basic arithmetic operations as far as taking the square root, although he explains how to find the cube and cube-root of an integer and later gives rules facilitating the computation of squares and square roots. He then gives rules for dealing with five types of combinations of fractions, <math>\tfrac{a}{c} + \tfrac{b}{c}</math>, <math>\tfrac{a}{c} \cdot \tfrac{b}{d}</math>, <math>\tfrac{a}{1} + \tfrac{b}{d}</math>, <math>\tfrac{a}{c} + \tfrac{b}{d} \cdot \tfrac{a}{c} = \tfrac{a(d+b)}{cd}</math>, and <math>\tfrac{a}{c} - \tfrac{b}{d} \cdot \tfrac{a}{c} = \tfrac{a(d-b)}{cd}</math>.<ref>{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 422 | title = | quote = The reader is apparently expected to be familiar with basic arithmetic operations as far as the square-root; Brahmagupta merely notes some points about applying them to fractions. The procedures for finding the cube and cube-root of an integer, however, are described (compared the latter to Aryabhata's very similar formulation). They are followed by rules for five types of combinations: [...]}}</ref> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | ==== Series ==== | + | |
| - | Brahmagupta then goes on to give the sum of the squares and cubes of the first ''n'' integers. | + | |
| - | <blockquote>12.20. The sum of the squares is that [sum] multiplied by twice the [number of] step[s] increased by one [and] divided by three. The sum of the cubes is the square of that [sum] Piles of these with identical balls [can also be computed].<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12">{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 421–427 | title = }}</ref></blockquote> | + | |
| - | It is important to note here Brahmagupta found the result in terms of the ''sum'' of the first ''n'' integers, rather than in terms of ''n'' as is the modern practice.<ref name="Plofker 423">{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 423 | title = | quote = Here the sums of the squares and cubes of the first ''n'' integers are defined in terms of the sum of the ''n'' integers itself;}}</ref> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | He gives the sum of the squares of the first n natural numbers as n(n+1)(2n+1)/6 and the sum of the cubes of the first n natural numbers as (n(n+1)/2)². | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | ==== Zero ==== | + | |
| - | Brahmagupta made use of an important concept in mathematics, the [[0 (number)|number zero]]. The ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' is the earliest known text to treat zero as a number in its own right, rather than as simply a placeholder digit in representing another number as was done by the [[Babylonians]] or as a symbol for a lack of quantity as was done by [[Ptolemy]] and the [[Ancient Rome|Romans]]. In chapter eighteen of his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', Brahmagupta describes operations on negative numbers. He first describes addition and subtraction, | + | |
| - | <blockquote>18.30. [The sum] of two positives is positives, of two negatives negative; of a positive and a negative [the sum] is their difference; if they are equal it is zero. The sum of a negative and zero is negative, [that] of a positive and zero positive, [and that] of two zeros zero.<BR> | + | |
| - | [...]<BR> | + | |
| - | 18.32. A negative minus zero is negative, a positive [minus zero] positive; zero [minus zero] is zero. When a positive is to be subtracted from a negative or a negative from a positive, then it is to be added.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta">{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 428–434 | title = }}</ref></blockquote> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | He goes on to describe multiplication, | + | |
| - | <blockquote>18.33. The product of a negative and a positive is negative, of two negatives positive, and of positives positive; the product of zero and a negative, of zero and a positive, or of two zeros is zero.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | But then he spoils the matter some what when he describes division, | + | <center><math>x = \frac{e-c}{b-d}</math></center> |
| - | <blockquote>18.34. A positive divided by a positive or a negative divided by a negative is positive; a zero divided by a zero is zero; a positive divided by a negative is negative; a negative divided by a positive is [also] negative.<BR> | + | |
| - | 18.35. A negative or a positive divided by zero has that [zero] as its divisor, or zero divided by a negative or a positive [has that negative or positive as its divisor]. The square of a negative or of a positive is positive; [the square] of zero is zero. That of which [the square] is the square is [its] square-root.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | Here Brahmagupta states that <math>\tfrac{0}{0} = 0</math> and as for the question of <math>\tfrac{a}{0}</math> where <math>a \neq 0</math> he did not commit himself.<ref name="Boyer Brahmagupta p220">{{cite book|last=Boyer|authorlink=Carl Benjamin Boyer|title=|year=1991|chapter=China and India|pages=220|quote=However, here again Brahmagupta spoiled matters somewhat by asserting that <math>0 \div 0 = 0</math>, and on the touchy matter of <math>a \div 0</math>, he did not commit himself:}}</ref> His rules for [[arithmetic]] on [[negative number]]s and zero are quite close to the modern understanding, except that in modern mathematics division by zero is left [[defined and undefined|undefined]]. | + | Además, dio dos soluciones equivalentes para la '''ecuación general de segundo grado''', que vienen a ser equivalentes, respectivamente, a las siguientes expresiones algebraicas: |
| - | === Diophantine analysis === | + | <center><math>x = \frac{\sqrt{4ac+b^2}-b}{2a} </math></center> |
| - | ==== Pythagorean triples ==== | + | |
| - | In chapter twelve of his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', Brahmagupta finds Pythagorean triples, | + | |
| - | <blockquote>12.39. The height of a mountain multiplied by a given multiplier is the distance to a city; it is not erased. When it is divided by the multiplier increased by two it is the leap of one of the two who make the same journey.<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | or in other words, for a given length ''m'' and an arbitrary multiplier ''x'', let a = ''mx'' and ''b = m + mx/(x + 2)''. Then ''m'', ''a'', and ''b'' form a Pythagorean triple.<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/> | + | |
| - | ==== Pell's equation ==== | + | y |
| - | Brahmagupta went on to give a recurrence relation for generating solutions to certain instances of Diophantine equations of the second degree such as <math>Nx^2 + 1 = y^2</math> (called [[Pell's equation]]) by using the [[Euclidean algorithm]]. The Euclidean algorithm was known to him as the "pulverizer" since it breaks numbers down into ever smaller pieces.<ref>{{cite book | first = John | last = Stillwell | year = 2004 | pages = 44–46 | title = | quote = In the seventh century CE the Indian mathematician Brahmagupta gave a recurrence relation for generating solutions of <math>x^2 - Dy^2 = 1</math>, as we shall see in Chapter 5. The Indians called the Euclidean algorithm the "pulverizer" because it breaks numbers down to smaller and smaller pieces. To obtain a recurrence one has to know that a rectangle proportional to the original eventually recurs, a fact that was rigorously proved only in 1768 by Lagrange.}}</ref> | + | |
| - | <blockquote>The nature of squares:<BR>18.64. [Put down] twice the square-root of a given square by a multiplier and increased or diminished by an arbitrary [number]. The product product of the first [pair], multiplied by the multiplier, with the product of the last [pair], is the last computed.<BR>18.65. The sum of the thunderbolt products is the first. The additive is equal to the product of the additives. The two square-roots, divided by the additive or the subtractive, are the additive ''rupas''.<ref name="Plofker Chapter 18 Brahmasphutasiddhanta"/></blockquote> | + | <center><math>x = \frac{\sqrt{ac+\frac{b^2}{4}}-\frac{b}{2}}{a} </math></center> |
| - | The key to his solution was the identity,<ref name="Stillwell p. 72-74"/> | + | El contina resolviendo sistemas de ecuaciones indeterminados, enunciando que la variable elegida debe primero aislarse, y que luego la ecuación debe dividirse por el coeficiente de la variable elegida. |
| - | :<math>(x^2_1 - Ny^2_1)(x^2_2 - Ny^2_2) = (x_1 x_2 + Ny_1 y_2)^2 - N(x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)^2</math> | + | Al igual que el álgebra de [[Diofanto]], el álgebra de Brahmagupta es sincopada. La suma la indicaba colocando los números uno al lado del otro, la resta colocando un punto sobre el sustraendo, la división colocando el divisor debajo del dividendo, similar a nuestra notación, pero sin la barra. La multiplicación, las raices y las incógnitas las representaba mediante abrebiaturas de términos apropiados. |
| + | Fue el primero en dar una solución general a la '''ecuación lineal de Diofanto''' <math>ax + by = c</math>, donde a, b, y c son enteros. También es muy posible que diese todas las soluciones de dicha ecuación, mientras que Diofanto se sintió satisfecho con dar una sola solución de una ecuación indeterminada. En la medida en que Brahmagupta utilizó algunos ejemplos iguales a los de Diofanto, vemos la posibilidad de que ambos hubiesen usado las mismas fuentes, posiblemente babilónicas. No se sabe hasta que punto el uso de la notación sincopada en el álgebra de Brahmagupta es debido a los griegos o si tanto griegos como hindues derivan su uso de una fuente común usase notación sincopada, no se conoce y es posible que tanto el griego y el indio síncopa pueden derivarse de una fuente común, las matemáticas babilónicas. | ||
| - | which is a generalization of an identity that was discovered by [[Diophantus]], | + | ===Aritmética=== |
| + | *'''Fracciones:''' Al comienzo del capítulo doce de su ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', titulado ''Cálculo'', Brahmagupta detalla operaciones con fracciones. Da por supuesto que el lector conoce las operaciones aritméticas básicas, como tomar la raíz cuadrada, aunque si explica cómo hallar el cubo y la raíz cúbica de un número entero y, posteriormente, da normas que facilitan el cálculo de cuadrados y raíces cuadradas. A continuación, da las normas para abordar cinco tipos de combinaciones de fracciones, | ||
| - | :<math>(x^2_1 - y^2_1)(x^2_2 - y^2_2) = (x_1 x_2 + y_1 y_2)^2 - (x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)^2.</math> | + | <center><math>\cfrac{a}{c} + \cfrac{b}{c}</math>;{{b}} <math>\cfrac{a}{c} \cdot \cfrac{b}{d}</math>;{{b}} <math>\cfrac{a}{1} + \cfrac{b}{d}</math>;{{b}} <math>\cfrac{a}{c} + \cfrac{b}{d} \cdot \cfrac{a}{c} = \cfrac{a(d+b)}{cd}</math>;{{b}} <math>\cfrac{a}{c} - \cfrac{b}{d} \cdot \cfrac{a}{c} = \cfrac{a(d-b)}{cd}</math></center> |
| - | Using his identity and the fact that if <math>(x_1,</math> <math>y_1)</math> and <math>(x_2,</math> <math>y_2)</math> are solutions to the equations <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_1</math> and <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_2</math>, respectively, then <math>(x_1 x_2 + N y_1 y_2,</math> <math>x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)</math> is a solution to <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_1 k_2</math>, he was able to find integral solutions to the Pell's equation through a series of equations of the form <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_i</math>. Unfortunately, Brahmagupta was not able to apply his solution uniformly for all possible values of ''N'', rather he was only able to show that if <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k</math> has an integral solution for k = <math>\pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 4</math> then <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = 1</math> has a solution. The solution of the general Pell's equation would have to wait for [[Bhaskara II]] in c. 1150 CE.<ref name="Stillwell p. 72-74">{{cite book | first = John | last = Stillwell | year = 2004 | pages = 72–74 | title = }}</ref> | + | *'''Series:''' |
| + | Brahmagupta continua dando la suma de los cuadrados y los cubos de los primeros "n" enteros. Traduciendo algebraicamente sus palabras sería: | ||
| - | ===Geometry === | + | #Suma de los cuadrados de los n primeros números naturales: <math>n\cdot(n+1)\cdot \frac{2n+1}{6}</math> |
| - | ==== Brahmagupta's formula ==== | + | #Suma de los cubos de los n primeros números naturales:<math>\left( \cfrac {n\cdot(n+1)}{2} \right)^2</math>. |
| - | [[Image:Brahmaguptas formula.svg|200px|thumb|right|Diagram for reference]] | + | |
| - | {{main|Brahmagupta's formula}} | + | |
| - | Brahmagupta's most famous result in geometry is his [[Brahmagupta's formula|formula]] for [[cyclic quadrilaterals]]. Given the lengths of the sides of any cyclic quadrilateral, Brahmagupta gave an approximate and an exact formula for the figure's area, | + | *'''El cero y los números negativos:''' |
| - | <blockquote>12.21. The approximate area is the product of the halves of the sums of the sides and opposite sides of a triangle and a quadrilateral. The accurate [area] is the square root from the product of the halves of the sums of the sides diminished by [each] side of the quadrilateral.<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | Brahmagupta hace uso del '''número cero''' en su ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', siendo este el primer texto conocido en el cual se trata al cero con entidad propia, más que como un simple dígito usado para representar otros números, como hacían los babilonios, o como símbolo para indicar la carencia de una cantidad, como hacía Ptolomeo y los romanos. En el capítulo octavo de ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', Brahmagupta describes operaciones con '''númeroas negativos'''. Primero describe la suma y la resta, luego prosigue con la multiplicación dando una correcta regla de los signos, pero al dar la división lo estropea permitiendo la división por cero. Brahmagupta, por ejemplo, dice que: <math>\frac{0}{0} = 0</math> |
| - | So given the lengths ''p'', ''q'', ''r'' and ''s'' of a cyclic quadrilateral, the approximate area is <math>(\tfrac{p + r}{2}) (\tfrac{q + s}{2})</math> while, letting <math>t = \tfrac{p + q + r + s}{2}</math>, the exact area is | + | |
| - | : <math>\sqrt{(t - p)(t - q)(t - r)(t - s)}.</math> | + | ===Análisis diofántico=== |
| + | *'''Ternas pitagóricas:''' En el capítulo doce de ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', Brahmagupta halla ternas pitagóricas. Expresandolo en términos algebraicos: | ||
| + | Para una longitud dada <math>m\;</math> y un multiplicador arbitrario <math>x\;</math>, sean <math>a=mx\;</math> y <math>b=m+ \cfrac{mx}{(x + 2)}</math>. Entonces <math>m\;</math>, <math>a\;</math>, y <math>b\;</math> forman una terna pitagórica. | ||
| - | Although Brahmagupta does not explicitly state that these quadrilaterals are cyclic, it is apparent from his rules that this is the case.<ref>{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 424 | title = | quote = Brahmagupta does not explicitly state that he is discussing only figures inscribed in circles, but it is implied by these rules for computing their circumradius.}}</ref> [[Heron's formula]] is a special case of this formula and it can be derived by setting one of the sides equal to zero. | + | *'''Ecuación de Pell:''' Brahmagupta da una relación de recurrencia para generar soluciones de ciertos tipos de ecuaciones diofánticas de segundo grado, tales como <math>Nx^2 + 1 = y^2</math> (llamada ecuación de Pell), usando el algoritmo de [[Euclides]]. El algoritmo de Euclides le era conocido con el nombre de "pulverizador" ya que simplificaba los números. |
| - | ==== Triangles ==== | + | La clave para su solución era la identidad: |
| - | Brahmagupta dedicated a substantial portion of his work to geometry. One theorem states that the two lengths of a triangle's base when divided by its altitude then follows, | + | |
| - | <blockquote>12.22. The base decreased and increased by the difference between the squares of the sides divided by the base; when divided by two they are the true segments. The perpendicular [altitude] is the square-root from the square of a side diminished by the square of its segment.<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | Thus the lengths of the two segments are <math>b \pm (c^2 - a^2)/b</math>. | + | |
| - | He further gives a theorem on [[rational triangles]]. A triangle with rational sides ''a'', ''b'', ''c'' and rational area is of the form: | + | <center><math>(x^2_1 - Ny^2_1)(x^2_2 - Ny^2_2) = (x_1 x_2 + Ny_1 y_2)^2 - N(x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)^2</math></center> |
| - | :<math>a = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{v}+v\right), \ \ b = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{w}+w\right), \ \ c = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{v} - v + \frac{u^2}{w} - w\right) </math> | + | que es una generalización de una identidad descubierta por [[Diofanto]], |
| - | for some rational numbers ''u'', ''v'', and ''w''.<ref>{{Harv|Stillwell|2004|p=77}}</ref> | + | <center><math>(x^2_1 - y^2_1)(x^2_2 - y^2_2) = (x_1 x_2 + y_1 y_2)^2 - (x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)^2.</math></center> |
| - | ==== Brahmagupta's theorem ==== | + | Usando esta identidad y el hecho de que si<math>(x_1,</math> <math>y_1)\;</math> and <math>(x_2,\;</math> <math>y_2)\;</math> son soluciones de las ecuaciones <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_1\;</math> y <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_2\;</math>, respectivamente, entonces <math>(x_1 x_2 + N y_1 y_2,\;</math> <math>x_1 y_2 + x_2 y_1)\;</math> es una solución de <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_1 k_2\;</math>, él supo encontrar soluciones enteras de la ecuación de Pell equation mediante una serie de ecuaciones de la forma <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k_i\;</math>. Por desgracia, Brahmagupta no fue capaz de aplicar su solución de forma uniforme para todos los posibles valores de ''N'', sino que sólo pudo demostrar que si <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = k\;</math> tiene una solución entera para <math>k = \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 4</math>, entonces <math>x^2 - Ny^2 = 1\;</math> tiene una solución. la solución de la ecuación general de Pell tendría que esperar a [[Bhaskara II]] (c. 1150) |
| - | {{main|Brahmagupta theorem}} | + | |
| - | [[Image:Brahmaguptra's theorem.svg|thumb|right|Brahmagupta's theorem states that ''AF'' = ''FD''.]] | + | |
| - | Brahmagupta continues, | + | ===Geometría === |
| - | <blockquote>12.23. The square-root of the sum of the two products of the sides and opposite sides of a non-unequal quadrilateral is the diagonal. The square of the diagonal is diminished by the square of half the sum of the base and the top; the square-root is the perpendicular [altitudes].<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | *'''Fórmula de Brahmagupta:''' El resultado en geometría más famoso de Brahmagupta es su fórmula para los cuadriláteros cíclicos (aquellos inscritos en una circunferencia). |
| - | So, in a "non-unequal" cyclic quadrilateral (that is, an isosceles [[trapezoid]]), the length of each diagonal is <math>\sqrt{pr + qs}</math>. | + | [[Image:Cuadrilatero_ciclico.png|200px|thumb|right|Cuadrilátero cíclico]] |
| + | Dadas las longitudes de los lados de un cuadrilátero cíclico cualquiera, Brahmagupta dió una fórmula aproximada y otra exacta para el área de dicha figura. la traducción algebraica diría: Dadas las longitudes <math>p\;</math>, <math>q\;</math>, <math>r\;</math> y <math>s\;</math> de un cuadrilátero cíclico, | ||
| - | He continues to give formulas for the lengths and areas of geometric figures, such as the circumradius of an isosceles trapezoid and a scalene quadrilateral, and the lengths of diagonals in a scalene cyclic quadrilateral. This leads up to [[Brahmagupta's theorem|Brahmagupta's famous theorem]], | + | *Area aproximada: <math>A=(\cfrac{p + r}{2}) (\cfrac{q + s}{2})</math> |
| - | <blockquote>12.30-31. Imaging two triangles within [a cyclic quadrilateral] with unequal sides, the two diagonals are the two bases. Their two segments are separately the upper and lower segments [formed] at the intersection of the diagonals. The two [lower segments] of the two diagonals are two sides in a triangle; the base [of the quadrilateral is the base of the triangle]. Its perpendicular is the lower portion of the [central] perpendicular; the upper portion of the [central] perpendicular is half of the sum of the [sides] perpendiculars diminished by the lower [portion of the central perpendicular].<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | *Area exacta:<math>\sqrt{(t - p)(t - q)(t - r)(t - s)}</math>, donde <math>t = \cfrac{p + q + r + s}{2}</math>. |
| - | ==== Pi ==== | + | Aunque Brahmagupta no enuncia explícitamente que se trate de cuadriláteros cíclicos, parece deducirse de sus reglas que ese es el caso. |
| - | In verse 40, he gives values of [[pi|''π'']], | + | |
| - | <blockquote>12.40. The diameter and the square of the radius [each] multiplied by 3 are [respectively] the practical circumference and the area [of a circle]. The accurate [values] are the square-roots from the squares of those two multiplied by ten.<ref name="Plofker Brahmagupta quote Chapter 12"/></blockquote> | + | |
| - | So Brahmagupta uses 3 as a "practical" value of ''π'', and <math>\sqrt{10}</math> as an "accurate" value of ''π''. | + | |
| - | ==== Measurements and constructions ==== | + | La '''fórmula de [[Heron]]''' se obtiene como caso particular de la de Brahmagupta, haciendo uno de los lados igual a cero. |
| - | In some of the verses before verse 40, Brahmagupta gives constructions of various figures with arbitrary sides. He essentially manipulated right triangles to produce isosceles triangles, scalene triangles, rectangles, isosceles trapezoids, isosceles trapezoids with three equal sides, and a scalene cyclic quadrilateral. | + | |
| - | After giving the value of pi, he deals with the geometry of plane figures and solids, such as finding volumes and surface areas (or empty spaces dug out of solids). He finds the volume of rectangular prisms, pyramids, and the frustrum of a square pyramid. He further finds the average depth of a series of pits. For the volume of a [[frustum]] of a pyramid, he gives the "pragmatic" value as the depth times the square of the mean of the edges of the top and bottom faces, and he gives the "superficial" volume as the depth times their mean area.<ref>"{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 427 | title = | quote = After the geometry of plane figures, Brahmagupta discusses the computation of volumes and surface areas of solids (or empty spaces dug out of solids). His straight-forward rules for the volumes of a rectangular prism and pyramid are followed by a more ambiguous one, which may refer to finding the average depth of a sequence of puts with different depths. The next formula apparently deals with the volume of a frustum of a square pyramid, where the "pragmatic" volume is the depth times the square of the mean of the edges of the top and bottom faces, while the "superficial" volume is the depth times their mean area.}}</ref> | + | *'''Triángulos:''' Uno de los teoremas en la obra de Brahmagupta dice que las medidas de los dos segmentos en que la altura de un triángulo divide a la base son: |
| + | <center><math>b \pm \cfrac{c^2 - a^2}{b}</math></center> | ||
| - | === Trigonometry === | + | Además da un teorema sobre triángulos racionales (cuyos lados son números racionales): |
| - | {{Mergefrom|Brahmagupta interpolation formula|Talk:Brahmagupta interpolation formula#Proposal to merge into Brahmagupta article|subst:DATE|date=September 2008}} | + | Un triángulo con lados racionales <math>a\;</math>, <math>b\;</math> y <math>c\;</math> y área racional es de la forma: |
| - | In Chapter 2 of his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', entitled ''Planetary True Longitudes'', Brahmagupta presents a sine table: | + | |
| - | <blockquote>2.2-5. The sines: The Progenitors, twins; Ursa Major, twins, the Vedas; the gods, fires, six; flavors, dice, the gods; the moon, five, the sky, the moonl the moon, arrows, suns [...]<ref>{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 419 | title =}}</ref></blockquote> | + | <center><math>a = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{v}+v\right), \ \ b = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{w}+w\right), \ \ c = \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{u^2}{v} - v + \frac{u^2}{w} - w\right) </math></center> |
| - | Here Brahmagupta uses names of objects to represent the digits of place-value numerals, as was common with numerical data in Sanskrit treatises. Progenitors represents the 14 Progenitors ("Manu") in Indian cosmology or 14, "twins" means 2, "Ursa Major" represents the seven stars of Ursa Major or 7, "Vedas" refers to the 4 Vedas or 4, dice represents the number of sides of the tradition die or 6, and so on. This information can be translated into the list of sines, 214, 427, 638, 846, 1051, 1251, 1446, 1635, 1817, 1991, 2156, 2312, 1459, 2594, 2719, 2832, 2933, 3021, 3096, 3159, 3207, 3242, 3263, and 3270, with the radius being 3270.<ref name="Plofker 419–420"/> | + | para algunos racionales <math>u\;</math>, <math>v\;</math>, y <math>w\;</math>. |
| - | In his ''Paitamahasiddhanta'', Brahmagupta uses the initial sine value of 225 with a radius of approximately 3438, although the rest of the sine table is lost. The value of 3438 for the radius is a traditional value that was also used by Aryabhata, although it is not known why Brahmagupta used 3270 instead of the 3438 in his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta''.<ref name="Plofker 419–420">{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 419–420 | title = | quote = Brahmagupta's sine table, like much other numerical data in Sanskrit treatises, is encoded mostly in concrete-number notation that uses names of objects to represent the digits of place-value numerals, starting with the least significant. [...]<BR>There are fourteen Progenitors ("Manu") in Indian cosmology; "twins" of course stands for 2; the seven stars of Ursa Major (the "Sages") for 7, the four Vedas, and the four sides of the traditional dice used in gambling, for 6, and so on. Thus Brahmagupta enumerates his first six sine-values as 214, 427, 638, 846, 1051, 1251. (His remaining eighteen sines are 1446, 1635, 1817, 1991, 2156, 2312, 1459, 2594, 2719, 2832, 2933, 3021, 3096, 3159, 3207, 3242, 3263, 3270. The ''Paitamahasiddhanta'', however, specifies an initial sine-value of 225 (although the rest of its sine-table is lost), implying a trigonometric radius of ''R'' = 3438 aprox= C(')/2π: a tradition followed, as we have seen, by Aryabhata. Nobody knows why Brahmagupta chose instead to normalize these values to R = 3270.}}</ref> | + | *Teorema de Brahmagupta: |
| + | [[Image:Brahmagupta_teorema.png|thumb|right|El teorema de Brahmagupta dice que ''AF'' = ''FD''.]] | ||
| + | Brahmagupta continua diciendo que, en un cuadrilátero cíclico "no desigual" (trapezoide equilatero), la longitud de las diagonales es: | ||
| + | <center><math>\sqrt{pr + qs}</math></center> | ||
| + | Sigue dando las fórmulas de las longitudes y áreas de figuras geométricas como la medida del radio de la circunferencia circunscrita al trapezoide isósceles y del cuadrilátero escaleno, y las medidas de las diagonales de un cuadrilátero cíclico escaleno. Esto lleva al famoso teorema de Brahmagupta. (ver dibujo adjunto) | ||
| - | == Astronomy == | + | *'''Pi:''' En el verso 40, da valores del número Pi: 3 como valor práctico de Pi y <math>\sqrt{10}</math> como valor más preciso. |
| - | It was through the ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' that the Arabs learned of Indian astronomy.<ref>[http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/Projects/Pearce/Chapters/Ch8_3.html Brahmagupta, and the influence on Arabia]. Retrieved 23 December 2007.</ref> The famous [[Abbasid]] caliph [[Al-Mansur]] (712–775) founded [[Baghdad]], which is situated on the banks of the [[Tigris]], and made it a center of learning. The caliph invited a scholar of [[Ujjain]] by the name of Kankah in 770 A.D. Kankah used the ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' to explain the Hindu system of arithmetic astronomy. [[Muhammad al-Fazari]] translated Brahmugupta's work into Arabic upon the request of the caliph. | + | |
| - | In chapter seven of his ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', entitled ''Lunar Crescent'', Brahmagupta rebuts the idea that the Moon is farther from the Earth than the Sun, an idea which is maintained in scriptures. He does this by explaining the illumination of the Moon by the Sun.<ref name="Plofker 420"/> | + | *'''Medidas y construcciones:''' |
| + | En algunos de los versos anteriores al 40, Brahmagupta da la construcción de varias figuras con lados arbitrarios. El manipuló esencialmente triángulos rectángulos para obtener trángulos isósceles, triángulos escalenos, rectángulos, trapezoides isósceles, trapezoides isósceles con tres lados iguales, y cuadriláteros cíclicos escalenos. | ||
| - | <blockquote>7.1. If the moon were above the sun, how would the power of waxing and waning, etc., be produced from calculation of the [longitude of the] moon? the near half [would be] always bright.<BR> | + | Tras dar el valor de Pi, trata aspectos de la geometría planas y de sólidos, como encontrar sus volúmenes y superficies. Halla el volumen de prismas rectos, pirámides, y troncos de pirámides de base cuadrada. |
| - | 7.2. In the same way that the half seen by the sun of a pot standing in sunlight is bright, and the unseen half dark, so is [the illumination] of the moon [if it is] beneath the sun.<BR> | + | |
| - | 7.3. The brightness is increased in the direction of the sun. At the end of a bright [i.e. waxing] half-month, the near half is bright and the far half dark. Hence, the elevation of the horns [of the crescent can be derived] from calculation. [...]<ref>{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 420 | title =}}</ref></blockquote> | + | |
| - | He explains that since the Moon is closer to the Earth than the Sun, the degree of the illuminated part of the Moon depends on the relative positions of the Sun and the Moon, and this can be computed from the size of the angle between the two bodies.<ref name="Plofker 420">{{cite book | first = Kim | last = Plofker | year = 2007 | pages = 419–420 | title = | quote = Brahmagupta discusses the illumination of the moon by the sun, rebutting an idea maintained in scriptures: namely, that the moon is farther from the earth than the sun is. In fact, as he explains, because the moon is closer the extent of the illuminated portion of the moon depends on the relative positions of the moon and the sun, and can be computed from the size of the angular separation α between them.}}</ref> | + | ===Trigonometría=== |
| + | En el capítulo 2 de ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', titulado ''Longitudes Planetarias Verdaderas'', Brahmagupta presenta una tabla de senos, usando nombres de objetos para representar los números, algo que era común en los tratatados en sanscrito. Así, por ejemplo, "Osa mayor" representa el 7 (por las 7 estrellas de dicha constelación), "gemelos" al 2, "Vedas" el 4 (por los 4 Vedas), Progenitores el 14, etc. esta información, traducida en números, da la lista de senos: 214 (gemelos, Progenitores), 427 (Osa Mayor, gemelos, Vedas), 638, 846, 1051, 1251, 1446, 1635, 1817, 1991, 2156, 2312, 1459, 2594, 2719, 2832, 2933, 3021, 3096, 3159, 3207, 3242, 3263, y 3270, siendo el radio 3270. | ||
| - | Some of the important contributions made by Brahmagupta in astronomy are: methods for calculating the position of heavenly bodies over time ([[ephemeris|ephemerides]]), their rising and setting, [[conjunction (astronomy)|conjunction]]s, and the calculation of solar and lunar [[eclipse]]s.<ref>Dick Teresi, ''Lost Discoveries: The Ancient Roots of Modern Science'', Simon and Schuster, 2002. p. 135. ISBN 074324379X.</ref> Brahmagupta criticized the [[Puranic]] view that the Earth was flat or hollow. Instead, he observed that the Earth and heaven were spherical and that the Earth is moving. In 1030, the [[Islamic astronomy|Muslim astronomer]] [[Abū al-Rayhān al-Bīrūnī|Abu al-Rayhan al-Biruni]], in his ''Ta'rikh al-Hind'', later translated into [[Latin]] as ''Indica'', commented on Brahmagupta's work and wrote that critics argued: | + | ==Astronomía== |
| + | Fue a traves de el ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' como los árabes aprendieron la astronomía hindú. El famoso califa abasida Al-Mansur (712–775), fundó Baghdad, situada a orillas del Tigris, e la hizo centro de aprendizaje. El califa invitó a un estudiante de Ujjain llamado Kankah en 770 a.C. Kankah usó el ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' para explicar el sistema hindú de astronomía aritmética. Muhammad al-Fazari tradujo el trabajo de Brahmugupta al árabe a demanda del califa. | ||
| - | {{quote|"If such were the case, stones would and trees would fall from the earth."<ref>[[Al-Biruni]] (1030), ''Ta'rikh al-Hind'' (''Indica'')</ref>}} | + | En el capítulo siete de ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'', titulado ''Creciente Lunar'', Brahmagupta refuta la idea de que la Luna se encuentra más alejada que el Sol de la Tierra, idea que se mantuvo en las escrituras. El hace ésto explicando la iluminación de la Luna por el Sol. También explicó que, como la Luna está más cerca de la Tierra que el Sol, la cantidad de parte iluminada de la Luna depende de la posición relativa del Sol y la Luna, y esto puede calcularse a partir del ángulo que forman los dos cuerpos. |
| - | According to al-Biruni, Brahmagupta responded to these criticisms with the following argument on [[gravitation]]: | + | Algunas de las aportaciones de importancia hechas por Brahmagupta a la astronomía son: métodos para calcular la posición de cuerpos celestes en el tiempo (efemérides), su aparición y su ocultación, conjunciones, y el cálculo de los eclipses solares y lunares. Brahmagupta criticó el punto de vista puránico de que la Tierra era plana o hueca. Por el contrario, observó que la Tierra y el cielo eran esféricos y que la Tierra se mueve. En el año 1030, el astrónomo musulmán, Abu al-Rayhan al-Biruni, en su ''Ta'rikh al-Hind'', posteriormente traducido al latín como ''Indica'', comentó el trabajo de Brahmaguptas y escribió que los críticos argumentaron: |
| - | {{quote|"On the contrary, if that were the case, the earth would not vie in keeping an even and uniform pace with the minutes of heaven, the [[prana]]s of the times. [...] All heavy things are attracted towards the center of the earth. [...] The earth on all its sides is the same; all people on earth stand upright, and all heavy things fall down to the earth by a law of nature, for it is the nature of the earth to attract and to keep things, as it is the nature of water to flow, that of fire to burn, and that of wind to set in motion… The earth is the only low thing, and seeds always return to it, in whatever direction you may throw them away, and never rise upwards from the earth."<ref>Brahmagupta, ''Brahmasphutasiddhanta'' (628) ([[cf.]] [[al-Biruni]] (1030), ''Indica'')</ref>}} | + | "Si eso es así, las piedras y los árboles se caerían de la Tierra." |
| - | About the Earth's gravity he said: "Bodies fall towards the earth as it is in the nature of the earth to attract bodies, just as it is in the nature of water to flow."<ref>Thomas Khoshy, ''Elementary Number Theory with Applications'', Academic Press, 2002, p. 567. ISBN 0124211712.</ref> | + | De acuerdo con al-Biruni, Brahmagupta respondió a estas críticas con el siguiente argumento sobre gravitación: |
| + | ... Todas las cosas pesadas son atraidas hacia el centro de la Tierra... La Tierra es igual por todos lados; todo el mundo sobre la Tierra permanece derecho, y todas las cosas pesadas caen a al Tierra por una ley de la naturaleza, porque está en la naturaleza de la Tierra atraer y mantener las cosas, como está en la naturaleza del agua fluir, en la del fuego quemar, y en la del viento mantenerse en movimientootion..." | ||
| [[Categoría: Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Historia de las Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Matemáticos]] | [[Categoría: Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Historia de las Matemáticas]][[Categoría: Matemáticos]] | ||
Revisión actual
Brahmagupta (598–668), matemático y astrónomo indú.
Tabla de contenidos |
Vida y obra
Brahmagupta nació en el año 598 en Bhinmal, ciudad en el estado de Rajasthan, al noroeste de la India. Probablemente vivió la mayor parte de su vida en Bhillamala (moderna Bhinmal, en Rajasthan) en el imperio de Harsha, durante el reinado del Rey Vyaghramukha. Como resultado de ello, Brahmagupta es a menudo citado como Bhillamalacarya que quiere decir, el maestro de Bhillamala Bhinmal.
Fue el jefe del observatorio astronómico en Ujjain, y durante su mandato allí escribió cuatro textos sobre las matemáticas y la astronomía: Cadamekela en el 624, Brahmasphutasiddhanta en 628, Khandakhadyaka en 665, y Durkeamynarda en 672. El Brahmasphutasiddhanta (Tratado corregido de Brahma) es posiblemente su obra más famosa. El historiador Al-Biruni (c. 1050) en su libro Tariq al-Hind, afirma que el califa Abbasid al-Ma'mun, que tenía una embajada en la India, llevó de3 allí un libro a Bagdad que fue traducido al árabe como Sindhind. Se presume que Sindhind no es otro que Brahmagupta-Brahmasphuta Siddhanta.
Aunque Brahmagupta estaba familiarizado con las obras de los astrónomos siguiendo la tradición de Aryabhatiya, no se sabe si está familiarizado con la labor de Bhaskara I, un contemporáneo. Brahmagupta tenía una cantidad de críticas dirigidas hacia la labor de los astrónomos rivales, y en su Brahmasphutasiddhanta se encuentra uno de los primeros cismas de fe entre matemáticos indios. La división fue principalmente sobre la aplicación de las matemáticas al mundo físico, más que sobre las matemáticas en si mismas. En el caso de Brahmagupta, los desacuerdos se debieron en gran parte de la elección de las teorías y parámetros astronómicos. A lo largo de los primeros diez capítulos astronómicos aparecen críticas a las teorías rivales, y el undécimo capítulo está completamente dedicado a la crítica de estas teorías, aunque las críticas no aparecen en el duodécimo y décimo octavo capítulos.
Matemáticas
La obra más famosa de Brahmagupta es su Brahmasphutasiddhanta. Compuesta en verso elíptico, practica común en las matemáticas indueshematics]], la obra tiene, en consecuencia, un cierto halo poético. Como en ella no se dan demostraciones, no se sabe como Brahmagupta obtenía los resultados matemáticos.
Algebra
Brahmagupta da la solución de la ecuación lineal general en el capítulo dieciocho de Brahmasphutasiddhanta, que aunque expresada en el libro en palabras, viene a ser equivalente a la siuiente expresión algebraica:
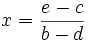
Además, dio dos soluciones equivalentes para la ecuación general de segundo grado, que vienen a ser equivalentes, respectivamente, a las siguientes expresiones algebraicas:
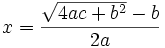
y
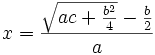
El contina resolviendo sistemas de ecuaciones indeterminados, enunciando que la variable elegida debe primero aislarse, y que luego la ecuación debe dividirse por el coeficiente de la variable elegida.
Al igual que el álgebra de Diofanto, el álgebra de Brahmagupta es sincopada. La suma la indicaba colocando los números uno al lado del otro, la resta colocando un punto sobre el sustraendo, la división colocando el divisor debajo del dividendo, similar a nuestra notación, pero sin la barra. La multiplicación, las raices y las incógnitas las representaba mediante abrebiaturas de términos apropiados. Fue el primero en dar una solución general a la ecuación lineal de Diofanto ax + by = c, donde a, b, y c son enteros. También es muy posible que diese todas las soluciones de dicha ecuación, mientras que Diofanto se sintió satisfecho con dar una sola solución de una ecuación indeterminada. En la medida en que Brahmagupta utilizó algunos ejemplos iguales a los de Diofanto, vemos la posibilidad de que ambos hubiesen usado las mismas fuentes, posiblemente babilónicas. No se sabe hasta que punto el uso de la notación sincopada en el álgebra de Brahmagupta es debido a los griegos o si tanto griegos como hindues derivan su uso de una fuente común usase notación sincopada, no se conoce y es posible que tanto el griego y el indio síncopa pueden derivarse de una fuente común, las matemáticas babilónicas.
Aritmética
- Fracciones: Al comienzo del capítulo doce de su Brahmasphutasiddhanta, titulado Cálculo, Brahmagupta detalla operaciones con fracciones. Da por supuesto que el lector conoce las operaciones aritméticas básicas, como tomar la raíz cuadrada, aunque si explica cómo hallar el cubo y la raíz cúbica de un número entero y, posteriormente, da normas que facilitan el cálculo de cuadrados y raíces cuadradas. A continuación, da las normas para abordar cinco tipos de combinaciones de fracciones,
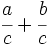 ;
; 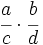 ;
; 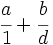 ;
; 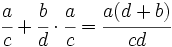 ;
; 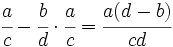
- Series:
Brahmagupta continua dando la suma de los cuadrados y los cubos de los primeros "n" enteros. Traduciendo algebraicamente sus palabras sería:
- Suma de los cuadrados de los n primeros números naturales:
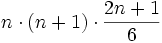
- Suma de los cubos de los n primeros números naturales:
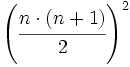 .
.
- El cero y los números negativos:
Brahmagupta hace uso del número cero en su Brahmasphutasiddhanta, siendo este el primer texto conocido en el cual se trata al cero con entidad propia, más que como un simple dígito usado para representar otros números, como hacían los babilonios, o como símbolo para indicar la carencia de una cantidad, como hacía Ptolomeo y los romanos. En el capítulo octavo de Brahmasphutasiddhanta, Brahmagupta describes operaciones con númeroas negativos. Primero describe la suma y la resta, luego prosigue con la multiplicación dando una correcta regla de los signos, pero al dar la división lo estropea permitiendo la división por cero. Brahmagupta, por ejemplo, dice que: 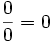
Análisis diofántico
- Ternas pitagóricas: En el capítulo doce de Brahmasphutasiddhanta, Brahmagupta halla ternas pitagóricas. Expresandolo en términos algebraicos:
Para una longitud dada 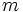 y un multiplicador arbitrario
y un multiplicador arbitrario 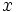 , sean
, sean 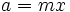 y
y 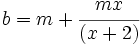 . Entonces
. Entonces 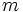 ,
, 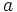 , y
, y 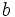 forman una terna pitagórica.
forman una terna pitagórica.
- Ecuación de Pell: Brahmagupta da una relación de recurrencia para generar soluciones de ciertos tipos de ecuaciones diofánticas de segundo grado, tales como Nx2 + 1 = y2 (llamada ecuación de Pell), usando el algoritmo de Euclides. El algoritmo de Euclides le era conocido con el nombre de "pulverizador" ya que simplificaba los números.
La clave para su solución era la identidad:
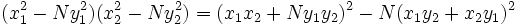
que es una generalización de una identidad descubierta por Diofanto,
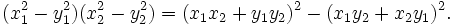
Usando esta identidad y el hecho de que si(x1,  and
and 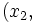
 son soluciones de las ecuaciones
son soluciones de las ecuaciones 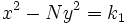 y
y 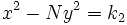 , respectivamente, entonces
, respectivamente, entonces 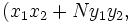
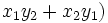 es una solución de
es una solución de 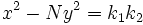 , él supo encontrar soluciones enteras de la ecuación de Pell equation mediante una serie de ecuaciones de la forma
, él supo encontrar soluciones enteras de la ecuación de Pell equation mediante una serie de ecuaciones de la forma 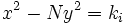 . Por desgracia, Brahmagupta no fue capaz de aplicar su solución de forma uniforme para todos los posibles valores de N, sino que sólo pudo demostrar que si
. Por desgracia, Brahmagupta no fue capaz de aplicar su solución de forma uniforme para todos los posibles valores de N, sino que sólo pudo demostrar que si 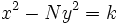 tiene una solución entera para
tiene una solución entera para 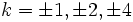 , entonces
, entonces 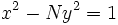 tiene una solución. la solución de la ecuación general de Pell tendría que esperar a Bhaskara II (c. 1150)
tiene una solución. la solución de la ecuación general de Pell tendría que esperar a Bhaskara II (c. 1150)
Geometría
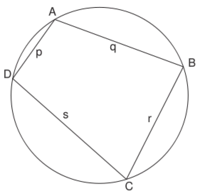
- Fórmula de Brahmagupta: El resultado en geometría más famoso de Brahmagupta es su fórmula para los cuadriláteros cíclicos (aquellos inscritos en una circunferencia).
Dadas las longitudes de los lados de un cuadrilátero cíclico cualquiera, Brahmagupta dió una fórmula aproximada y otra exacta para el área de dicha figura. la traducción algebraica diría: Dadas las longitudes 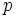 ,
, 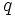 ,
, 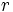 y
y 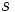 de un cuadrilátero cíclico,
de un cuadrilátero cíclico,
- Area aproximada:
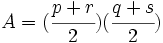
- Area exacta:
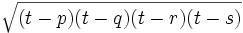 , donde
, donde 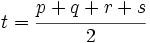 .
.
Aunque Brahmagupta no enuncia explícitamente que se trate de cuadriláteros cíclicos, parece deducirse de sus reglas que ese es el caso.
La fórmula de Heron se obtiene como caso particular de la de Brahmagupta, haciendo uno de los lados igual a cero.
- Triángulos: Uno de los teoremas en la obra de Brahmagupta dice que las medidas de los dos segmentos en que la altura de un triángulo divide a la base son:
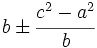
Además da un teorema sobre triángulos racionales (cuyos lados son números racionales):
Un triángulo con lados racionales 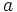 ,
, 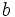 y
y 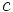 y área racional es de la forma:
y área racional es de la forma:
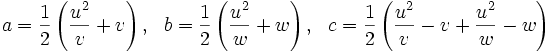
para algunos racionales 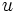 ,
, 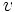 , y
, y 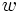 .
.
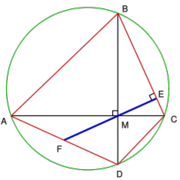
- Teorema de Brahmagupta:
Brahmagupta continua diciendo que, en un cuadrilátero cíclico "no desigual" (trapezoide equilatero), la longitud de las diagonales es:
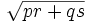
Sigue dando las fórmulas de las longitudes y áreas de figuras geométricas como la medida del radio de la circunferencia circunscrita al trapezoide isósceles y del cuadrilátero escaleno, y las medidas de las diagonales de un cuadrilátero cíclico escaleno. Esto lleva al famoso teorema de Brahmagupta. (ver dibujo adjunto)
- Pi: En el verso 40, da valores del número Pi: 3 como valor práctico de Pi y
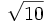 como valor más preciso.
como valor más preciso.
- Medidas y construcciones:
En algunos de los versos anteriores al 40, Brahmagupta da la construcción de varias figuras con lados arbitrarios. El manipuló esencialmente triángulos rectángulos para obtener trángulos isósceles, triángulos escalenos, rectángulos, trapezoides isósceles, trapezoides isósceles con tres lados iguales, y cuadriláteros cíclicos escalenos.
Tras dar el valor de Pi, trata aspectos de la geometría planas y de sólidos, como encontrar sus volúmenes y superficies. Halla el volumen de prismas rectos, pirámides, y troncos de pirámides de base cuadrada.
Trigonometría
En el capítulo 2 de Brahmasphutasiddhanta, titulado Longitudes Planetarias Verdaderas, Brahmagupta presenta una tabla de senos, usando nombres de objetos para representar los números, algo que era común en los tratatados en sanscrito. Así, por ejemplo, "Osa mayor" representa el 7 (por las 7 estrellas de dicha constelación), "gemelos" al 2, "Vedas" el 4 (por los 4 Vedas), Progenitores el 14, etc. esta información, traducida en números, da la lista de senos: 214 (gemelos, Progenitores), 427 (Osa Mayor, gemelos, Vedas), 638, 846, 1051, 1251, 1446, 1635, 1817, 1991, 2156, 2312, 1459, 2594, 2719, 2832, 2933, 3021, 3096, 3159, 3207, 3242, 3263, y 3270, siendo el radio 3270.
Astronomía
Fue a traves de el Brahmasphutasiddhanta como los árabes aprendieron la astronomía hindú. El famoso califa abasida Al-Mansur (712–775), fundó Baghdad, situada a orillas del Tigris, e la hizo centro de aprendizaje. El califa invitó a un estudiante de Ujjain llamado Kankah en 770 a.C. Kankah usó el Brahmasphutasiddhanta para explicar el sistema hindú de astronomía aritmética. Muhammad al-Fazari tradujo el trabajo de Brahmugupta al árabe a demanda del califa.
En el capítulo siete de Brahmasphutasiddhanta, titulado Creciente Lunar, Brahmagupta refuta la idea de que la Luna se encuentra más alejada que el Sol de la Tierra, idea que se mantuvo en las escrituras. El hace ésto explicando la iluminación de la Luna por el Sol. También explicó que, como la Luna está más cerca de la Tierra que el Sol, la cantidad de parte iluminada de la Luna depende de la posición relativa del Sol y la Luna, y esto puede calcularse a partir del ángulo que forman los dos cuerpos.
Algunas de las aportaciones de importancia hechas por Brahmagupta a la astronomía son: métodos para calcular la posición de cuerpos celestes en el tiempo (efemérides), su aparición y su ocultación, conjunciones, y el cálculo de los eclipses solares y lunares. Brahmagupta criticó el punto de vista puránico de que la Tierra era plana o hueca. Por el contrario, observó que la Tierra y el cielo eran esféricos y que la Tierra se mueve. En el año 1030, el astrónomo musulmán, Abu al-Rayhan al-Biruni, en su Ta'rikh al-Hind, posteriormente traducido al latín como Indica, comentó el trabajo de Brahmaguptas y escribió que los críticos argumentaron:
"Si eso es así, las piedras y los árboles se caerían de la Tierra."
De acuerdo con al-Biruni, Brahmagupta respondió a estas críticas con el siguiente argumento sobre gravitación: ... Todas las cosas pesadas son atraidas hacia el centro de la Tierra... La Tierra es igual por todos lados; todo el mundo sobre la Tierra permanece derecho, y todas las cosas pesadas caen a al Tierra por una ley de la naturaleza, porque está en la naturaleza de la Tierra atraer y mantener las cosas, como está en la naturaleza del agua fluir, en la del fuego quemar, y en la del viento mantenerse en movimientootion..."